How Inherited Annuities Are Taxed
Understanding how inherited annuities are taxed starts with knowing the difference between qualified and non-qualified annuities.
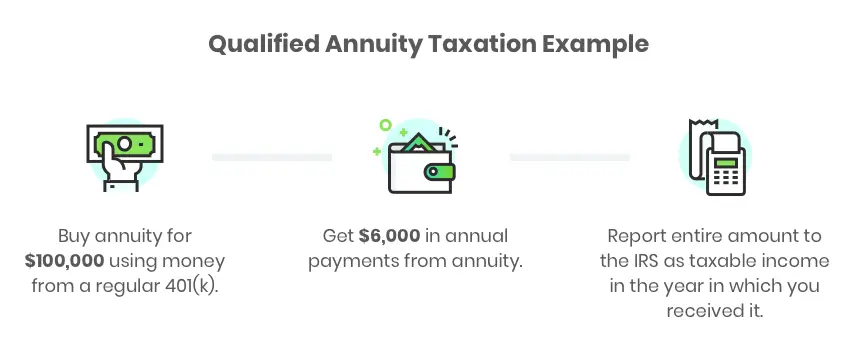
A qualified annuity is an annuity thats purchased using pre-tax dollars through a tax-advantaged account, such as a 401 plan or an individual retirement account. Any distributions paid to the annuitant from a qualified annuity are treated as taxable income in the year theyre received. Withdrawals made before age 59 1/2 are subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty. Qualified annuities must also follow the required minimum distribution rules.
A non-qualified annuity, on the other hand, is funded using after-tax dollars. That kind of sounds like a Roth account but theres a catch. The contributions made to a non-qualified annuity arent taxable. However, any growth or earnings on your initial investment are tax deferred. In other words, you have to pay ordinary income tax on the earnings part of your distributions. But, there is no 10% early withdrawal penalty to worry about and you dont have to deal with RMDs either.
Annuity Taxes Put Into Practice
Remember the basis, or;post-tax purchase money for non-qualified annuities, that we spoke about earlier? Well, you can now take the basis and divide it by the expected return. The result of this equation is the percentage of each payment that will not be taxable. To make things more tangible, multiply this percentage by the amount of each payment to figure out the exact dollar amount that wont be subject to federal income taxes.
For example, say you paid $90,000 for a lifetime annuity with an expected return of $120,000. Dividing the basis by the expected return gives you 75%. Then, by multiplying 75% by the amount of each payment, youll see how much of the payment will not incur taxes. So if your $120,000 annuity assumes your life expectancy is 20 years, your monthly payments would be $400. Of that, $300, or 75%, would be tax-free.
This is a much simpler example that what youll likely encounter in real life. There are different situations in which you might be subject to more or less taxation. In fact, if you live longer than the IRS longevity table says you will, you will likely pay taxes on all your lifetime annuity payments that occur after your maximum age that the IRS longevity table forecasted. It may not be a bad idea to consult with a financial advisor. In particular, tax professional could help you before you buy or take withdrawals from an annuity.
Tips For Your Retirement Savings
- If you feel youve exhausted every option to boost your retirement savings, you might want to consult a financial advisor who has dealt with retirement planning before. Rather than search for an advisor on your own, the SmartAsset financial advisor matching tool;can pair you with up to three local experts are equipped to meet your unique needs.
- Dont focus only on the balance of your 401, IRA or another retirement savings vehicle. Be sure you dont forget about Social Security benefits. It would be difficult for most retirees to live solely off of Social Security. But they payments it can be a helpful addition to any savings plan. SmartAssets Social Security calculator;can help you estimate what youll receive.
You May Like: How Are Property Taxes Calculated In Texas
Tax Implications On Annuity Payouts
Generally, monthly income payments from a non-qualified annuity consists of two portions: 1) the tax-free portion that is deemed as repayment of the annuitants net cost of the annuity, and 2) the remaining portion that is taxable as earnings. Accordingly, its usually wise to plan annuity income payments to spread the principal amount evenly across the total number of payments.
How Your Annuity Income Is Protected

Canadian life insurance companies have the obligation to be members of a consumer protection agency called Assuris. Assuris protects policyholders up to a certain amount if the annuity provider is unable to pay. You will then continue to receive at least some of your money if your provider goes out of business.
The income you receive from an annuity covered by Assuris is insured as follows:
- 100% for monthly payments up to $2,000
- 85% for monthly payments above $2,000
For example, if your regular annuity income is $1,500 per month, you will continue to receive the full amount. If your regular annuity income is $3,000 per month, then you will continue to receive 85% of this amount, or $2,550.
Recommended Reading: Can You Claim Rent On Your Taxes
Variable Annuities Within Retirement Accounts
If;the variable annuity is held in a retirement account, the;variable annuity is taxed like anything else within that account. For instance, if one of the investment options in your 403 plan is a variable annuity, when you defer salary to contribute to the annuity within that plan, those deferrals will reduce your taxable income and when you take money out of the plan it will be taxable as income.
