The Foolish Bottom Line
Nobody likes paying taxes, but the payroll taxes in the U.S. fund some pretty important programs. And as a final thought, it’s entirely possible that one parts of the payroll tax could increase in the not-too-distant future, as both Social Security and Medicare face long-term funding shortfalls.
The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.
How Do I Handle Independent Contractors Or Self
Independent contractors and self-employed individuals are not employees. However, employers should review the status of the worker to ensure that the individual is properly classified as an independent contractor. Businesses that engage them are not responsible for any employment taxes on payments made to them. These workers pay self-employment tax on their net earnings from self-employment , which is essentially the employee and employer share of FICA. If a self-employed person also has wages from a job, the wages are coordinated with the SE tax so that the wage-base ceiling can be properly applied.
If total payments to such worker in the year are $600 or more, the business must file an annual information returnâForm 1099-NECâto report the payments to the worker and to the IRS.
A Payroll Tax Withholding Example
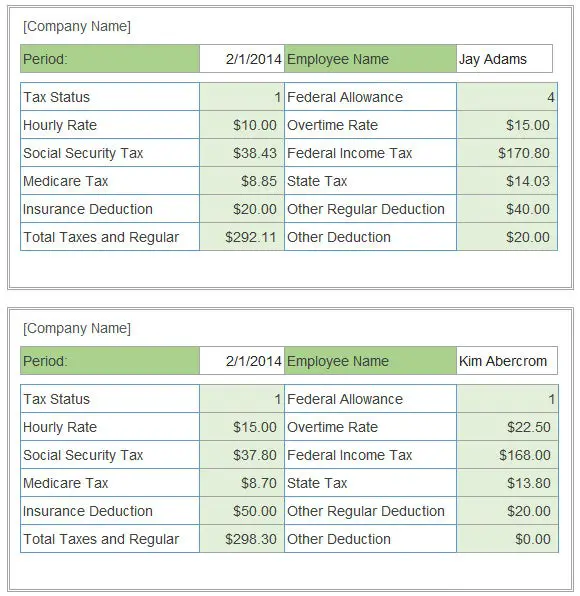
Lets say a business has an employee named Bob who is married, has two children and a spouse who also works. How would his federal tax withholding each pay period be determined if he earns $1,000 per week?
First, see if Bobs wages need to be adjusted. Since he isnt claiming any additional income from investments, dividends or retirement and hes chosen the standard deduction, his wages remain $1000.
Second, look at the weekly pay period bracket table on 15-T. For married filing jointly with the Form W-4 Step 2 checkbox withholding option, the tentative withholding amount is $88.
Third, account for tax credits. Bob has two children, so he may get $4000 in tax credits. Divide this number by 52 since hes paid weekly and subtract the result from $88 . The result is $11.08.
Finally, if Bob requested an additional $1000 withheld from his taxes each year on his Form W-4, divide that number by 52. The result is $19.23, which when added to $11.08, equates to a final withholding amount of $30.31 per pay period.
You May Like: When Do You File Tax Returns
What Your Employee Is On The Hook For: Income Taxes
Withholding taxes are pay-as-you-go individual income tax installments, that you collect and remitthroughout the year. Income taxes are levied federally and by most states, but they can also be leviedat the city or county level.
As an employer, its up to you to withhold the amount calculated by your employee from their overall pay,then deposit it as appropriate. As long as you do this accurately and on time, you should be problem free.
Your employees are responsible for helping you understand much income tax you should deduct by filling outForm W-4. Then you can use theIRS withholding calculatorto understand what tax rate to apply for each employee.
Income tax rates vary by state, like a flat tax of 3.07% in Pennsylvania or a tax that varies by incomelevel, reaching rates as high as 13.3% in California. Nine states dont collect individual income tax atall although there may be alternate taxes your employees will need to account for.
Other Terms Similar To Payroll Taxes That Can Assist You

- FICA: Represents the Social Security tax and Medicare tax an employer must withhold from employees paychecks plus the employers share of those 2 taxes.
- FUTA: An employer-paid federal payroll tax that is used to help fund the unemployment insurance system. Also provides a fund that states can borrow from for unemployment benefits purposes.
- SUTA : A state payroll tax that is used to help fund the unemployment insurance system. In most states, only the employer pays SUTA tax. A few states, including New Jersey and Pennsylvania, require employees to pay SUTA via payroll deduction.
