Why Do I Need To Know My Tax Liability For My Business
Tax liability is like any other liability. You need to know how much you will owe for the year to ensure that you have the means to pay it. For example, if your rent payment is $1,000 a month, you know that you have a rent liability of $12,000 for the year, even though you expense the rent monthly.
Its important to calculate your tax liability for several reasons, but one of the main reasons is that it allows you to properly budget for the expense. Calculating your tax liability can also help you make more targeted business decisions or take a closer look at your expense deductions. Finally, knowing the tax liability for your business helps you have more accurate financial statements.
If you dont estimate your tax liability properly throughout the year, your liabilities will be understated on your financial statements, rendering them useless. Even if your tax liability is zero, you need to know.
What’s The Difference Between Estate Tax And Inheritance Tax
Estate tax is based on a percentage of the net value of an estate. Inheritance tax is based on the value of a single bequest. The estate pays the estate tax, while the beneficiary is responsible for paying the inheritance tax. Some people provide in their wills that the estate should pay any inheritance taxes on behalf of beneficiaries, too.
Penalty For Underpayment Of Estimated Tax
If you didnt pay enough tax throughout the year, either through withholding or by making estimated tax payments, you may have to pay a penalty for underpayment of estimated tax. Generally, most taxpayers will avoid this penalty if they owe less than $1,000 in tax after subtracting their withholdings and credits, or if they paid at least 90% of the tax for the current year, or 100% of the tax shown on the return for the prior year, whichever is smaller. There are special rules for farmers, fishermen, and certain higher income taxpayers. Please refer to Publication 505, Tax Withholding and Estimated Tax, for additional information.
However, if your income is received unevenly during the year, you may be able to avoid or lower the penalty by annualizing your income and making unequal payments. Use Form 2210, Underpayment of Estimated Tax by Individuals, Estates, and Trusts , to see if you owe a penalty for underpaying your estimated tax. Please refer to the Form 1040 and 1040-SR Instructions or Form 1120 Instructions PDF, for where to report the estimated tax penalty on your return.
The penalty may also be waived if:
You May Like: What Is The Small Business Tax Rate
Whats The Difference Between Refundable And Nonrefundable Tax Credits
Both refundable and nonrefundable tax credits reduce taxes owed dollar-for-dollar. Refundable tax credits can be used to lower a taxpayers liability below $0, with the remaining value of the credit being available as a tax refund. Nonrefundable tax credits can be used to reduce a taxpayers liability no lower than $0.
The Earned Income Tax Credit , for example, is a fully refundable tax credit. In fact, most households receive the EITC as a refund. In 2016, 27.3 million tax returns claimed the EITC for a total of $66.7 billion, of which $57.1 billion was refunded.
In contrast, the $500 Child and Dependent Care Tax Credit is nonrefundable. If a taxpayer qualifying for the credit owes just $400, their tax liability will be reduced to $0 and they will not receive a refund for the remaining $100 of the credit.
Credits can also be partially refundable, such as the Child Tax Credit . If the CTC is greater than the taxpayers liability, they may receive a refund only up to $1,400 based on an earned income formula. The maximum credit amount is reduced by 5 percent once adjusted gross income reaches $200,000 for single filers and $400,000 for married filing jointly.
Filing An Amended Return
If you file your income tax return and later become aware of any changes you must make to income, deductions, or credits, you must file an amended Louisiana return. To file a paper amended return:
- Mail an amended return that includes a payment to the following address: Louisiana Department of Revenue
You May Like: How To File Taxes With An Itin Number
Example: Death In 2017 No Lifetime Gifts
Now let’s use the same numbers, but assume you died in 2017 when the estate tax exemption was much less. Your gross estate was still $8 million and your allowable debts, expenses, and deductions were still $500,000. Your net estate was $7.5 million.
Again, you would subtract your available estate tax exemption from your net estate to arrive at your taxable estate. Your estate would owe a tax of $804,000 if you didn’t make any taxable gifts during your lifetime that exceeded the annual exemption amounts:
$7,500,000 net estate less $5,490,000 estate tax exemption equals $2,010,000 taxable estate
Your taxable estate is then multiplied by the 40% tax rate to arrive at your federal estate tax liability, which in this example equals $804,000.
Calculating Tax Liabilities In 5 Steps
The Indeed Editorial Team comprises a diverse and talented team of writers, researchers and subject matter experts equipped with Indeed’s data and insights to deliver useful tips to help guide your career journey.
Tax liability is an important number that accountants monitor to ensure they can pay the proper amount in taxes for the businesses they work for There are many factors involved in tax liability, and it’s helpful to learn about each part to file taxes correctly. You can learn how to calculate tax liabilities by following a few simple steps. In this article, we explain what tax liabilities are and provide steps for calculating tax liabilities.
Related:The 5 Common Types of Business Structures
Also Check: What Happens When You Owe Back Taxes
Penalties Related To Estimated Taxes
If a taxpayer underpaid their taxes they may have to pay a penalty. This applies whether they paid through withholding or through estimated tax payments. A penalty may also apply for late estimated tax payments even if someone is due a refund when they file their tax return.