Annuity Early Withdrawal Penalties
An annuity can be a smart addition to your retirement plan but its important to keep in mind that if you make a withdrawal prior to the designated time period, you can expect to pay early withdrawal penalties on your annuity.;
- Annuity withdrawals made before you reach age 59½ are typically subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty tax. For early withdrawals from a qualified annuity, the entire distribution amount may be subject to the penalty. If you withdraw money early from a non-qualified annuity, typically only earnings and interest will be subject to the penalty.
- While there arent many exceptions to the 10% early withdrawal penalty, you can explore potential options with your tax advisor that may be available to you based upon your individual circumstances. ;
- In addition to potential tax penalties, withdrawals may also be subject to surrender charges by the annuity issuer. This may happen if the amount withdrawn exceeds any penalty-free amount during the surrender charge period. Surrender charges vary by the annuity product you purchase, so make sure to check with the annuity issuer before withdrawing money from an annuity.
If you are considering withdrawing from your annuity early, its a good idea to speak with a tax professional.;
You May Like: Can You Change Your Taxes After Filing
What Is A Joint And Survivor Annuity
A joint and survivor annuity is an annuity contract that guarantees payments so long as the contract owner or a secondary annuitant lives. Payments are slightly lower, but they last longer. Provisions can be added for making payments to a third party should both annuitants die before payments exceed the principal.
How Is An Annuity Taxed
Daniel Schorn
Many of the financial tools that you use for retirement have complicated tax rules. For instance, the money you put in 401s, Roth accounts and non-qualified investment accounts will be taxed at some point â but how and when differs depending on the type of account, how long youâve held your money in the account, and possibly even how much income you make.
Another tool often included in a diversified retirement plan is an annuity. Annuities, which can help you save for retirement or generate a guaranteed lifetime income after you retire, can protect you from the risk of outliving your assets.
But how is an annuity taxed? Understanding how they are taxed will help you get a clearer picture of how much money youâll likely have in retirement. First, letâs review some annuity basics.
Read Also: Do I Pay Taxes On Stimulus Check
Taxation During The Deferral Period
Registered
– Registered annuities are non-taxable during the deferral period .
Non-registered
– All annuities are taxed on an annual basis and receive accrual tax treatment . Once income payments begin, and assuming all conditions are met, the tax treatment will change to prescribed* . The tax treatment remains accrual if the conditions are not met or the client requests that the tax treatment remain accrual. * For an annuity with prescribed taxation if income is deferred more than one year from purchase, tax treatment will be accrual until payments start.
Annuity And Taxes In Action
Do you remember the basis for non-qualified annuities? You can now divide the basis by the expected return. Based on this equation, you can calculate the percentage of payments that will be tax-free. If you multiply this percentage by the amount of each payment, you can determine the exact amount thats not taxable under federal income tax laws.
Take, for instance, a lifetime annuity that you paid $90,000 for. Its expected return is $120,000. Youll get 75% when you divide the basis by the expected return . You can find out how much of the payment will not incur taxes by multiplying 75% by the amount of each payment. If you assume a lifetime of 20 years, your monthly payment would be $400 if you purchased a $120,000 annuity. There would be a tax-free portion of $300 on that amount.
In real life, youll likely encounter a more complicated scenario. This is because taxation depends on a variety of factors that are based on the IRS longevity table. For example, if you live over the maximum age youre forecast to live, youll probably pay taxes on all the lifetime annuity payments youll receive after you reach the maximum age forecast by the IRS.
Because this is extremely complicated, its a good idea to speak with a financial advisor. An annuity tax professional, specifically, will assist in making the right financial decision before you buy an annuity or make a withdraw.
Read Also: How Much Is New York State Sales Tax
Speak To An Annuities Expert
Annuities are a popular option for many people as a means to bolster their retirement income, however, its important to understand how taxes are applied on the annuity you choose both for the income you receive and any death benefit features included.
This is where we can help. The advisors we work with can help you better understand the full tax treatment on any annuities you wish to buy after you reach retirement.
All advice is free and any information is always given in the strictest confidence.
Call us on 0808 189 0463 or make an enquiry to get started.
Annuities Offer Powerful Tax Advantages And A Few Pitfalls How To Cut Your Taxes And Avoid Surprises

Annuities are designed to build wealth and income for your retirement through tax deferral. Interest earned in a deferred annuity is not taxed until withdrawn. Deferring taxes accelerates savings growth because interest compounds faster without withdrawals needed to pay taxes.
Compounding occurs when interest is paid on previously earned interest. Most investments that earn interest, such as money market accounts, savings accounts, certificates of deposit and most bonds, create taxable income. Since youre paying federal income tax on it each year, youll have less after-tax interest to compound, and your savings wont grow as fast.
With a tax-deferred investment, all of your interest is compounded until withdrawn.
Annuities have some unique tax advantages. In some cases, they can even be used to pay for long-term care without the usual taxes on distributions!; But there are some potential tax pitfalls.
Don’t Miss: How Much Do I Need To Make To File Taxes
Why People Buy Annuities
Many people buy annuities to give them retirement income for the rest of their lives. An annuity contract can also be a means of building assets for other purposes with a more limited time span.
