Example Of Determining Holding Period
Consider this hypothetical situation in which you have dividends reported on Form 1099-DIV as qualified from shares in XYZ fund. You purchased 10,000 shares of XYZ fund on April 27 of the tax year. You sold 2,000 of those shares on June 15, but continue to hold the remaining 8,000 shares. The ex-dividend date for XYZ fund was May 2.
Therefore, during the 121-day window, you held 2,000 shares for 49 days and 8,000 shares for at least 61 days .
The dividend income from the 2,000 shares held 49 days would not be qualified dividend income. The dividend income from the 8,000 shares held at least 61 days should be qualified dividend income.
What Are The Tax Rates For Dividends In Different Tax Brackets
Ordinary dividends are taxed using the ordinary income tax brackets for tax year 2021.
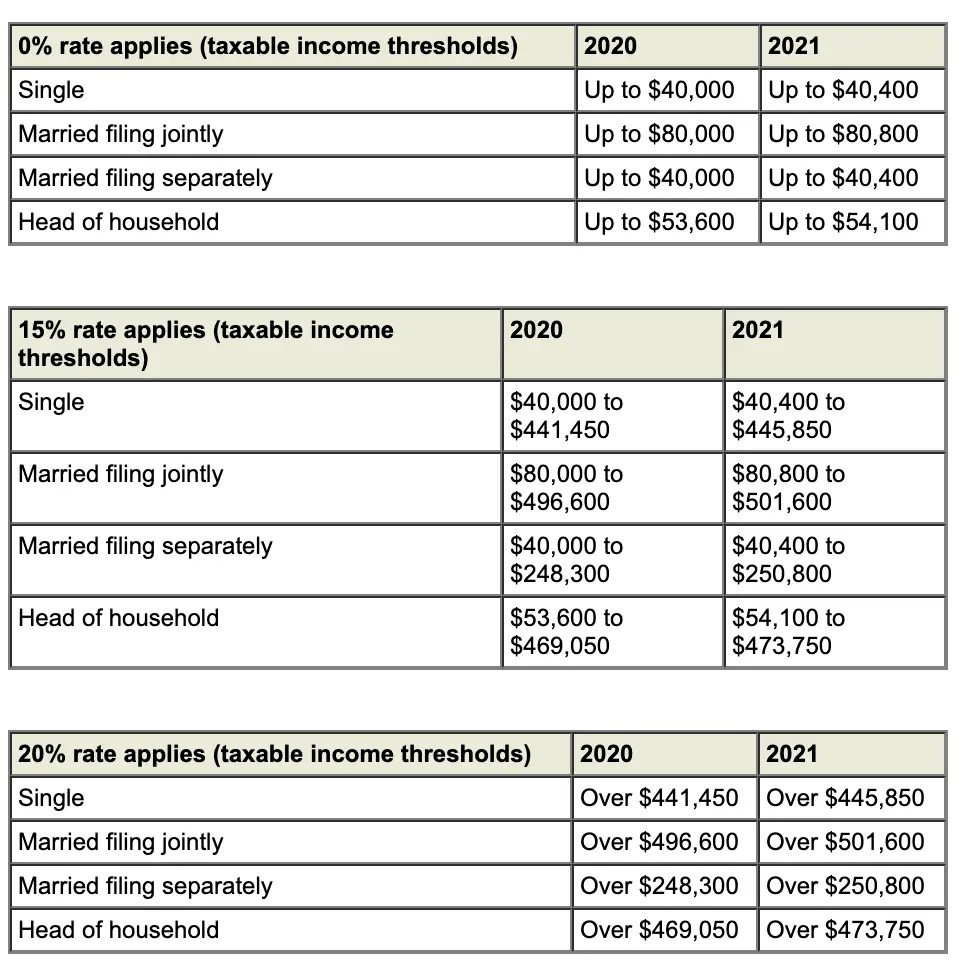
Qualified dividend taxes are usually calculated using the capital gains tax rates. For 2021, qualified dividends may be taxed at 0% if your taxable income falls below
- $40,001 for those filing single or married filing separately,
- $54,101 for head of household filers, or
- $80,801 for married filing jointly or qualifying widow filing status.
