Gross Payment Of Pids For Certain Categories Of Shareholder
Under the REITs rules, certain categories of shareholder are entitled to receive PIDs without deduction of tax. Shareholders qualifying for gross payment are principally UK resident companies, UK public bodies, UK charities, UK pension funds, and the managers of ISAs, PEPs, Child Trust Funds, and partnerships where all members qualify as one of the aforementioned bodies. Most shareholders, including all individuals and all non-UK residents, do not qualify.
The completed forms should be submitted to the Companys Registrars, Link Asset Services, The Registry, 34 Beckenham Road, Beckenham, Kent BR3 4TU. It is only necessary to complete a form once. For qualifying shareholders who have not previously submitted a form, this must be received by the Registrars by the record date to qualify for gross payment of the PID element of upcoming dividends.
Us Real Estate Investment Trusts
Background
Income from REITs is subject to different U.S. withholding regulations depending on how the components of the income distribution are classified. Such income can include dividends, REITs capital gains dividends and return of capital.
Under the American Jobs Creation Act of 2004, REITs capital gains dividends could be considered as ordinary dividends and reported as such under the following conditions:
- The distribution is received in respect of a class of stock that is regularly traded on an established securities market located in the U.S.A.;
- The beneficial owner did not, in the aggregate, own more than 5% of the outstanding shares of the class of stock at any time during the taxable year; and
- The beneficial owner is a non-U.S. person.
In December 2015, the President of the United States signed into Law H.R. 2029, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2016. The law has modified the holding threshold in order for REITs capital gains dividends to be classified as ordinary dividends from 5% to 10%.
At the time of the initial income distribution, the classification may not yet be known, in which case, the REITs income will be taxed as an ordinary dividend during the year of the distribution.
Dividends are consequently paid by Clearstream Banking1 according to the tax certification provided by customers for Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 purpose.
Reclassification
At the end of the tax period, REITs can reclassify their income payments as follows:
| Original payment |
The Basics Of Reit Taxation
An REIT is a real estate investment trust. When you invest in an REIT, youre investing in a real estate firm managing commercial or residential properties, such as a shopping mall or apartment complex. Some REITs come with high returns and dividends, but they may also be considered riskier investments. This passive investing method is often popular when real estate markets boom, but its important to understand the tax structure before committing to this investment option.
There are three types of REITs:
In all three, investors receive regular dividendsprofit sharing payments from the real estate firms paid monthly, quarterly, or annually. Investors are required to pay taxes on dividends, and the majority of REIT dividends are taxed at ordinary income rates.
Capital gains taxes can also apply when you invest in a REIT.
Lets walk through everything you need to know about REITs, how theyre taxed, and how to set yourself up for success when investing in a REIT that pays dividends.
Recommended Reading: How Much Money Is Taken Out Of Paycheck For Taxes
Tax Tips For Real Estate Investment Trusts
OVERVIEW
A real estate investment trust, or REIT, is essentially a mutual fund for real estate. As the name suggests, the trust invests in real estate related investments. Investors buy shares in the trust, and the REIT passes income from its holdings to those investors. Because real estate generates different kinds of cash flow, the income that investors receive from a REIT can fall into different categories, each with its own tax rules.
How To Invest In Reits

If youre interested in investing in REITs, you can do so through a traditional or online broker. A few examples of fund REITs include:
- Vanguard REIT ETF
- Fidelity Real Estate Index Fund
- S&P Global REIT
You can also invest in REITs directly. For example, these REITs are available for direct investments:
- Brandywine Realty Trust
- Hannon Armstrong Sustainable Infrastructure Capital
- Safehold
- Annaly Capital Management
Read Also: How To Find Tax Lien Properties
How Much Do Reit Get Taxed
Because they can be allocated to ordinary income, capital gains, and return of capital, REIT dividends can be taxed at various rates. In general, the 20 percent maximum capital gains tax rate applies to the sale of REIT stock.
