Estimate Your Tax Bracket
Having a rough idea of your tax bracket can help you estimate the tax impact of major financial decisions.
Have you ever been asked for your approximate tax bracket by an advisor, attorney, financial provider, or even a Fidelity representative? Knowing your tax bracket can be useful in many scenarios, including when you open new accounts.
While your tax bracket won’t tell you exactly how much you’ll pay in taxes, it can help you assess the tax impact of financial decisions. For instance, if you’re in the 35% tax bracket, you could save 35 cents in federal tax for every dollar spent on a tax-deductible expense, such as mortgage interest or charity.
How Much You Owe
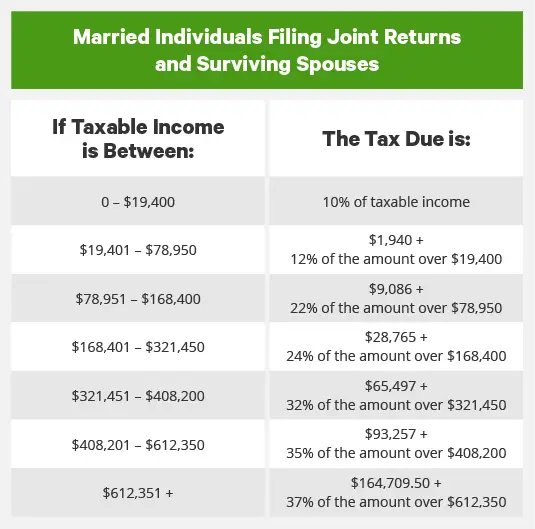
After you figure out your taxable income, you can determine how much you owe by using the tax tables included in the Form 1040 Instructions. Though these tables look complicated at first glance, theyre actually quite straightforward. You simply look up your income, find the column with your filing status , and the intersection of those two figures is your tax.
For simplicitys sake, the tax tables list all income over $3,000 in $50 chunks. The tables only go up to $99,999, so if your income is $100,000 or higher, you must use a separate worksheet to calculate your tax.
To illustrate, lets say your taxable income is $41,049. Using the tables, youd go to the 41,000 section and find the row applicable to incomes between $41,000 and $41,050. Then, you can easily find the tax you owe:
- $4,774 for single filers
- $4,525 for married couples filing jointly
- $4,774 for married couples filing separately
- $4,639 for heads of household
The Irs Just Changed Its Tax Brackets Here’s The Impact On Your Taxes
The IRS said it is adjusting many of its rules to account for the impact of inflation, ranging from individual income tax brackets for 2023 to the standard deduction. The changes could mean tax savings for some taxpayers next year.
The higher limits are aimed at avoiding “bracket creep” due to inflation, which can push workers who received annual cost-of-living pay increases into higher tax brackets even though their standard of living hasn’t changed.
The IRS makes such adjustments annually, but this year’s hot inflation means that many of the changes are more significant than in a typical year. Americans are struggling with stubbornly high inflation, which is eating into their purchasing power as average wage gains lag the sharp rise in prices.
The higher provision thresholds could provide relief to some taxpayers who fall into lower tax brackets as a result, said Tim Steffen, director of tax planning with Baird, in an email. For instance, Steffen noted that a married couple earning $200,000 in both 2022 and 2023 would save $900 in taxes next year because more of their income would be taxed at a lower rate.
Here are the changes announced by the IRS on October 18, with the inflation-adjusted provisions taking effect for the 2023 tax year. Taxpayers will file their 2023 tax returns in early 2024.
Also Check: Is Roth Ira Pre Tax
What Are Tax Brackets
Tax brackets were created by the IRS to determine how much money you need to pay the tax agency each year.
The amount you pay in taxes depends on your income. If your taxable income increases, the taxes you pay will increase.
But figuring out your tax obligation isnt as easy as comparing your salary to the brackets shown above.
Why Knowing Your Tax Bracket In Retirement Matters
Knowing what your tax bracket is in retirement is important because it can help you better plan for your taxes.
In some cases, you may be able to use your knowledge to lower your overall tax liability in one year or over multiple years.
