How Does Inheritance Tax Work
When people use the term “inheritance tax,” they generally refer to a levy against money or property that a person or entity inherits from someone who gives it to them in a will. However, there is sometimes confusion between an inheritance tax and the federal estate tax, which is different. In fact, there is no federal inheritance tax, although there is an estate tax. The IRS defines the estate tax as:
a tax on your right to transfer property at your death. It consists of an accounting of everything you own or have certain interests in at the date of death. The fair market value of these items is used, not necessarily what you paid for them or what their values were when you acquired them. The total of all of these items is your “Gross Estate.” The includible property may consist of cash and securities, real estate, insurance, trusts, annuities, business interests, and other assets.
Currently, six states impose an inheritance tax, and twelve have an estate tax . The notable difference between the two types of assessment is who pays the tax and how they work. The beneficiary of the gift is responsible for paying any owed inheritance tax, while the estate pays the estate tax. The determination of estate taxes due is calculated before distributing assets to the named beneficiaries.
What About Retirement Accounts And Real Estate
One important note: Someinheritances on retirement accounts or a traditional IRA) are subject to other pesky taxes, like income taxes. Retirement accounts like these can get sticky, and distributions are typically taxable. We know, its a lot, but hang in there.
Similarly, if you inherit a piece of property and sell it, you may have to pay a capital gains tax. That just means youre taxed on any profit you make above the value of the property at the time of your loved ones death and when you inherited it.
Both of these situations can get really confusing really fast, so you should get with a tax pro to make sure youre covering all your bases.
How Do Inheritance Taxes Work
Now for some good news. Uncle Sam doesnt have an inheritance tax and inheritances are not considered taxable income in most casesso you won’t have to report your inheritance on your state or federal income tax return.
For example, if your father-in-law from Tennessee, a no-inheritance-tax state, leaves you $50,000, and you live in, say, New Jersey a state with an inheritance tax exemption threshold of $25,000 for children-in-law that wouldnt be considered income, and you would be free to enjoy the inheritance without worrying about taxes.4
On the other hand, lets say your father-in-law lived in New Jersey, and he left you $50,000. You would pay an inheritance tax of 11% on $25,000 when it passes to you.5
Each state is different and taxes can change at the drop of a hat, so its a good idea to check tax laws in your state, or better yet, talk to a tax pro!
Don’t Miss: How To File Taxes For Personal Business
Migration Responses To Inheritance Taxation Appear Generally Limited
Mobility responses to inheritance taxation may be lower than in the case of other taxes on wealthy households, such as taxes on net wealth or personal income. A recurrenttax on net wealth may provide stronger incentives to migrate than a one-off or infrequent tax on wealth transfers. There are very few studies on migration responses to wealth taxes, but these find substantial within-country migration responses to net wealth taxes. In the case of Switzerland, Brülhart et al. find that 24% of the aggregate response to changes in net wealth taxes is due to taxpayer mobility. Looking at Spain, Agrawal, Foremny and Martínez-Toledano find evidence of wealthy individuals flocking to Madrid following the reintroduction of the net wealth tax in 2011, with Madrid serving as an internal tax haven with a tax rate of 0%. They find that five years after the reform, the stock of wealthy individuals in the region of Madrid increased by 10% relative to other regions. Recent studies looking at personal income taxes have also found sizeable tax-induced migration among wealthy taxpayers, although behavioural responses are highly context- and population-specific and the ultimate economic effects of such migration may be limited.
What Happens To The Deceased’s Earned Income
Earned incomesalary, business income and pension income received up to the date of deathmust be included in the deceased’s final tax return.
For certain types of income, a return for rights or things can be filed to limit the taxes payable. For example, a return for rights or things can be filed for unpaid dividends declared before the date of death.
Recommended Reading: How To Do State Taxes For Free
Inheritance And Gift Taxation Can Strengthen Horizontal And Vertical Equity
An inheritance tax can enhance horizontal equity. According to the horizontal equity principle, people receiving the same amount of income or assets should be taxed similarly. Thus, there should not be a difference in the tax burden of people in equal circumstances depending on whether they receive transfers from others in the form of earnings or in the form of gifts and inheritances. An inheritance tax can therefore be justified to level the playing field between inheritances and earnings from work or savings.