The qualified dividend tax rate increases to 15% for taxable income above
- $40,001 through $250,800 for married filing separately filers,
- $40,001 through $445,850 for single filers,
- $54,101 through $473,750 for head of household filers, or
- $80,801 through $501,600 for married filing jointly or qualifying widow filers.
Qualified dividend income above the upper limits of the 15% bracket requires paying a 20% tax rate on any remaining qualified dividend income. Depending on your specific tax situation, qualified dividends may also be subject to the 3.8% Net Investment Income Tax.
The Additional Medicare Surcharge
Dividend income can also prompt the Additional Medicare Tax. This tax has been in place since the 2013 tax year. It’s in addition to any income tax you might pay on your dividends.
You must pay 0.9% of your net investment income toward this Medicare tax if you’re married filing jointly and your modified adjusted gross income is $250,000 or more. You must pay it if you’re married filing separately and your MAGI is more than $125,000. The income threshold for all other taxpayers is $200,000.
Also Check: Where Can I Get Taxes Done For Free
Are Qualified Dividends Taxable
Please note that the qualified dividends tax rate denotes the capital gains tax rate varying from 0%, 15%, or 20%, per the investors tax bracket. In other words, taxing these dividends at lower tax rates minimizes the tax income. Additionally, they are a proportion of corporate proceeds paid out to shareholders and are taxable earnings.
These dividends are certainly a form of investment income gained through mutual funds and shares containing stocks. Moreover, here lie the details,
| Taxable Income |
|---|
So, here are a few examples to understand the qualified dividends.
Example#1
Lets assume that a firm, ABC Co. pays a dividend worth $0.16 per share. Nonetheless, just 50% of the dividends per shareDividend Per ShareDividends per share are calculated by dividing the total amount of dividends paid out by the company over a year by the total number of average shares held.read more are documented as qualified dividends. Also, the investor possesses 10,000 shares, out of which 7000 are held for the qualified dividends holding period.
Qualified dividends amount = Shares held for holding period x Dividend per share
= 7000 x $0.08
Thus, the amount = $560
Example#2
The Biden administration has recently commenced a proposal regarding qualified taxable dividends for taxpayers possessing an AGI of over $1 million. To clarify, it would charge them at normal income tax rates than the long-term lower capital gains rates .
Ordinary Vs Qualified Dividends
Qualified and unqualified dividends may have differences that appear to be minor, but they have a significant impact on overall returns. Overall, most regular dividends distributed by companies in the U.S. can be classified as qualified.
The biggest difference between qualified and unqualified dividends, as far as their impact at tax time is the rate at which these dividends are taxed. Unqualified dividends are taxed at an individuals normal income tax rate, as opposed to the preferred rate for qualified dividends as listed above. This means that individuals occupying any tax bracket will see a difference in their tax rates depending upon whether they have qualified or ordinary dividends.
Also Check: How Many Years Do You Have To File Taxes
How Dividends Are Taxed Qualified Versus Non
How dividends are taxed and how much tax you have to pay on your dividend income depends on the dividend classification and your total taxable income. There are mainly two forms of income from stocksdividends and capital gains. Dividends are the periodic distributions that companies make to eligible shareholders, while capital gains are the difference between a stocks buying and selling price.
Reverse The Crush
In the U.S., most of the dividends are ordinary dividends reflected in box 1a of Form 1099-DIV. How much tax you pay on dividends depends on whether the IRS classifies the dividend as qualified or non-qualified. Irrespective of how the dividend is classified, the investor has to pay taxes on the dividend income. In some countries, the companies distributing the dividends have pay taxes on investors behalf.
Qualified Dividends On Your Tax Reporting Statement
Qualified dividends are reported on Form 1099-DIV in line 1b or column 1b. However, not all dividends reported on those lines may have met the holding period requirement. Those non-qualified dividends, as well as other ordinary dividends, may be taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, which can be as high as 37%.
If you neither bought nor sold securities in the tax year, the potential qualified dividends reported on your Form 1099-DIV should meet the holding period requirement and qualify for the lower tax rate, unless you hedged the securities.