Annuities can be used to fund an Individual Retirement Account. They also may be used in Keogh-type retirement plans for the self employed.
Taxation Of Nonqualified Annuities After Annuitization
After annuitizing a nonqualified;annuity , payments from the annuity are taxed in the same way as payments from any other nonqualified immediate annuity. That is, part of each payment is nontaxable because it is considered to be a return of your basis , while the remaining portion of each payment is taxable as ordinary income. Eventually, if you live long enough to receive all of your basis back , further payments will be entirely taxable.
Read Also: How Is Capital Gains Tax Calculated On Sale Of Property
Natural Owner Of An Annuity
The owner of an annuity may be a natural or non-natural person. A natural person is a human being, for example. Some examples of non-natural persons are corporations, partnerships, and trusts.
We had heard about annuities and were investigating them for our IRAs. We also heard bad things about pushy brokers over the years. So when we went to the ImmediateAnnuities.com site we were skeptical about calling them. But whenever we called their staff was really friendly. They answered all our questions and one of their reps even told us that at our ages there was no advantage to buying the annuity with our IRAs. These guys are really honest!
An annuity contract will be treated as owned by a natural person even if the owner is a trust or other entity as long as that entity holds the annuity as an agent for a natural person. However, this special exception will not apply in the case of an employer who is the nominal owner of an annuity contract under a non-qualified deferred compensation arrangement for its employees. Immediate annuities are also excepted from the non-natural owner rule.
Basics Of Inherited Annuities
When someone purchases an annuity contract, they may have the option to name one or more beneficiaries. Those beneficiaries are then eligible to receive payments from the annuity if the original annuitant passes away.
There are a few reasons why someone might choose to name an annuity beneficiary. First, if a beneficiary is not named or if its not a joint and survivor annuity, which would continue paying benefits to a surviving spouse, any remaining money in the annuity would be lost. The financial institution the annuitant purchased the annuity from would get to keep any remaining benefits.
Second, naming beneficiaries to an annuity is one way to create a financial legacy for loved ones. If you have adult children, for example, you may want to name them as beneficiaries to a joint and survivor annuity so that they can receive any remaining benefits once you and your spouse die. An annuity can be used to supplement other financial resources, such as life insurance or a trust, inside of an estate plan.
Some annuities cant be inherited. If you purchase a single life or life only annuity, for example, the annuity would only pay benefits to you during your lifetime. There would be no death benefit to pass on to a beneficiary.
Recommended Reading: How To Do Taxes Freelance
How To Report Pension And Annuity Income
Separate any 1099-R statements you receive into two piles: those from your IRA, and those from your pension or annuity plans. You’ll report your IRA distributions on line 4a of the 2020 Form 1040. Report your pension and annuity distributions on line 5a.
These lines pertain only to the 2020 Form 1040 tax return. The IRS has revised Form 1040 several times since 2017, and the appropriate lines can be different for each tax year.
Are Inherited Annuities Taxable
Inherited annuities are taxable as income. The beneficiary of a tax-deferred annuity may choose from several payout options, which will determine how the income benefit will be taxed.
If the beneficiary is the spouse of the annuitant, the spouse can change the contract into his or her own name. After a change in ownership, the contract continues as if the surviving spouse owned the original contract. It maintains its tax-deferred status, meaning the beneficiary owes no immediate taxes.
The spouse could choose to take an immediate lump sum. This is an option for other beneficiaries, as well. In this situation, the beneficiary will owe taxes on the entire difference between what the owner paid for the annuity and the death benefit. This is the option with the highest tax consequences for the beneficiary.
The beneficiary can also withdraw the money over a period of five years. At that time, he will owe taxes only on the increased value of the portion that is withdrawn in the year. This option makes it less likely that the beneficiary will fall into a different tax bracket. Going to a higher tax bracket means higher taxes.
The option with the lowest tax exposure is to have the death benefits paid over the life expectancy of the beneficiary. This means that benefits will be paid out over a longer period of time.
Also Check: What Does Locality Mean On Taxes
An Ameriprise Financial Advisor Can Help
Annuities offer steady income and tax benefits making them a popular way to save for retirement. There are a variety of annuity products available to help meet retirement savings and income needs. ; An Ameriprise financial advisor can review your individual financial situation and partner with your tax professional to evaluate your annuity tax strategy.
related information
Or,;request an appointment online;to speak with an advisor.
There’s a sense of confidence that comes from feeling in control of your finances – and working with a financial advisor can help you get there. Please share your experience and tell your friends and family about me.
Background and qualification information is available at FINRA’s BrokerCheck website.
Investment products are not federally or FDIC-insured, are not deposits or obligations of, or guaranteed by any financial institution, and involve investment risks including possible loss of principal and fluctuation in value.
Considerations For Taking Early Withdrawals
There are two things to keep in mind when considering taking early withdrawals from your annuity.
One is the surrender period stated in your contract and set by the insurance company, and the other is the U.S. tax code. Both entities have stipulations for your withdrawals, and there are exceptions and provisions that affect the standard penalties for each.
Recommended Reading: How To Pay Llc Taxes