An inheritance tax, particularly a progressive one, would also enhance vertical equity. According to the vertical equity principle, taxpayers with a greater ability to pay tax should pay relatively more tax. By taxing wealth transfers, particularly at progressive rates, an inheritance tax ensures that those who receive more wealth pay more tax. In fact, inheritance taxes are often among the most progressive elements of countries tax systems , although effective progressivity is often lowered by the way inheritance and gift taxes are designed .
States With An Inheritance Tax
The federal government does not have an inheritance tax. The six states that impose an inheritance tax are:
Of course, state laws are subject to change, so if you are receiving an inheritance, check with your state’s tax agency. The tax rates on inheritances can be as low as 1% or as high as 20% of the value of property and cash you inherit.
Read Also: How Can I File An Amended Tax Return Online
Review Of The Arguments For And Against Inheritance Taxation
Chapter 2 reviews the arguments for and against inheritance taxation, drawing on theoretical and empirical literature. Through the lens of equity, efficiency, and administration, the chapter assesses the pros and cons of taxing inheritances. The chapter also discusses gift taxes, as a necessary and common complement to inheritance taxation.
This chapter reviews the arguments for and against inheritance taxation. Largely based on existing theoretical and empirical literature, it assesses the pros and cons of taxing inheritances based on equity, efficiency, and administrative considerations. In this chapter, the term inheritance taxation is used to refer to all taxes levied on wealth transfers upon the death of donors, whether they are levied on donors estates or on the wealth received by heirs . As a necessary complement to inheritance taxation, the chapter also considers taxes on gifts made during the donors lifetime. After briefly characterising inheritance taxation, the chapter starts by discussing the equity arguments in favour of inheritance taxation. The chapter then examines the efficiency effects of inheritance taxation on the behaviours of both donors and heirs. The last section of the chapter discusses the administrative implications of inheritance taxation. The chapter also compares the effects of inheritance taxes with the impact of other taxes that can be levied on wealthy households, including personal income taxes and net wealth taxes.
Specific State And Local Taxes
How do state estate and inheritance taxes work?
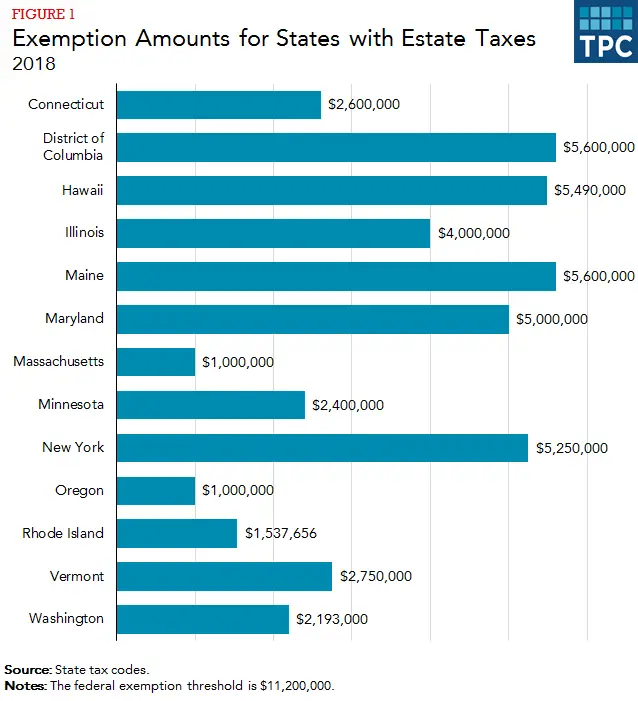
Twelve states and the District of Columbia have an estate tax and six have an inheritance tax . Before 2001, when a federal credit offset the cost of state taxes, all states taxed the transfer of wealth at death.
State and local governments collected $5 billion from estate and inheritance taxes in 2017, well less than 1 percent of combined state and local own-source general revenue. In 2000, the last year all states levied an estate tax, these taxes still provided less than 1 percent of combined state and local own-source general revenue.