- FICA tip credit: A credit that eligible food and beverage establishments can claim on a portion of their FICA taxes paid on employee tips.
- EFTPS (Electronic Federal Tax Payment System: The free 24/7 system that allows employers to make federal employment tax payments electronically via the Internet or by phone.
Recommended Reading: How Do Employers Pay Social Security Tax
Preparing For Employer Payroll Taxes When Hiring Employees
Before new hires start working, they typically fill out Form W-4 so that their employers can withhold the correct amount of federal income tax from their pay. They may also have to complete a separate withholding certificate for state income tax depending on the state. Some simply use the federal Form W-4 for this purpose and others dont collect income tax at all.
How Much Do Employers Pay In Payroll Taxes
So, how much is payroll tax? The cost of payroll taxes largely depends on the number of employees you have and how much you pay your employees. Why? Because payroll taxes are a percentage of each employees gross taxable wages and not a set dollar amount.
Payroll tax includes two specific taxes: Social Security and Medicare taxes. Both taxes fall under the Federal Insurance Contributions Act , and employers and employees pay these taxes.
Payroll tax percentage is 15.3% of an employees gross taxable wages. In total, Social Security is 12.4%, and Medicare is 2.9%, but the taxes are split evenly between both employee and employer.
So, how much is the employer cost of payroll taxes? Employer payroll tax rates are 6.2% for Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare.
If you are self-employed, you must pay the entirety of the 15.3% FICA tax, plus the additional Medicare tax, if applicable .
Recommended Reading: How Much To Do Tax Return
How Much Payroll Tax Will I Pay
Heres a Q & A recap of your employer payroll tax responsibilities:
- Do employers have to pay taxes on employees?
Never calculate payroll taxes again. Patriots online payroll will automatically calculate taxes so you can keep your time and money for what matters most: your small business. Start your free trial today!
This is not intended as legal advice for more information, please
Quarterly Tax Payment Due Dates
Quarterly FUTA taxes are due if you owe more than $500 in taxes each quarter.
The due dates are:
- Quarter Three: Oct. 31
- Quarter Four: Jan. 31
However, SUTA tax due dates vary by state. For example, in Michigan, the taxes are due on the 25th of the month instead of the end of the month: April 25, July 25, Oct. 25, and Jan. 25.
Failing to meet the deadline may result in a penalty or late tax payment interest assessment. Therefore, you not only have to know what taxes to withhold and pay but also when and how to pay itby state.
Don’t Miss: How To Claim Dependents On Taxes
Start Your Business With Shopify
Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools and services you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Understanding payroll taxes is crucial, whether you have just one employee or many. Payroll taxes began in response to the Great Depression, when the government began social welfare programs. The federal government passed the Federal Insurance Contributions Act in 1935, and employers began withholding money from employees paychecks to fund Social Security. Payroll taxes expanded to finance Medicare in 1965.
As a business owner, withholding the right amount of payroll taxes and paying them on time helps you avoid penalties and fines from the IRS.
How To Calculate Federal Income Tax Withholding Using The Wage Bracket Method
When using the Wage Bracket Method, there are two possible calculations: one for employees with a Form W-4 from 2019 or earlier, the other for employees with a Form W-4 from 2020 or later.
Employees with a Form W-4 from 2019 or earlier:
In IRS Publication 15-T, find the worksheet marked âWage Bracket Method Tables for Manual Payroll Systems With Forms W-4 From 2019 or Earlier.â
Check Form W-4 to determine whether the employee files income tax as married or single and the number of allowances they claim.
Enter the employeeâs total taxable wages for the payroll period on line 1a. This includes any earnings an employee pays taxes on, including salaries and cash tips.
Use the amount on line 1a to look up the Tentative Withholding Amount. Find the table that corresponds to your payroll period and the marital status of the employee
Find the wage amount on the left side of the table. Once youâve identified the row, use the number of allowances the employee has reported on Form W-4 to locate the corresponding column. The cell where these two meet will give you the tentative withholding amount for this employee.
Take the tentative withholding amount from this table and input it on line 1b.
On line 2a, enter any additional amount to be withheld as reported on Form W-4
Add lines 1b and 2a to find the amount to withhold from the employeeâs wages and record it in line 2b.