The majority of REIT dividends are taxed up to the maximum rate of 37 percent as ordinary income , plus a separate 3.8 percent investment income surtax. In general, taxpayers may also deduct 20 percent of the combined qualified business income amount by Dec. 31, 2025, which includes qualified REIT dividends. The highest effective tax rate on qualified REIT dividends is usually 29.6 percent, taking into account the 20 percent deduction.
In the following instances, however, REIT dividends will qualify for a lower tax rate:
- Where the individual taxpayer is subject to a lower rate of income tax scheduled;
- Where a REIT makes a distribution of capital gains or a return on the distribution of capital;
- If dividends received from a taxable REIT subsidiary or other corporation are distributed by a REIT ; and
- A REIT pays corporate taxes and retains income when authorized .
In addition, the maximum capital gains rate of 20 percent generally applies to the sale of REIT stock.
Holding Reit In Retirement Plans
The various types of tax treatment dont really matter if you hold an interest in a REIT as part of a tax-advantaged retirement savings plan, such as an IRA or 401. Thats because when earned, investment returns are not taxed in such plans.
With traditional IRAs and 401k plans, you pay income tax when you withdraw money from your account. And you dont pay withdrawal tax at all if its a Roth IRA or Roth 401. It doesnt matter whether it was a dividend, capital gain, or return of capital if you take money out of one of these retirement accounts because all the distributions are usually considered ordinary income.
Read Also: How Do I Pay My State Taxes In Missouri
How Are The Dividends You Receive From A Reit Taxed
Last, but definitely not least, the most important question for dividend growth investors. ;Dividends received from traditional equity securities are subject to capital gains taxes. However, this is not the case for REITs, since REITs do not pay taxes at the corporate level
Dividends and distributions from a REIT are not a straightforward distribution. There are several components to each dividend and distribution. ;Each REIT must provide investors with the following allocations for each dividend and distribution to ensure property tax treatment:
- Dividends Taxed as ordinary income, not a capital gain. ;
- Qualified Dividends Taxed as a capital gain
- Nontaxable Return on Capital ;Taxed as a capital gain
There was one huge change in taxation for REIT investors as well as a part of Tax Reform.; ;As a part of the bill, there is a 20% deduction on pass-through income.; Since a REIT passes through its income to shareholders, the individual holder will receive a huge benefit as a part of tax reform!
Prior to tax reform, since the majority of your dividend is taxed as ordinary income at a higher tax rate, I held all REITs in my Roth IRA so any future distributions are not taxed.; ; However, this 20% reduction is huge and would potentially impact future investment decisions (in terms of where I hold the investment.
How To Avoid The Complicated And Expensive Tax On Reit Dividends
This discussion is a moot point if you hold your REITs in tax-advantaged retirement accounts. REITs are popular retirement investments for this reason. You dont have to worry about paying dividend taxes each year. And you don’t need to worry about complicated capital gains taxes when you sell shares of a REIT.
If you own REITs in tax-deferred accounts, like a traditional IRA or 401k, you wont pay taxes until you withdraw money from the account. Funds in these accounts can continue to grow tax-deferred as long as theyre in the account. And they’re treated as taxable income when the money is eventually withdrawn. Plus, contributions to these accounts are generally tax-deductible in the year theyre made.
On the other hand, if you own REITs through an after-tax account like a Roth IRA or Roth 401k, you wont ever have to pay taxes on your REIT dividends and capital gains, even when you withdraw from the account. The drawback is that contributing to a Roth account doesnt get you any immediate tax benefit. But that’s a small price to pay to avoid future taxation on qualified withdrawals.
Don’t Miss: How To Calculate Sales Tax From Total
Reit Dividends Can Be Complicated
Does a REIT dividend meet the IRS definition of a qualified dividend, or is it considered ordinary income? The answer could be yes to both.
In most cases, REIT dividends are made up of as many as three different types of income:
· Ordinary Income: Most rental income generated by REITs and passed through to investors is considered ordinary income, just as if it had been earned through an LLC or partnership and passed through to an owner.