Also Check: What Is The Tax Assessed Value Of My Home
What Are The Requirements For Qualified Dividends
To qualify for the qualified dividend rate, the payee must own the stock for a long enough time, generally 60 days for common stock and 90 days for preferred stock. To qualify for the qualified dividend rate, the dividend must also be paid by a corporation in the U.S. or with certain ties to the U.S.
Qualified Dividend Income Percentage
All or a portion of your ordinary income dividend from a fund may be taxed at a reduced capital gains rate rather than the higher marginal rates applicable to ordinary income. The amount of your dividend subject to this lower rate is reported in Box 1b of your Form 1099-DIV mailed in late January. The tax forms for the T. Rowe Price Real Assets, Real Estate, Global Real Estate, and Small-Cap Value Funds mail in mid-February.
The tables below report the percentage of the ordinary dividend paid by the T. Rowe Price funds that qualify for the lower dividend rate. The data is provided here for informational purposes only and to assist you in your tax planning. In preparing your tax return, please use the amount in Box 1b of your Form 1099-DIV.
To treat a dividend as qualifying for lower rates, you must have held your shares on which you received the dividend for at least 61 days during the 121-day period beginning 60 days before the ex-dividend date of the distribution. Find your fund’s ex-dividend date.
In addition, the ordinary dividend of a fund includes net short-term capital gains and foreign taxes paid, which may not qualify for the lower rates. As a result, the percentage of the Box 1a amount that qualifies for the lower tax rate can vary widely from year to year, depending on the amount of short-term gains and foreign taxes reported by the fund.
Recommended Reading: How To Stop Property Tax Auction
The Dividend Tax Rate For 2020
Currently, the maximum tax rate for qualified dividends is 20%, 15%, or 0%, depending on your taxable income and tax filing status. For anyone holding nonqualified dividends in 2020, the tax rate is 37%.
Dividends are taxed at different rates depending on how long youve owned the stock. While nonqualified dividends are taxed at the same rate as ordinary income, other dividends are taxed at a lower rate.
Unqualified Dividends Vs Qualified Dividends
Dividends paid out of earnings of a company are either classified as unqualified or qualified. An unqualified dividend is also sometimes called an ordinary dividend.
The main difference between a qualified dividend versus an ordinary dividend is that a qualified dividend is taxed at a rate ranging from 0% to 20%, depending on the income bracket. This compares to taxes paid on unqualified dividends, which are taxed as ordinary income and ranges from 10% to 37%.
Qualified dividends were introduced through the passage of the Jobs and Growth Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2003 and aimed to remedy a prevalent issue with the U.S. tax code at the time companies opting to conduct share buybacks in lieu of paying out dividends.
It was due to share buybacks being taxed at the capital gains tax rate, which was lower than the ordinary income tax rate faced by ordinary dividends. The establishment of qualified dividends was to incentivize companies to pay out dividends to shareholders by lowering the applicable tax rate for dividends.
Also Check: How To Receive Child Tax Credit
How To Figure The Qualified Dividends On A Tax Return
Figuring tax on qualified dividends is not as hard as it looks.
Duncan Smith/Photodisc/Getty Images
Figuring the tax on qualified dividends can throw even the most seasoned tax accountants for a loop. There are definitions to memorize, tax codes to adhere to and numbers to crunch. Even with all that, the process is bearable as long as you understand how to differentiate qualified dividends from other types of distributions. Managing that distinction is the hard part. Figuring the tax is relatively straightforward if you use the worksheet provided by the Internal Revenue Service.
How Do I Know If My Dividends Are Qualified Or Not
Don’t worry you don’t have to keep track of ex-dividend dates and figure out which dividends are and aren’t qualified on your own. Around January 31 of each year, you should receive Form 1099-DIV from any company or brokerage that paid you at least $10 in dividends or other distributions during the prior year. Your total dividends are shown in Box 1a of Form 1099-DIV, and qualified dividends appear in Box 1b.
Read Also: Why Do My Taxes Still Say Processing
Ordinary Dividends Vs Qualified Dividends
There are two forms of dividends: ordinary and qualified. Ordinary, or non-qualified, dividends are much more common than their counterpart. Just like qualified dividends, they are paid out from company or corporations earnings to its stock holders. These payments tend to come from sources outside of stocks, though. Examples of this include savings accounts, certificates of deposit and REITs. Reporting an ordinary dividend is a little different from a qualified dividend since it is not taxed in the same way.