Employees with a Form W-4 from 2020 or later:
Read Also: Did I Make Enough To File Taxes
Benefits Of Using A Payroll Calculator
There are many benefits of using a payroll calculator, including the ability to estimate your paycheck in advance. You can also use the same tool to calculate hypothetical changes, such as withholding more money from each paycheck or increasing your retirement contributions.
Another benefit of a salary paycheck calculator is its ability to answer questions regarding your finances accurately. Examples include:
Wage Limits And Payroll Taxes

For 2021, the wage base limit is $142,800. If an employee earns that amount with one employer, then their payroll taxes are capped at that wage. If someone has more than one employer and earns more than that amount, theyll have to make a claim adjusting any overpaid Social Security taxes.
The Medicare tax has no wage-based limit, as all covered wages are subject to it. However, if you make over $200,000 a year, your employer will withhold an additional 0.9% Medicare tax.
Key takeaway: Payroll taxes include payments for Social Security and Medicare. There are also federal income taxes that must be paid. These payments do not go into a specific fund like the Social Security and Medicare taxes do.
Recommended Reading: Does California Have An Inheritance Tax
Federal Payroll Tax Rates
In most cases, the federal payroll tax rate is about 15.3%, with the employee covering 7.65% and the employer covering 7.65%. If youre self-employedas a sole proprietor or business owneryoure responsible for the full 15.3%, usually referred to as self-employment tax.
Potential additional taxes and credits based on your circumstances could change what your business is responsible for paying.
Employers and employees pay federal employment taxes that include payments toward Social Security, Medicare and unemployment insurance.
Social Security and Medicare taxes are collectively known as FICA taxes, for the Federal Insurance Contributions Act included in the 1930s New Deal legislation that introduced Social Security. Unemployment tax is known as FUTA tax for the Federal Unemployment Tax Act of 1939 that introduced that benefit.
The rates have gone up over time, though the rate has been largely unchanged since 1992. Federal payroll tax rates for 2022 are:
- Social Security tax rate: 6.2% for the employee plus 6.2% for the employer
- Medicare tax rate: 1.45% for the employee plus 1.45% for the employer
- Additional Medicare: 0.9% for the employee when wages exceed $200,000 in a year
- FUTA tax rate: 6% for the employer on the first $7,000 paid to the employee
Increasing Payroll Taxes Would Strengthen Social Security
Social Security faces a significant though manageable long-term funding shortfall, which policymakers should address primarily by increasing Social Securitys tax revenues. If policymakers elect to reduce Social Security benefits, those cuts will need to be limited and carefully targeted to avoid causing significant hardship. Moreover, the cuts will almost certainly be phased in slowly, which means they could not produce significant savings for many years. Increasing Social Securitys revenues will be necessary.
Social Securitys tax base has eroded since the last time policymakers addressed solvency.Boosting Social Securitys payroll tax revenue also is justified by recent trends: Social Securitys tax base has eroded since the last time policymakers addressed solvency in 1983, largely due to increased inequality and the rising cost of non-taxed fringe benefits, such as health insurance. And it enjoys broad support: the majority of Americans oppose cuts to Social Security and support strengthening the program by contributing more in taxes.
This paper presents three approaches to increasing payroll taxes that would improve the programs solvency:
Also Check: Will Student Loans Take My Tax Refund 2020
Additional Medicare Tax Withholding Rate
Additional Medicare Tax applies to an individual’s Medicare wages that exceed a threshold amount based on the taxpayer’s filing status. Employers are responsible for withholding the 0.9% Additional Medicare Tax on an individual’s wages paid in excess of $200,000 in a calendar year, without regard to filing status. An employer is required to begin withholding Additional Medicare Tax in the pay period in which it pays wages in excess of $200,000 to an employee and continue to withhold it each pay period until the end of the calendar year. There’s no employer match for Additional Medicare Tax. For more information, see the Instructions for Form 8959 and Questions and Answers for the Additional Medicare Tax.
How To Calculate And Report Deductions
Maddy Price / The Balance
Employers calculate payroll taxes using an employee’s gross or total wage earnings and various deductions to arrive at net or take-home pay. This seems simple enough on the surface, but calculating the deductions requires attention to detail and extreme accuracy.