ESTATE TAX
An estate tax is paid by the estate itself on the transfer of property at the time of a persons death. States must allocate assets across jurisdictions if the deceased person lived or owned property in multiple jurisdictions.
Before 2001, all 50 states and the District of Columbia had an estate tax because the federal estate tax provided a state tax credit worth 16 percent of the taxable value of the estate. Thus, states could raise revenue without increasing the net tax burden on their residents by linking directly to the federal credit, and all states did this by setting their estate tax rate equal to the maximum credit. However, federal tax changes in 2001 replaced the credit with a less valuable deduction, and many states eliminated their tax.
INHERITANCE TAX
BACKGROUND
Also Check: What Happens If I File Taxes Late
Exemptions From Inheritance Tax
You do not pay inheritance tax on a surviving dependants pension or state pension. The surviving dependants pension, however, is deducted from the partners exemption. In certain special situations you pay less or no inheritance tax. Contact the Tax and Customs Administration for more information.
Inheritance Taxation Has Administrative Advantages Over Other Forms Of Wealth Taxation
The cost of administering and complying with inheritance taxes may seem high in comparison to the limited revenues they typically raise. Chapter 3 contains information on the revenues raised from inheritance and gift taxes, as well on the administrative and compliance procedures they involve. Inheritance taxes generally require a full statement of the donors wealth i.e. assets at death, detailed valuations where necessary and the computation and payment of the tax on a wide range of assets for which different reliefs apply. While these administrative and compliance costs may seem high, they include a number of unavoidable fixed costs that are linked to the legal recognition of transmissions and changes in property ownership. In addition, part of these administrative and compliance costs arise from the way inheritance and estate taxes have been designed, particularly from their narrow tax bases, and could therefore be reduced through tax reform.
Recommended Reading: How Is An Inherited Ira Taxed
What Is An Estate Or Inheritance Tax
An estate tax is a tax on property transferred from deceased persons to their heirs. A state applies a tax rate to the value of an estate that exceeds a certain threshold both the rate and the exemption threshold differ by state. A typical state with an estate tax exempts $2 to $5 million per estate and applies rates ranging from 1 percent to 16 percent to the value of property left to any heirs except a spouse. On average, fewer than 3 percent of estates very large ones owned by the wealthiest individuals owe state estate taxes.
Some states levy an inheritancetax rather than an estate tax. It is levied on the recipients of the estate instead of the deceased persons estate.
For example, consider an unmarried woman who owns a house, stocks, cash, and other assets worth $30 million. She leaves those assets to her three children in equal shares upon her death. In a state with an estate tax, the tax is based on the value of the entire $30 million estate and is subtracted from the value of the estate before its distribution to the heirs. In a state with an inheritance tax, the children each receive their $10 million bequest and then owe inheritance tax on that bequest.
How Does Inheritance Work And What Should You Expect

The 2019 Survey of Consumer Finances found that the average inheritance in the U.S. is $110,050 for the middle class. Yet an HSBC survey found that Americans in retirement expect to leave nearly $177,000 to their heirs. As it turns out, the passing of property and assets doesnt always go as expected or planned. Plus, though it may seem like a windfall, getting an inheritance is rarely as easy as depositing a check. If you have questions surrounding the specifics of your inheritance, consider speaking with a financial advisor.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is Tax Preparation
How To Decrease A Taxable Part Of An Estate In Montana
Montana residents can easily decrease the taxable part of their estate using the fact that the state has no gift tax. In other words, you can simply gift away a part of your property to your children, grandchildren, or any other heirs and therefore protect the overall estate.
However, there is a Federal Gift Tax that prevents people from simply gifting away million-worth shares of their estate at once, avoiding the Federal Estate Taxation.
Nevertheless, the Federal Gift Tax has an annual exclusion of $16,000 . You can also make such gifts to as many people as possible.
It means that a married couple that has 3 children and 5 grandchildren can cut the taxable part of their estate by $256,000 every year without having to report those acts to IRS or affecting the lifetime exemption.