· Qualified REIT Dividends: Depending on how a REIT made its money for a certain time period, a portion of the dividend distributions can be considered a qualified dividend. These may also be referred to as capital gain distributions.
· Return of Capital: If a portion of a REIT’s income comes from selling assets, some of its distributions can be considered a return of investor capital, which is not taxable. However, it’s important to note that a return of capital serves to lower the investors’ cost basis, which could result in higher capital gains tax when shares are eventually sold. Some REITs refer to these simply as nontaxable distributions.
Real Estate Investment Trusts
Company profits are subject to corporate taxes and dividends paid are typically subject to qualified dividend tax rates. When it comes to real estate investment trusts, or REITs, taxation is a bit more fornitureindustrialisassari.it only can REITs avoid corporate tax altogether, but REIT dividends have a complex tax treatment you should know about.
Read Also: How To File Taxes Doordash
Dividends And Our Obligations As A Reit
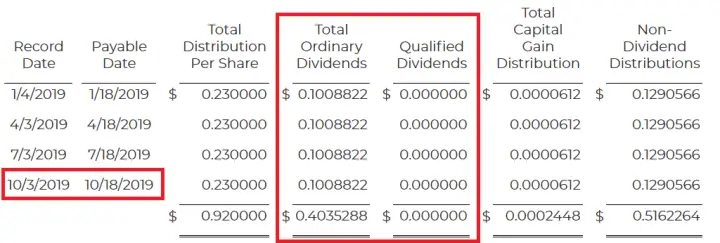
As a Real Estate Investment Trust , British Land must follow certain rules relating to money it distributes to shareholders, and how those distributions are taxed. 90% of the tax-exempt profit from British Land’s property rental business has to be distributed to shareholders. This is known as a Property Income Distribution, or ‘PID’. British Land can also distribute taxed income from its other activities, known as a Non-Property Income Distribution, or ‘non-PID’.
These distributions are commonly made by way of dividend payments. Dividends can be entirely PID, entirely non-PID, or a combination of the two; the Board will decide the most appropriate make-up on a dividend-by-dividend basis. Further, the PID/non-PID make-up of the Scrip Dividend Alternative may be different to that of the underlying cash dividend.
Key Terminology What The F
When we screen for undervalued dividend growth stocks, one of the key components of our metrics is Earnings-Per-Share . ;EPS is a GAAP metric that represents a companys net income dividend by shares outstanding. GAAP stands for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, the accounting framework by nearly all publicly traded companies.; There is some comfort in a companys EPS figure, as this is an audited number within a companys financial statements.
Even though a REIT is required to pay out 90% of its income, EPS is not the top metric used to evaluate a REIT. ;;The industry standard is a non-GAAP metric: Fund From Operations or Adjusted Funds From Operations .
FFO is a figure that begins with Net Income, and then adds back depreciation, amortization, and gains/losses on the sale of properties. The theory behind using FFO over EPS or other cash flow metrics is that it provides a better picture of a REITs true cash flows. ;Depreciation, amortization, and gains/losses on sales are all non-cash items on an income statement.
Since FFO is a non-GAAP metric, it can be calculated differently for each company. ;So please make sure you understand each companys method for calculating FFO and AFFO to ensure you are making an apples to apples comparison. ;;
Read Also: How To Reduce Income Tax
Withholding Tax On Pids
For most shareholders, PIDs are paid after deducting withholding tax at basic rate income tax, currently 20%. So, if a PID of £100 is paid, the company will pay £20 to HMRC and £80 to the shareholder.
Because of the withholding tax, a UK individual taxable at the basic rate should have no further tax to pay. Higher rate taxpayers and additional rate taxpayers will have an additional tax liability of 20% and 30% of the gross PID respectively. Someone who does not pay tax, perhaps because of personal allowances, may in their tax return reclaim the tax withheld.