You report any income from an ordinary dividend in box 1a on the 1099-DIV form, just like you would any income. So, its taxed like the wages you earn from your job. If you receive more than $1,500 in these ordinary dividends, though, you have to use another form called the Schedule B , Interest and Ordinary Dividends.
In comparison, qualified dividends are taxed as long-term capital gains instead of regular income. This taxation comes at lower rates. For example, look at the 2021 tax year brackets. Single filers and joint filers alike can pay from 10% to 37% on ordinary income, whereas the capital gains rate caps at 20%. Remember, your qualified dividends are also reported on the 1099-DIV form but in box 1b.
How Often Are Dividends Paid
Aside from real estate investment trusts , most businesses have a lot of freedom as to how often they pay out dividends, when they choose to do so, and how much that payment will be. Many companies that offer dividends do so quarterly. But this isn’t a requirement. They can change their plans at any time up until the dividend is announced.
Recommended Reading: What Is Texas State And Local Tax Rate
What Is Dividends Tax
- South African tax resident company or
- Foreign Company whose shares are listed on a South African Exchange.
- align South Africa with the international norm where the recipient of the dividend, not the company paying it, is liable for the tax
- make South Africa a more attractive destination for international investment by eliminating the perception of a higher corporate tax rate coupled with lower accounting profits ).
What Is The Exemption Limit For Dividend Income
However, the company declaring the dividend will have to deduct TDS under section 194 of the Income-tax Act, 1961. As per this section, 10% TDS is applicable for dividend income above Rs.5000 for an individual this rate will be increased to 20% in the absence of PAN submission by the recipient of dividend income.
You May Like: How To File My Taxes For The First Time
What Is Form 1099
Form 1099-DIV Dividends and Distributions is the form financial institutions typically use to report information to you and the IRS about dividends and certain other distributions paid to you.
The financial institutions are required to fill out this form if your total dividends and other distributions for a year exceed $10. It includes information about the payer of the dividends, the recipient of the dividends, the type and amount of dividends paid, and any federal or state income taxes withheld.
The Dividend Tax Rate For 2021 And 2022
Earning dividends is a great incentive for investing in certain companies and mutual funds. Dividends are particularly useful for people who want to supplement their retirement income. However, like all income, youll need to pay taxes on any dividends you receive. Which dividend tax rates you pay depend on how long youve held your investments, the size of your dividends and how much other income you have. It can also be helpful to consult with a financial advisor to learn more about dividends and their taxes.
Read Also: How Do You Get The Eitc Tax Credit
How Is Dividend Income Taxed
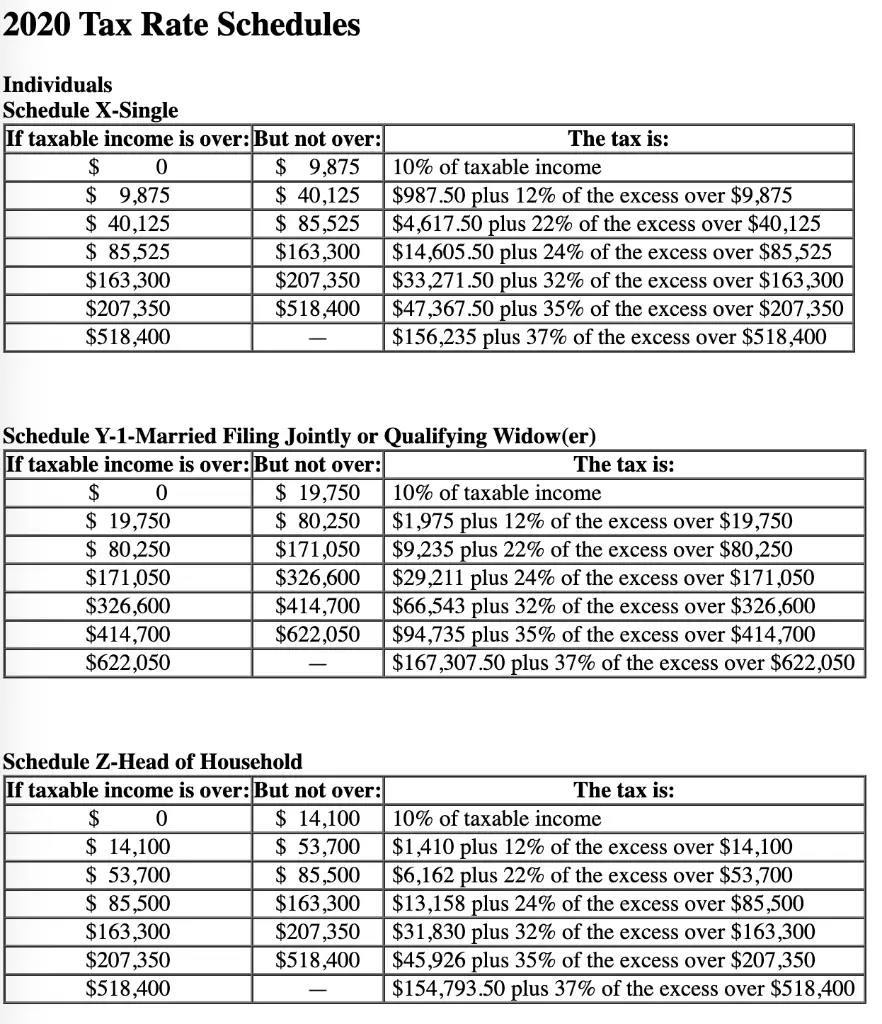