For instance, funds taken out of Roth accounts in retirement are generally tax-free. These could include Roth IRA and Roth 401 funds.
On the other hand, you may have to pay taxes on money withdrawn from tax-deferred accounts. These could include traditional IRAs, 401s and other workplace retirement plans.
Taxable investment accounts may also be required to pay taxes depending on the assets you sell.
Don’t Miss: What Form Is The State Tax Return
How To Determine Your Tax Bracket
As mentioned above, determining your tax bracket hinges on two things: filing status and taxable income. Here are some useful details:
The IRS recognizes five different filing statuses:
- Single Filing Unmarried, legally separated and divorced individuals all qualify all single.
- A married couple agrees to combine income and deduct the allowable expenses.
- A married couple files separate tax returns to keep an individual income lower. This is beneficial in certain situations like repaying student loans under an income-driven repayment plan.
- Head of Household Unmarried individuals who paid more than half the cost of keeping up a home for the year and have a qualifying person living with them in their home for more than half the year.
- Qualifying Widow A widow can file jointly in the year of their spouses death. A qualifying widow has a dependent child and can use the joint tax rates and the highest deduction amount for the next two years after their spouses death.
Popular Tax Deductions And Tax Credits For Individuals
There are hundreds of deductions and credits out there. Here’s a drop-down list of some common ones, as well as links to our other content that will help you learn more.
This could get you up to $3,600 per child for the 2021 tax year. Some families recieved half of the credit as advance payments.
Generally, its meant to cover a percentage of day care and similar costs for a child under 13, a spouse or parent unable to care for themselves, or another dependent so you can work. For the 2021 tax year, it’s up to 50% of $8,000 of expenses for one dependent or $16,000 for two or more dependents.
This lets you claim all of the first $2,000 you spent on tuition, books, equipment and school fees but not living expenses or transportation plus 25% of the next $2,000, for a total of $2,500.
You can claim 20% of the first $10,000 you paid toward tuition and fees, for a maximum of $2,000. Like the American opportunity tax credit, the lifetime learning credit doesnt count living expenses or transportation as eligible expenses. You can claim books or supplies needed for coursework.
Deduct up to $2,500 from your taxable income if you paid interest on your student loans.
For the 2021 tax year, this item covers up to $14,440 in adoption costs per child.
This credit can get you between $1,502 to $6,728 for the 2021 tax year depending on how many kids you have, your marital status and how much you make. Its something to explore if your AGI is less than about $57,000.
You May Like: What Does Agi Mean For Taxes
How Will The New Monthly Child Tax Credit Payments Work
The monthly payments will start on July 15 and will continue through the end of the year. Since the monthly payments will provide only half the years credit, taxpayers can claim the remaining amount on their 2021 tax return when they file in 2022.
Earlier this year, the IRS announced it would roll out a portal for taxpayers to opt in for the payments. However, the IRS more recently announced the monthly child tax credit payments will be sent automatically, and most taxpayers will not need to take any action. The only people who will need to take action are those who do not want to receive the advance payments and taxpayers who had changes to their income, filing status or number of children. The IRS has not yet released additional details about when taxpayers can make these changes.
The monthly child tax credit payments will be paid through direct deposit, paper check or debit cards. The IRS hopes to send most payments through direct deposit to ensure payments are timely, fast and secure.
Individuals who qualify will receive a monthly payment of $300 for each child under the age of 6, and $250 per month for each child age 6 through 17. A family that qualifies for the full credit with two children ages 5 and 3 would receive a monthly payment of $600.
Income Tax In California: How Is It Calculated And Collected
If you are resident in California, or if you are a non-resident but do business in California, you are required to submit an income tax return if you have earned over a certain threshold. The threshold is subject to change, but you can see a recent chart here.
Calculating your income tax can be done on your own or with the help of a professional service. The FTB offers an online tax calculator to make things easier. You need to know your filing status, which can be one of these five:
- Head of household
- Qualifying widow
You also need to know which form you will be using to file. There are three different forms, and which one you use will depend on the amount of your taxable income, your filing status, your residency status .
