The 0% Bracket Is A ‘really Good Tax Planning Opportunity’
With taxable income below the thresholds, you can sell profitable assets without tax consequences. And for some investors, selling may be a chance to diversify amid market volatility, Lucas said.
“It’s there, it’s available, and it’s a really good tax planning opportunity,” he added.
Whether you’re taking gains or tax-loss harvesting, which uses losses to offset profits, “you really have to have a handle on your entire reportable picture,” said Jim Guarino, a CFP, CPA and managing director at Baker Newman Noyes in Woburn, Massachusetts.
That includes estimating year-end payouts from mutual funds in taxable accounts which many investors aren’t expecting in a down year and may cause a surprise tax bill, he said.
“Some additional loss harvesting might make a lot of sense if you’ve got that additional capital gain that’s coming down the road,” Guarino said.
Of course, the decision hinges on your taxable income, including payouts, since you won’t have taxable gains in the 0% capital gains bracket.
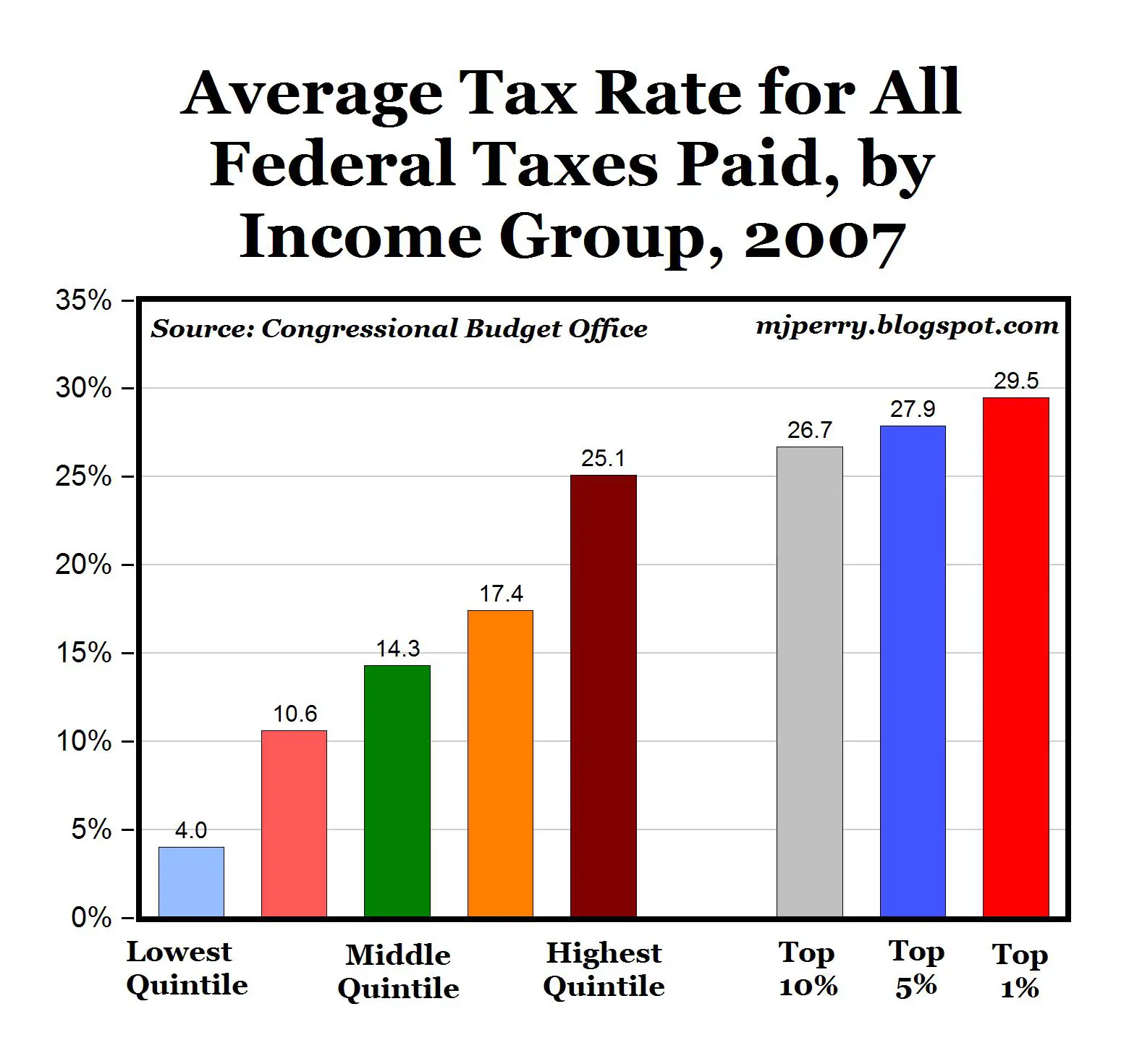
The Tax Cuts And Jobs Act Reduced Average Tax Rates Across Income Groups
The 2018 tax year was the first under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act . Due to the TCJAs changes, average tax rates fell for taxpayers across all income groups. Overall, the average tax rate for all taxpayers fell from 14.6 percent in 2017 to 13.3 percent in 2018. The bottom 50 percent, taxpayers making below $43,614 in AGI in 2018, saw their average tax rate fall from 4.0 percent in 2017 to 3.4 percent in 2018. The top 1 percent, taxpayers making $540,009 and above in AGI in 2018, saw their average tax rate fall from 26.8 percent in 2017 to 25.4 percent in 2018.