What Are Qualified Dividends
Qualified dividends are dividends that meet certain requirements as stipulated by the IRS and are therefore subject to lower taxes. Qualified dividends are taxed at the long-term capital gains tax rate.
They were first introduced in the Bush tax cuts of 2003 in order to benefit investors who invest for the long term, i.e. retirement.
In table below you can see the difference in taxation between ordinary dividends which are taxed as ordinary income and qualified dividends which are taxed as long-term capital gains.
| Income | |
| 37% | 20% |
Especially, with lower income the long-term capital gains rate has a lot of advantages as you basically pay no tax up to around $40,000 in income.
As outlined by the IRS in their Publication 550 certain requirements have to be met in order for the dividends to qualify for the lower tax rate.
To qualify for the maximum rate, all of the following requirements must be met.
- The dividends must have been paid by a U.S. corporation or a qualified foreign corporation.
- The dividends are not of the type listed later under Dividends that are not qualified dividends.
- You meet the holding period.
The holding period means that you must have held the stock for more than 60 days during the 121-day period that begins 60 days before the ex-dividend date.
The ex-dividend date is the first date following the declaration of a dividend on which the buyer of a stock is not entitled to receive the next dividend payment.
Also Check: What Does Locality Mean On Taxes
An Example: The Qbi Deduction In Practice
Lets assume that someone earns $1,000 in qualifying dividends from their investment in Arrived and $1,000 extra from their job. Assume that this person is in the 24% tax bracket.;
The extra $1,000 of income from the job is taxed at the ordinary rates. Theyd pay an additional $240 of income taxes for the $1,000 that earned .;
After paying your taxes, this person is left with $760 from the $1,000 of income.;
The dividend income is treated differently. They get to deduct 20% of the income before calculating the taxes youll owe. So for the $1,000 of Arrived dividends, the investor immediately deducts 20%. The 20% deducted from the dividends means a taxable income of $800. .;
Now this person pays 24% income tax on $800 of income, which is $192. . After paying the taxes, theyre left with $808 .;
Overall, this person pays 24% of their income from their job in taxes but only 19.2% of their Arrived income !;
The QBI deduction effectively lowers your tax rate by 20% for your REIT dividends. Our example investor pays 19.2% on their REIT income but 24% on the income from their job.;
This makes a huge difference! REITs, as passthrough entities, qualify for the Qualified Business Income deduction and pass huge tax savings on to their investors.;
Reits Dont Pay Any Corporate Tax
When it comes to stock investing, you should know there are two types of taxation. First, when you sell for a profit, there are individual taxes that youll pay on dividends and capital gains tax you pay.
Second, before the company distributes income to shareholders, corporate taxes can be assessed on the profits of a company. These are related to your earnings only indirectly, but theyre worth considering.
A special case is REIT taxation. REITs pay no corporate tax whatsoever in exchange for meeting certain requirementsin particular, paying at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders as dividends.
Also Check: How Is Capital Gains Tax Calculated On Sale Of Property
Type Of Payment Determines Tax Treatment
Payments from REITs are referred to as “dividends,” but they’re a bit more complicated than dividends you receive from buying stock. Because REITs generate income in different ways, there are three types of dividends:
- Ordinary income: Money made from collecting rent or mortgage payments.
- Capital gains: Money made from selling property for more than the REIT paid for it.
- Return of capital: This is essentially the REIT giving you some of your own money back.
In general, “what happens in the REIT” dictates the tax treatment. Capital gains distributions, for example, are subject to capital gains taxes.
Picking The Best Canadian Reits
To find the best Canadian REITs fitting my criteria, I choose to go through the following steps.
- Sort the REITs based on the Chowder Score
- Sort the REITs by Dividend Increases
Get all the details you need to make an investment decision with the;Dividend Snapshot Canadian REIT List. A comprehensive list of metrics and a payout ratio calculated based on the companys FFO. Dont be fooled by the highest yield and get the right fit for your portfolio and income.
Also Check: What Do I Do If I Owe Taxes