The three forms are:
- Form 540 NR: Long or Short
You can find full details of which form you should choose on the FTB website. Once youve used the form to find your taxable income, simply enter it into the calculator to find out how much you owe.
For many taxpayers, your state income taxes will be withheld from your paycheck, based on the withholding allowances you chose on Form DE4. If you filled out the form correctly, it is likely that when you file your income tax return, you will not owe additional taxes, and might even get a refund.
Recommended Reading: How To File My Taxes For The First Time
Marginal Tax Rate Thresholds Will Change
The new marginal tax rate the rate you pay on an additional dollar of income thresholds are as follows:
-
37% for incomes over $578,125
-
35% for incomes over $231,250
-
32% for incomes over $182,100
-
24% for incomes over $95,375
-
22% for incomes over $44,725
-
12% for incomes over $11,000
-
10% for incomes of $11,000 or less
What Is A Capital Gains Tax
A capital gains tax is a tax that investors pay on the profit from the sale of an asset. How much capital gains are taxed depends on how long the asset was held before selling, as well as taxable income and filing status.
Capital gains taxes apply to what the IRS calls “capital assets.”
» Selling a home? Taxes on the sale of a home can work differently.
You May Like: What Do You Need To Do Your Taxes On Turbotax
Idaho To Consider Flat Income Tax In Special Session
Inflation is when the general price of goods and services increases across the economy, reducing the purchasing power of a currency and the value of certain assets. The same paycheck covers less goods, services, and bills. It is sometimes referred to as a hidden tax, as it leaves taxpayers less well-off due to higher costs and bracket creep, while increasing the governments spending power.
A tax bracket is the range of incomes taxed at given rates, which typically differ depending on filing status. In a progressive individual or corporate income tax system, rates rise as income increases. There are seven federal individual income tax brackets the federal corporate income tax system is flat.
The standard deduction reduces a taxpayers taxable income by a set amount determined by the government. It was nearly doubled for all classes of filers by the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act as an incentive for taxpayers not to itemize deductions when filing their federal income taxes.
An individual income tax is levied on the wages, salaries, investments, or other forms of income an individual or household earns. The U.S. imposes a progressive income tax where rates increase with income. The Federal Income Tax was established in 1913 with the ratification of the 16th Amendment. Though barely 100 years old, individual income taxes are the largest source of tax revenue in the U.S.
Personal Income Tax Brackets And Rates
| Taxable Income – 2022 Brackets | |
| Over $227,091 | 20.5% |
Tax rates are applied on a cumulative basis. For example, if your taxable income is more than $43,070, the first $43,070 of taxable income is taxed at 5.06%, the next $43,071 of taxable income is taxed at 7.70%, the next $12,760 of taxable income is taxed at 10.5%, the next $21,193 of taxable income is taxed at 12.29%, the next $42,738 of taxable income is taxed at 14.70%, the next $64,259 is taxed at 16.80%, and any income above $227,091 is taxed at 20.5%.
Recommended Reading: How Much Taxes On 1099 Form
How To Determine Your Federal Tax Bracket
This article was co-authored by Cassandra Lenfert, CPA, CFP®. Cassandra Lenfert is a Certified Public Accountant and a Certified Financial Planner in Colorado. She advises clients nationwide through her tax firm, Cassandra Lenfert, CPA, LLC. With over 15 years of tax, accounting, and personal finance experience, Cassandra specializes in working with individuals and small businesses on proactive tax planning to help them keep more money to reach their goals. She received her BA in Accounting from the University of Southern Indiana in 2006.wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 100% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 119,660 times.
Taxpayers in the United States pay federal income tax according to how much taxable money they make each year. The tax bracket, listed in a tax table or tax schedule, tells you approximately how much tax you will pay. It is important to note that your tax bracket is not the percentage of your income that you will pay in taxes. The actual amount you will pay in taxes is found through a formula when you complete your annual tax filing. However, by finding your taxable income and tax bracket, you will be able to ballpark your taxes and properly evaluate certain financial decisions.