You can download the full data set in Excel or PDF form above.
How Do Tax Credits Affect Your Tax Bracket
Tax credits lower your tax bill dollar-for-dollar, but they dont affect your marginal tax bracket. However, they do lower your effective tax rate. You cant lower your tax bracket by claiming a credit. While you might have the goal of falling into a lower tax bracket, your primary goal should be to get your effective tax rate as low as possible. Deductions can help get you into a lower tax bracket and have a lower effective tax rate, but tax credits will help you lower your effective tax rate more given their ability to reduce your tax bill dollar-for-dollar.
Recommended Reading: How Much Tax Should I Have Paid
Recomputation Of Estimated Tax
If, after paying any installment of estimated tax, the taxpayer determines that a new estimate is required, the payment amounts for the remaining installments may be increased or decreased, as the case may be. The amount required by the new estimate is computed by calculating the difference between the previous estimated tax amount and the new estimated tax amount and dividing that difference between the number of installments remaining to be paid.
The Forbes 400 Paid An Average Income Tax Rate Of 82 Percent From 2010 To 2018
The study, by economists Greg Leiserson of the Council of Economic Advisers and Danny Yagan of the Office of Management and Budget, used annual Forbes 400 lists and public data to estimate the incomes and federal income taxes paid by members of that elite group. The main reason the top 400 pay such a low tax rate is that a very large share of their income is in the form of unrealized capital gainsappreciation in the value of their assets, mostly stocks and other business interests. Because of a tax code feature known as stepped-up basis, unrealized gain on an asset is never subject to income tax if the asset is not sold during the owners lifetime. As a result, much of the income of the wealthiest families in the country never appears on their income tax returns.
See also
4 Facts That Disprove Opponents Claims About Bidens Tax Compliance Proposal
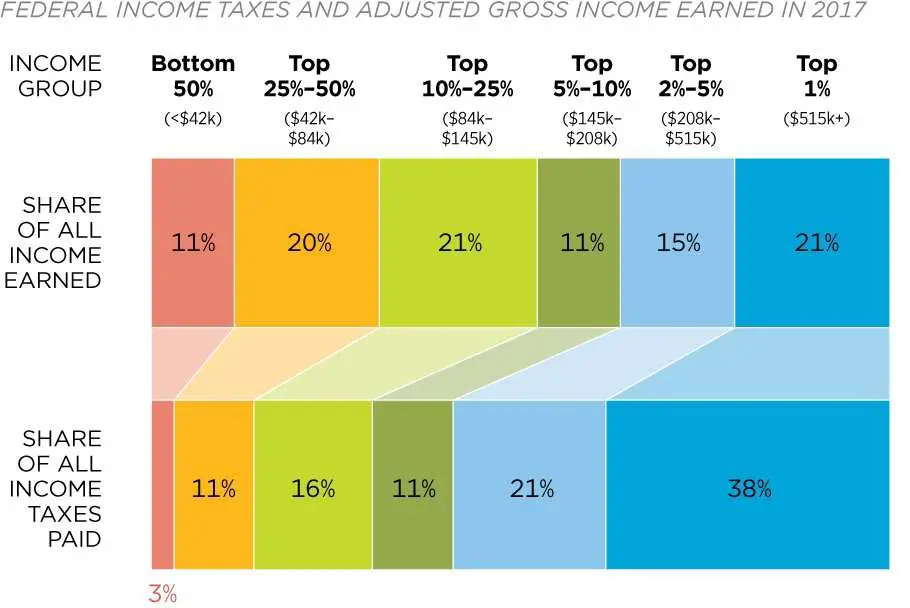
In contrast to the White House analysis, many effective tax rate measures exclude unrealized gains, meaning they are incomplete when it comes to the very wealthy. The measure of income used in the White House studyone that includes unrealized gainsprovides a broader perspective. This approach to measuring income comes close to the concept known as Haig-Simons income: consumption plus change in net wealth. The congressional Joint Committee on Taxation has said that, Economists generally agree that, in theory, a Haig-Simons measure of income is the best measure of economic well-being.