The absence of gift tax in Montana, as well as federal tax exemptions, allows you to easily protect your legacy for your future heirs. Addressing a professional advisor, you are guaranteed to get the most out of your estate planning and reduce its taxable part without any adverse side effects.
How Can I Avoid Estate Taxes
Keeping your estate under the threshold is one way to avoid paying taxes. Other methods include setting up trusts, such as an intentionally defective grantor trust, which separates income tax from estate tax treatment, transferring your life insurance policy, so it won’t be counted as part of your estate, and making strategic use of gifting.
Recommended Reading: What All Do I Need To Do My Taxes
Real Tax Experts On Demand With Turbotax Live Basic
Get unlimited advice and an expert final review. Done right, guaranteed.
-
Estimate your tax refund andwhere you stand
-
Know how much to withhold from your paycheck to get
-
Estimate your self-employment tax and eliminate
-
Estimate capital gains, losses, and taxes for cryptocurrency sales
The above article is intended to provide generalized financial information designed to educate a broad segment of the public it does not give personalized tax, investment, legal, or other business and professional advice. Before taking any action, you should always seek the assistance of a professional who knows your particular situation for advice on taxes, your investments, the law, or any other business and professional matters that affect you and/or your business.
Do You Have To Report The Sale Of Inherited Property In Canada
All property sales must be reported properly as part of your income tax in Canada. If you are selling inherited a real estate that was a primary residence, you will need to report it and pay 50% of the capital gains tax with your income tax. The tax will be charged based on the difference in the fair market value of the property from when you received it to when you sold it.
You May Like: How Do Tax Returns Work
What Happens When You Inherit Real Estate
First, you need to determine if the residence is principal or secondary. If you intend to live there full-time, it is a principal residence. Cottages or other similar properties where you wouldnt be living there full-time are secondary residences. One thing to keep in mind? Turning the property into a rental would make it a secondary residence.
You dont have to pay capital gains taxes on a principal residence. However, if it is a secondary property, you will have to pay tax on 50% of the capital gain in the year you inherit the real estate. Normally, this is processed on the final tax return of the deceased individual.
When To Pay Inheritance Tax
Inheritance tax must be paid within 60 days of the date on which the tax assessment is served. If an heir doesnt pay the inheritance tax by the 60-day deadline, theyll be charged penalties and interest on the overdue payment. The tax can also be paid in installments if the amount exceeds 1,000. In this case:
- At least 20% of the amount must be paid within the 60-day deadline, starting from the tax assessment notification.
- The remainder must be paid in eight or 12 quarterly installments, depending on the amount. The interest on these installments is calculated starting from the first day on which the initial sum is paid. Installments are due on the last day of each quarter.
When filling the declaration, youll need to enter the IBAN of the account from which the taxes will be debited, along with the account holders tax number. The electronic submission can be filed by the declarant themselves, or someone else entrusted with the task. The tax must be debited from a bank account affiliated with the Italian Revenue Agency or Poste Italiane S.p.A.
You May Like: How To Find Out Last Year’s Tax Return
The Double Taxation Argument Appears To Be Weak
Double taxation is a popular objection to inheritance taxes, but it is far from unique to inheritance taxation. If the wealth transferred is accumulated from wage earnings, savings or personal business income, then these flows will have in many cases already been taxed. However, multiple levels of taxation are far from unique to taxes on wealth transfers. Consumption taxes, for instance, are paid out of post-tax income. In the area of wealth taxation, the double taxation argument is stronger in the case of net wealth taxes, levied on self-made wealth on a recurrent basis, than in the case of inheritance taxes which are levied once at the end of the donors life . Economically, it is important to point out that what really matters is overall effective tax rates, rather than the number of times assets or income are subject to taxation.
The double taxation argument is weaker when inheritance taxation is considered from the perspective of beneficiaries. The inherited wealth is only taxed once in the hands of the recipient and the wealth received provides them with what can be viewed as an unearned gain, which can, in some circumstances, exacerbate existing inequalities. More generally, opponents of inheritance taxation on the grounds that it generates double taxation tend to look at it from the donors perspective, while those in favour of inheritance taxation tend to consider the issue from the recipients perspective .