In general, taxpayers dont have to pay a penalty if they meet any of these conditions:
- They owe less than $1,000 in tax with their tax return.
- Throughout the year, they paid the smaller of these two amounts:
- at least 90 percent of the tax for the current year
- 100 percent of the tax shown on their tax return for the prior year this can increase to 110 percent based on adjusted gross income
To see if they owe a penalty, taxpayers should use Form 2210.
The IRS may waive the penalty if someone underpaid because of unusual circumstances and not willful neglect. Examples include:
- casualty, disaster or another unusual situation.
- an individual retired after reaching age 62 during a tax year when estimated tax payments applied.
- an individual became disabled during a tax year when estimated tax payments applied.
There are special rules for underpayment for farmers and fishermen. Publication 505 has more information.
How To Figure Estimated Taxes
The IRS recommends that everyone do a paycheck checkup in 2019, even if they did one in 2018, to determine if they need to adjust their tax withholding or make estimated tax payments throughout the year. Although especially important for anyone with a tax bill for 2018, its also important for anyone whose refund is larger or smaller than expected. By changing withholding now or making estimated tax payments, any taxpayer can better ensure they get the refund they want next year. For those who owe, making estimated tax payments in 2019 is the best way to head off another tax-time surprise a year from now.
Taxpayers should also make adjustments throughout the year if changes occur. When figuring their estimated taxes each year, taxpayers need to account for life events, like marriage or the birth of a child, that may affect their taxes. They should also adjust for recent changes in the tax law.
Individuals, sole proprietors, partners and S corporation shareholders generally use the worksheet in Form 1040-ES. Theyll need to know their expected adjusted gross income. Theyll also need to estimate their taxable income, taxes, deductions and credits. Some taxpayers find it helpful to use information from their prior years tax return when they complete the worksheet. Their estimates should be as accurate as possible to avoid penalties.
Also Check: Why Do I Owe Taxes This Year 2021
Calculating Taxable Income Using Exemptions And Deductions
Of course, calculating how much you owe in taxes is not quite that simple. For starters, federal tax rates apply only to taxable income. This is different than your total income, otherwise known as gross income. Taxable income is always lower than gross income since the U.S. allows taxpayers to deduct certain income from their gross income to determine taxable income.
To calculate taxable income, you begin by making certain adjustments from gross income to arrive at adjusted gross income . Once you have calculated adjusted gross income, you can subtract any deductions for which you qualify to arrive at taxable income.
Note that there are no longer personal exemptions at the federal level. Prior to 2018, taxpayers could claim a personal exemption, which lowered taxable income. The tax plan signed in late 2017 eliminated the personal exemption, though.
Deductions are somewhat more complicated. Many taxpayers claim the standard deduction, which varies depending on filing status, as shown in the table below.
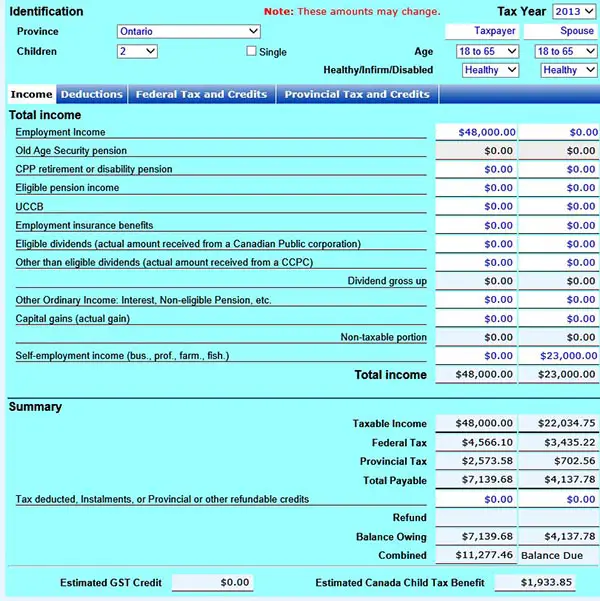
Here’s How To Calculate Your Tax Liability:
Income Estimation
Income estimation takes out the surprise, and most importantly gives you an estimate of what to expect for your tax liability. For convenience, calculate your quarterly income. Quarterly income may vary slightly, yet, by adjusting the figures for each quarter, either increase or decrease – the estimate is feasible.
Tax Deductible Estimation
This estimation is also possible quarterly. Based on your estimated total income, remove the tax deductions from it. This leaves the taxable income for a quarter. Do the same calculation for each quarter if differences in income vary.
For individual tax, a graduated tax system is used, and this affects how you get taxed. A certain part of the taxable income is taxed at a rate based on the income level. An example of such is taxpayers with spouses filling tax jointly. The Knowledge of your tax deductibles allows you to calculate the taxable income for each quarter.
Tax Payment
For Single Filers
You May Like: Which Pages Of Tax Return To Print
An Example Makes This Clearer
Letâs look at an example to see how a hypothetical flow-through entity would determine the amount of federal income tax it owes based on these tax tables. Suppose Wallyâs Widgets ends up with taxable income of $300,000 in 2018, and that Wally files a joint tax return with his wife, Wendy.