Also Check: What Is New York State Tax Rate
Acquire A Higher Salary
This is easier said than done, but is actually the easiest way to become a one-percent earner here in Canada. The acquisition of a higher salary, depending on the industry you’re in, can be done so through promotion.
However, for the most part, it will require a person to get an education in a niche industry, and then work their way up into one of the top positions in that industry. Think of a lawyer, dentist, doctor, or a CFA for example.
What Is Adjusted Gross Income Definition
Adjusted gross income, or AGI, is your total gross income minus certain tax deductions and other adjustments. Gross income includes such types of earnings as wages, dividends, alimony, government benefits, retirement distributions, capital gains and income from any other source. Adjusted gross income is calculated by subtracting such deductions and adjustments as alimony paid, retirement plan contributions, student loan interest and health insurance premiums.
Don’t Miss: How Do Small Businesses Pay Taxes
What Are The 2022 Federal Income Tax Brackets
Single filing status
| If taxable income is over: | but not over: |
| 10% of the amount over $0 | |
| $10,276 | $1,028 plus 12% of the amount over $10,275 |
| $41,776 | $4,808 plus 22% of the amount over $41,775 |
| $89,076 | $15,214 plus 24% of the amount over $89,075 |
| $170,051 | $34,648 plus 32% of the amount over $170,050 |
| $215,951 | $49,336 plus 35% of the amount over $215,950 |
| $539,901 | $162,718 plus 37% of the amount over $539,900 |
| If taxable income is over: | but not over: |
| 10% of the amount over $0 | |
| $20,551 | $2,055 plus 12% of the amount over $20,550 |
| $83,551 | $9,615 plus 22% of the amount over $83,550 |
| $178,151 | $30,427 plus 24% of the amount over $178,150 |
| $340,101 | $69,295 plus 32% of the amount over $340,100 |
| $431,901 | $98,671 plus 35% of the amount over $431,901 |
| $647,851 | $174,254 plus 37 % of the amount over $647,850 |
| If taxable income is over: | but not over: |
| 10% of the amount over $0 | |
| $10,276 | $1,028 plus 12% of the amount over $10,275 |
| $41,776 | $4,808 plus 22% of the amount over $41,775 |
| $89,076 | $15,214 plus 24% of the amount over $89,075 |
| $170,051 | $34,648 plus 32% of the amount over $170,050 |
| $215,951 | $49,336 plus 35% of the amount over $215,950 |
| $323,926 | $87,127 plus 37% of the amount over $323,925 |
Head of Household filing status
Highlights Of Changes For 2023
The contribution limit for employees who participate in 401, 403, most 457 plans, and the federal government’s Thrift Savings Plan is increased to $22,500, up from $20,500.
The limit on annual contributions to an IRA increased to $6,500, up from $6,000. The IRA catchup contribution limit for individuals aged 50 and over is not subject to an annual costofliving adjustment and remains $1,000.
The catch-up contribution limit for employees aged 50 and over who participate in 401, 403, most 457 plans, and the federal government’s Thrift Savings Plan is increased to $7,500, up from $6,500. Therefore, participants in 401, 403, most 457 plans, and the federal government’s Thrift Savings Plan who are 50 and older can contribute up to $30,000, starting in 2023. The catch-up contribution limit for employees aged 50 and over who participate in SIMPLE plans is increased to $3,500, up from $3,000.
The income ranges for determining eligibility to make deductible contributions to traditional Individual Retirement Arrangements , to contribute to Roth IRAs, and to claim the Saver’s Credit all increased for 2023.