Federal Income Tax Brackets And Rates
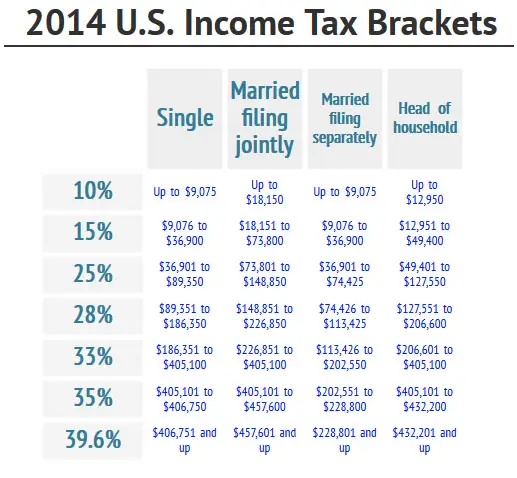
In 2023, the income limits for all tax brackets and all filers will be adjusted for inflation and will be as follows . There are seven federal income tax rates in 2023: 10 percent, 12 percent, 22 percent, 24 percent, 32 percent, 35 percent, and 37 percent. The top income tax rate of 37 percent will hit taxpayers with taxable income above $539,900 for single filers and above $693,750 for married couples filing jointly.
2023 Federal Income Tax Brackets and Rates for Single Filers, Married Couples Filing Jointly, and Heads of Households| Tax Rate |
|---|
Recommended Reading: How To Lie And Get More Money On Taxes
More About Tax Brackets
What Is My Tax Bracket?
The federal income tax system is progressive, which means different tax rates apply to different portions of your total income. Tax bracket refers to the highest tax rate charged on your income.
What Are Tax Tables?
Tax tables like the one above, help you understand the amount of tax you owe based on your filing status, income, and deductions and credits.
Tax brackets only apply to your taxable income. Your deductions and taxable income may drop you into a lower tax bracket or potentially a higher one.
Taxable Income vs. Nontaxable Income
Income comes in various forms, including wages, salaries, interest, tips and commissions. Nontaxable income wont be taxed, whether or not it is entered on your tax return.
File faster and easier with the free TurboTax app
- Limited interest and dividend income reported on a 1099-INT or 1099-DIV
- IRS standard deduction
- Earned Income Tax Credit
- Child tax credits
* More Important Details and Disclosures
How Do Deductions Affect Your Tax Bracket
Tax deductions reduce your taxable income, lowering the amount of income subject to taxes. Generally, deductions lower your tax by your marginal tax rate multiplied by the value of the deduction. For example, if you had a $1,000 tax deduction and are in the 22% marginal tax bracket, youd pay $220 less on your taxes. If you are on the lower edge of a tax bracket, claiming a deduction may get you into a lower one.
Don’t Miss: How To Avoid Capital Gains Tax On Home Sale
Check If You Can Lower Your Tax Bracket
You can use strategies to lower your tax rate, especially if your taxable income falls right on the cut-off between brackets. Before the tax year ends, you can consult with experts from tax resolution companies like Tax Samaritan to find ways to lower your tax bracket.
Some common strategies people do are delaying their income and making certain contributions. If youre considering itemizing deductions, you can make year-end charitable contributions.
Lifetime Learning Credit Education Credits
The Lifetime Learning Credit allows people to take credits for taking classes at a community college, university or other higher education institutions. The maximum amount of expenses you can deduct is up to $10,000 for an unlimited number of years. However, the maximum you can receive as a credit is $2,000 per tax return.
The credit allows for a dollar-for-dollar reduction on the amount of taxes owed. The expenses can include tuition, fee payments and required books or supplies for post-secondary education for yourself, spouse or dependent child. The credit is not refundable, which means the credit can be used to pay any taxes you owe, but you cant receive any of it as a refund.
The 2020 credit amount begins to decrease if your modified adjusted gross income is over a certain threshold . The credit is not available once your income exceeds certain amounts . The IRS has yet to announce the thresholds for the 2021 tax year.
Note: This credit cant be claimed in the same year as the American Opportunity Tax Credit if the expenses are claimed as the Lifetime Learning Credit.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If The Irs Rejects Your Tax Return