Read Also: How To Correct Taxes After Filing
What You Have To Pay: Unemployment Taxes
Unless your organization isexempt, you need to pay into federal and state unemployment insurance overand above what you pay each employee.
Unemployment insurance provides financial assistance to workers who:
- Are unemployed for reasons they dont have control over .
- Meet their states minimum requirements for time worked or wages earned.
Federally, contributions are governed by theFederal Unemployment Tax Act .Each state runs its own unemployment insuranceprogram, and your location can impact both yourSUI rateand potential tax credits. Heres why:
FUTAs maximum taxable earnings, whats called a wage base, is $7,000 anything an employee earnsbeyond that amount isnt taxed. The standard FUTA tax rate is 6%, so your max contribution per employeecould be $420. However, you can also claim a tax credit of up to 5.4% . Employers cantypically claim the full credit, as long as their unemployment taxes are paid in full and on time.
If you get the full credit, your net FUTA tax rate would be just 0.6% , plus whatever you owe to your state government.
But theres another way your location can impact your tax rate. If your state doesnt have the money topay out UI benefits, it may need to get an Unemployment Trust Fund loan, becoming whats called a.If your state doesnt pay off that loan in time, you could see your FUTA tax credit slowly carved back by 0.3% every year the loan is outstanding.
Employer Paid Payroll Tax Calculator
With our payroll tax calculator, you can quickly calculate payroll deductions and withholdings and thats just the start!
It only takes a few seconds to calculate the right amount to deduct from each employees paycheck, thus saving you time and providing peace of mind.
Additionally, our free payroll calculator allows you to summarize deductions, retirement savings options, required taxes, and more.
Without the use of an online payroll calculator, you may find yourself guessing as you address questions such as:
- How much money should you deduct from an employees paycheck?
- Which taxes are required and how do they impact running payroll?
- How do post-tax reimbursements impact payroll?
Below, youll find a basic employer tax calculator designed to help you answer these questions, among many others. Dont hesitate to experiment with the calculator, as this is the best way to understand how it works. And of course, let us know if you have any questions.
You May Like: When Are Tax Returns 2021
Youre Both Responsible For: Social Security And Medicare Contributions
Social Security and Medicare are federal programs that are primarily funded by taxes paid by bothemployers and employees, as set out byFICA,the Federal Insurance Contributions Act. These are taxes thatyou withhold from employees, but youre also on the hook for a contribution that matches what they put in.
The wage base for Medicare has no limit, so both you and your employee are liable for 1.45% taxes oneverything earned including the value of any non-cash benefits. An employee will also be taxed anadditional 0.9% on anything they earn over $200,000, but you dont need to match that amount.
Social Security has a wage base of $127,200, an amount that increases regularly to keep pace with inflation. Both you and your employeewill be taxed 6.2% up to $7,886.40 each with the current wage base.
Your employees FICA contributions should be deducted from their wages. Your contributions, however,should be paid in addition to other compensation.
See how simple Gustomakes payroll.
Pricing
Higher Earners In Scotland To Pay More Income Tax
John Swinney explains why he is asking higher earners to pay more in tax
Everyone earning more than £43,662 in Scotland will have to pay more income tax next year.
Deputy First Minister John Swinney said the higher rate of tax will increase from 41p to 42p in the pound in April, and the top rate from 46p to 47p.
The tax threshold for the top rate will also be lowered from £150,000 to £125,140.
This change has already been announced for other parts of the UK by Chancellor Jeremy Hunt.
Mr Swinney described the increase as an “extra penny to enable spending on patient care in our National Health Service”.
And he said he was asking people to “pay their fair share” so they could “help to create the fairer society in which we all want to live”.
But the Scottish Conservatives said making higher and middle earners in Scotland pay more more tax than their counterparts elsewhere in the UK risked undermining the country’s potential for economic growth.
Scottish Labour said the extra money would be used to “fix some of the damage done by 15 years of SNP cuts and failure” and predicted that people will not accept rising tax bills “if all they see is further decline in services”.
Mr Swinney had been due to deliver his budget statement at 14:30 – but Presiding Officer Alison Johnstone suspended the session for 30 minutes so she could investigate how details of the tax rises had been revealed by the BBC two hours earlier.
You May Like: How Much House Can I Afford After Taxes