Taxpayers can deduct contributions to a traditional IRA if they meet certain conditions. If during the year either the taxpayer or the taxpayer’s spouse was covered by a retirement plan at work, the deduction may be reduced, or phased out, until it is eliminated, depending on filing status and income. Here are the phaseout ranges for 2023:
You May Like: Can I File Taxes If I Get Ssi
Personal Income Tax Rates
For individuals, the top income tax rate for 2022 is 37%, except for long-term capital gains and qualified dividends .
P.L. 115-97 reduced both the individual tax rates and the number of tax brackets. P.L. 115-97 sunsets after 2025 many individual tax provisions, including the lower rates and revised brackets, in order to comply with US Senate budget rules.
How Do I Figure Out What My Marginal Tax Rate/tax Bracket Is
The easiest way to figure out your marginal tax rate is to look at the federal tax brackets and see in which bracket your taxable income ends. This represents your marginal tax rate. If you need help determining your tax bracket, visit TurboTaxsTax Bracket Calculator. Simply provide your filing status and taxable income to estimate your tax bracket.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Defer My Taxes
What Is An Effective Tax Rate
While it’s likely you will pay income tax at various rates or tax brackets, the actual percentage of your taxable income that goes to the IRS is referred to as your effective tax rate. Your last dollar of taxable income gets taxed at your highest marginal income tax rate, which is generally higher than your effective tax rate. For example, if half of your income is taxed at 10 percent and the other half at 12 percent, then your effective tax rate of 11 percent means that 11 cents of every dollar of taxable income you earned this year goes to the IRS. It doesnt mean every additional dollar of taxable income is taxed at 11 percent. Additional income is taxed at your marginal rate, 12 percent in this case.
The Federal Income Tax
The federal personal income tax that is administered by the Internal Revenue Service is the largest source of revenue for the U.S. federal government. Nearly all working Americans are required to file a tax return with the IRS each year. In addition to this, most people pay taxes throughout the year in the form of payroll taxes that are withheld from their paychecks.
Income taxes in the U.S. are calculated based on tax rates that range from 10% to 37%. Taxpayers can lower their tax burden and the amount of taxes they owe by claiming deductions and credits.
A financial advisor can help you understand how taxes fit into your overall financial goals. Financial advisors can also help with investing and financial plans, including retirement, homeownership, insurance and more, to make sure you are preparing for the future.
Don’t Miss: How Much Can You Make And Not File Taxes
Taxing Stock Buybacks Like Dividends
Policymakers also should consider reforming the preferential tax treatment of stock buybacks, in which a corporation distributes profits to shareholders by offering to buy back a certain number of shares, raising the stocks price and thereby increasing wealth for all stockholders . This policy would be an incremental step toward taxing unrealized capital gains.
Stock buybacks have tax advantages over dividends, the traditional way in which corporations distribute profits to shareholders. When a corporation pays dividends, shareholders recognize the dividends as income and pay tax on them. In a stock buyback, shareholders who sell their shares to the corporation at a gain recognize capital gain income but shareholders who choose not to sell their shares see the value of their shares rise. The deferral benefit means that their wealth increases, but they do not have to pay tax on that increase.
Moreover, foreign shareholders are generally subject to U.S. tax on dividends but not on most capital gains, including those gains that accrue from stock buybacks. As the Tax Policy Centers Steve Rosenthal recently explained, the share of publicly traded U.S. stocks held by foreign investors has tripled to 30 percent since the late 1990s, so treating buybacks as dividends is more important than ever in ensuring that foreign shareholders pay taxes.
Recommended Reading: Doordash Mileage Taxes
Your Federal Income Tax Rate Depends Upon Your Tax Bracket
Wages are taxed based on your income level and whether you file your taxes as single or married. These levels are called tax brackets. The brackets are cumulative, which means that your total income is taxed at different levels. Your federal income tax rate is also determined by whether you’re single or married.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 was signed into law in December 2017, altering the long-standing tax brackets for individuals however, that law is only applicable starting with the 2018 tax year, and those returns are not filed until 2019.
Also Check: Are Roth Ira Contributions Tax Deductible
Modified Adjusted Gross Income
Modified adjusted gross income is essentially your AGI after factoring in certain tax deductions or penalties, or certain additions to income.
MAGI is used for different tax credits and deductions. The modified adjusted gross income can add a bit back into your income, such as foreign earned income, student loan interest, IRA deductions, and tax-exempt interest earned from tax-free bonds such as municipal bonds.
Calculating your MAGI will also depend on which tax credits and deductions youre looking at, which is why you should do each deduction carefully. The IRS provides instructions on its website for calculating MAGI on specific forms such as Form 8960, which is used to calculate net investment income tax.