If the dividend is qualified, it would be taxed as capital gains and the tax rate would depend on your total taxable income. If you are a single filer, the long-term capital gains tax rate is 0 percent for income below $40,000, 15 percent for income between $40,001 and $441,450, and 20 percent if your income is above $441,450.
How Are Dividends Taxed
Yes the IRS considers dividends to be income, so you usually need to pay taxes on them. Even if you reinvest all of your dividends directly back into the same company or fund that paid you the dividends, you will pay taxes as they technically still passed through your hands. The exact dividend tax rate depends on what kind of dividends you have: non-qualified or qualified.
The federal government taxes non-qualified dividends according to regular income tax rates and brackets. Qualified dividends are subject to the lower capital gains tax rates. Naturally, there are some exceptions though.
If you are unsure what tax implications dividends will have for you, the best thing to do is talk to a financial advisor. A financial advisor will be able to look at how an investing decision will impact you while also considering your overall financial picture. Try using our free financial advisor matching tool to find options in your area.
Also Check: What Is The Last Day To File Taxes
Why Are Qualified Dividends Taxed More Favorably Than Ordinary Dividends
Qualified dividends are taxed at the same rate as long-term capital gains, lower than that of ordinary dividends, which are taxed as ordinary income. This was done to incentivize companies to reward their long-term shareholders with higher dividends and also incentivizes investors to hold their stocks for longer to collect these dividends payments.
Dividend Tax Rate 2021
Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This may influence which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list ofour partnersandhere’s how we make money.
Dividends arent free money theyre usually taxable income. But how and when you own an investment that pays them can dramatically change the dividend tax rate you pay. There are many exceptions and unusual scenarios with special rules see IRS Publication 550 for the details but heres generally how dividend tax works.
Don’t Miss: Why Do You Lose Child Tax Credit At Age 17
The Net Investment Income Tax
The Net Investment Income Tax is a heartier 3.8%. It kicks in at the income thresholds of your net investment income, or at the same $250,000/$125,000/$200,000 limits as the Additional Medicare Tax, whichever is less.
All taxable dividends are investment income, even if they’re taxed at ordinary rates.
Tax laws change periodically. You should always consult with a tax professional for the most up-to-date advice. The information contained in this article is not intended as tax advice. It’s not a substitute for tax advice.
How Do Interest Dividends On State Or Municipal Bonds Work
Mutual funds and ETFs may have state or municipal bonds as holdings. These bonds pay interest that’s often exempt from federal income tax. When mutual funds or ETFs distribute this interest, they usually do it through an interest dividend.
Interest dividends from state or municipal bonds aren’t typically taxable on the federal income tax level unless you’re subject to the Alternative Minimum Tax . This income is usually reported in box 11 of Form 1099-DIV.
Read Also: How To Get An Advance On Your Taxes