Wallyâs tax owed would be:
$28,765 + 24% of the amount over $168,400 .
The calculation: $28,765 + $31,584 = $60,349 total tax due for our friend Wally.
Determine Your Federal Estate Tax Liability
Now you can subtract your available federal estate tax exemption from the value of your net estate to arrive at your taxable estate.
The federal estate tax exemption for 2017 was $5.49 million, then it jumped to $11.18 million in 2018 under the terms of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act . The exemption is indexed for inflation, so it tends to increase incrementally from year to year. It’s $12.06 million in 2022, up from $11.7 million in 2021.
Your estate tax exemption will be reduced if you made any taxable gifts during your lifetime that exceeded the annual exclusion from gift taxes, $15,000 in 2021, increasing to $16,000 in 2022, and if you did not pay the gift tax on those transfers at the time. It will be equal to the difference between the total exemption available less the value of your lifetime gifts that exceeded the annual exclusions.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Cannot Pay Your Taxes
Does My State Have An Estate Or Inheritance Tax
In addition to the federal estate tax of 40 percent, some states levy an additional estate or inheritance tax. Twelve states and the District of Columbia impose estate taxes and six impose inheritance taxes. Maryland is the only state to impose both.
State inheritance and estate taxes, together with the federal estate tax, reduce investment, discourage business expansion, and can sometimes drive wealthy taxpayers out of state. They also yield estate planning and tax avoidance strategies that are inefficient, not only for affected taxpayers, but for the economy at large.
Due to these issues, most states have been moving away from estate or inheritance taxes or have raised their exemption levels in recent years.
How Do Sources Of Revenue In The Us Compare To Those In The Rest Of The World
In many ways, the United States is unique in how it raises revenue. One important difference is that it relies significantly more on individual income taxes compared to other countries in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development , a group of 36 countries with advanced economies.
The United States also relies much less on consumption taxes. This is because all OECD countries except the United States levy a value-added tax at a relatively high rate. State and local sales tax rates in the United States are low by comparison.
Read Also: Where To Get Taxes Done For Free
How To Figure Estimated Tax
Individuals, including sole proprietors, partners, and S corporation shareholders, generally use Form 1040-ES, to figure estimated tax.
To figure your estimated tax, you must figure your expected adjusted gross income, taxable income, taxes, deductions, and credits for the year.
When figuring your estimated tax for the current year, it may be helpful to use your income, deductions, and credits for the prior year as a starting point. Use your prior year’s federal tax return as a guide. You can use the worksheet in Form 1040-ES to figure your estimated tax. You need to estimate the amount of income you expect to earn for the year. If you estimated your earnings too high, simply complete another Form 1040-ES worksheet to refigure your estimated tax for the next quarter. If you estimated your earnings too low, again complete another Form 1040-ES worksheet to recalculate your estimated tax for the next quarter. You want to estimate your income as accurately as you can to avoid penalties.
You must make adjustments both for changes in your own situation and for recent changes in the tax law.
Corporations generally use Form 1120-W, to figure estimated tax.
Coronavirus Tax Relief For Self
Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act permits self-employed individuals making estimated tax payments to defer the payment of 50% of the social security tax on net earnings from self-employment imposed for the period beginning on March 27, 2020 and ending December 31, 2020. This means that 50% of the social security tax imposed on net earnings from self-employment earned during the period beginning on March 27, 2020, and ending December 31, 2020, is not used to calculate the installments of estimated tax due. Please refer to Publication 505, Tax Withholding and Estimated TaxPDF, for additional information.
Don’t Miss: When Are Individual Tax Returns Due
What Is Tax Liability
Generally, tax liability is the amount of money you owe to the government. The term tax liability is used most frequently when referring to federal income tax liability.
Individuals and organizations accrue tax liabilities with each taxable event they partake in. Taxable events include earning income, making sales, and issuing payroll. Individuals and businesses can reduce their total tax liabilities by claiming deductions, exemptions, and tax credits.
Calculating Income Tax Rate
The United States has a progressive income tax system. This means there are higher tax rates for higher income levels. These are called marginal tax rates,” meaning they do not apply to total income, but only to the income within a specific range. These ranges are referred to as brackets.
Income falling within a specific bracket is taxed at the rate for that bracket. The table below shows the tax brackets for the federal income tax, and it reflects the rates for the 2021 tax year, which are the taxes due in early 2022.
You May Like: What Is 1040 Sr Tax Form
Youre Our First Priorityevery Time
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesnt feature every company or financial product available on the market, were proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about , but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services.Here is a list of our partners.
Tax Liability Formula And Calculation
The calculation of liability for a business or an individual involves the following steps:
The following formula is used to compute net taxable income:
Net Taxable Income = Gross Income Deductions Exemptions
The formula for calculating tax liability is given below:
For Individuals:
Tax Liability = Employee Taxes Tax Credit
Recommended Reading: What Is The Last Date You Can File Your Taxes