For retirees, MAGI is a big deal because it determines Medicare insurance premiums. Generally speaking, the higher your MAGI, the higher premium you will pay for Medicare. This is determined by looking back two tax years.
Ontario Tax Brackets And Rates 2022
In 2022 tax brackets and Ontario personal basic amount were indexed by 1.024.
Basic personal amount for 2022 is $11,141.
| Taxable income |
|---|
Ontario surtax brackets also were indexed by 1.024 in 2022.
| Payable tax | |
|---|---|
| greater than $4,991 up to $6,387 | 20% |
Federal personal base amount is $14,398.
| Taxable income | |
|---|---|
| $5,369.85 + 20.50% for income over $50,197 | |
| $100,392 $155,625 | $15,659.83 + 26.00% for income over $100,392 |
| $155,625 $221,708 | $30,020.41 + 29.00% for income over $155,625 |
| over $221,708 | $49,184.48 + 33.00% for income of $221,708 and over |
Historical Ontario tax brackets are listed here and historical federal tax brackets and rates can be found here.
Also Check: How To File Past Years Taxes Online
Federal Income Tax Brackets And Rates
In 2023, the income limits for all tax brackets and all filers will be adjusted for inflation and will be as follows . There are seven federal income tax rates in 2023: 10 percent, 12 percent, 22 percent, 24 percent, 32 percent, 35 percent, and 37 percent. The top income tax rate of 37 percent will hit taxpayers with taxable income above $539,900 for single filers and above $693,750 for married couples filing jointly.
2023 Federal Income Tax Brackets and Rates for Single Filers, Married Couples Filing Jointly, and Heads of Households| Tax Rate |
|---|
How To Get Into A Lower Tax Bracket
You can lower your income into another tax bracket by using tax deductions, such as the write-offs for charitable donations, property taxes and the mortgage interest. Deductions help cut your taxes by reducing your taxable income.
Tax credits, such as the earned income tax credit, or child tax credit, can also put you into a lower tax bracket. They allow for a dollar-for-dollar reduction in the amount of taxes you owe.
Also Check: What Can I Itemize On My Taxes
Other College Tax Benefits
If youre a parent saving up for your childs college education, setting aside money in a college savings plan can provide some tax perks.
With a 529 college savings plan, for instance, all of the money you contribute grows tax-free, and any withdrawals you make to pay for eligible expenses are also tax-free. If you make ineligible distributions, though, the money will be subject to income tax and a 10 percent penalty.
Whats more, many states offer their own tax deductions and credits for 529 plan contributions. Check with your states 529 plan provider to find out if youre eligible.
Coverdell education savings accounts function similarly to 529 plans in that contributions grow tax-free and can be taken out for qualified educational expenses tax-free. However, youre limited to $2,000 in annual contributions per beneficiary. In contrast, 529 plans technically have limits, but theyre set by state and are generally very high.
If you contribute more than the maximum amount, the excess funds will be subject to a 6 percent tax each year in which they remain in the account. Nonqualified distributions are subject to income taxes and a 10 percent penalty.
How Federal Tax Brackets Work
Tax brackets are not as intuitive as they seem because most taxpayers have to look at more than one bracket to know their effective tax rate.
Instead of looking at what tax bracket you fall in based on your income, determine how many individual tax brackets you overlap based on your gross income.
Figuring that out is easier in practice:
- Example one: Say youre a single individual who earned $40,000 of taxable income in the 2021 tax year. Technically, youd be aligned in the 12 percent tax bracket, but your income wouldnt be levied a 12 percent rate across the board. Instead, you would follow the tax bracket up on the scale, paying 10 percent on the first $9,950 of your income and then 12 percent on the next chunk of your income between $9,951 and $40,525. Because you dont make above $40,525, none of your income would be hit at the 22 percent rate.
That often amounts into Americans being charged a rate thats smaller than their individual federal income tax bracket, known as their effective tax rate.
- Example two: Say youre a single individual in 2021 who earned $70,000 of taxable income. You would pay 10 percent on the first $9,950 of your earnings then 12 percent on the chunk of earnings from $9,951 to $40,525 , then 22 percent on the remaining income
- Your total tax bill would be $11,148.50. Divide that by your earnings of $70,000 and you get an effective tax rate of roughly 16 percent, which is lower than the 22 percent bracket youre in.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To File Your Taxes