Qualifying For The Tuition And Textbook Credit
Taxpayers who have one or more dependents attending grades K-12 in an Iowa school may take a credit for each dependent for amounts paid for tuition and textbooks. The credit is 25% of the first $1,000 paid for each dependent for tuition and textbooks. Dependents must have attended a school in Iowa that is accredited under section 256.11, not operated for a profit, and adheres to the provisions of the U.S. Civil Rights Act of 1964. If expenses qualify for both the tuition and textbook credit and 529 Plan, taxpayers may claim both.
A Tax Break For Dream Hoarders: What To Do About 529 College Savings Plans
Parents, students, and policymakers are increasingly worried about the cost of college. Much of this anxiety is overplayed in the media. A college education remains, for most, a sound investment. Debt levels remain at manageable levels, especially for those with the highest amounts, since they also earn the most.
Plan Benefits: They Grow Tax
Earnings on 529 accounts are not treated as taxable income. Lets say, for example, that you save $1,000 in a 529 investment account, which grows by 5% in a year to $1,050. That $50 in growth isnt taxable.
Plus, if you sold those 529 account investments to pay for your childs college, you wouldnt face federal income tax on the sale proceeds or account withdrawals as long as you use those funds to pay for qualified education-related expenses. But if you use 529 funds for nonqualified expenses, the earnings could be taxed as income. Other penalties might apply too.
The rules for spending 529 funds allow you to use the money for everything from tuition to paying for a students internet access. The Secure Act, which became law in 2019, further relaxed rules on how you use money in a 529 plan. It allows beneficiaries of 529 funds to use leftover money to repay up to $10,000 of their student loans. The law also lets borrowers apply money from their 529 plan to pay for home schooling expenses and apprenticeships as well as private primary and secondary education.
No matter the expenses that the 529 money goes toward, growing college funds in a 529 savings account without adding to your tax burden is a significant tax benefit.
You May Like: Where Can I Find My Property Tax Bill
Plans Are Highly Flexible
You can change your 529 plan investment options twice per calendar year and you can rollover your funds into another 529 plan once in a 12-month period.
Hint: There is no federal limit on the frequency of these changes if you replace the account beneficiary with another qualifying family member at the same time.
Plan State Income Tax Benefits
Over 30 states, including the District of Columbia, currently offer a state income tax credit or deduction up to a certain amount. For example, contributions to a New York 529 plan of up to $5,000 per year by an individual or $10,000 per year by a married couple filing jointly are deductible in computing state income tax. But that doesnt mean New York parents are limited to contributing $10,000 to their 529 plan. If the couple chooses to take advantage of the annual gift tax exclusion and deposits $15,000 this year, the entire amount will grow federal tax-free, but only the first $10,000 may be deducted from their state taxable income.
Don’t Miss: Where Can I File An Amended Tax Return For Free
What Are The Tax Benefits
The tax benefits of 529 plans are similar to those offered by qualified retirement plans like traditional IRAs and 401s. Money held in the account grows tax-free, which can boost the accounts value significantly over the long term. And funds can also be withdrawn tax-free if theyre used to pay for qualified education expenses. These are defined broadly and include tuition and fees, room and board, textbooks, supplies and computers.
State Income Tax Treatment Of Qualified Withdrawals
States differ in the 529 plan tax benefits they offer to their residents. For example, some states may offer no tax benefits, while others may exempt earnings on qualified withdrawals from state income tax and/or offer a deduction for contributions. However, keep in mind that states may limit their tax benefits to individuals who participate in the in-state 529 plan.
You should look to your own state’s laws to determine the income tax treatment of contributions and withdrawals. In general, you won’t be required to pay income taxes to another state simply because you opened a 529 account in that state. But you’ll probably be taxed in your state of residency on the earnings distributed by your 529 plan if the withdrawal in not used to pay the beneficiary’s qualified educations expenses.
529 account owners who are interested in making K-12 contributions or withdrawals should understand their state’s rules regarding how K-12 funds will be treated for tax purposes. States may not follow the federal tax treatment.
Also Check: How Much Tax Return Will I Get
Your Own State May Offer Tax Breaks As Well
In addition to the federal tax savings, over 30 states currently offer a full or partial tax deduction or credit for 529 plan contributions. You can generally claim state tax benefits each year you contribute to your 529 plan, so its a smart idea to continue keep making deposits until youve paid your last tuition bill.
Be sure to research all of your options. If your state doesnt offer benefits for residents, you can choose any other states plan.
The Cost Of 529 Plans Is Set To Rise
As 529 plans mature and more families use them to fund college costs, the price tag to the U.S. Treasury will also rise, unless some reforms are undertaken. Over the next decade, the federal government is set to spend almost $30 billion on 529 tax expenditures, according to Treasurys Office of Tax Analysis. Annual costs are projects to be just under $4 billion by 2026.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Out Of Paying School Taxes
Iowa Taxpayers Can Use College Savings Iowa 529 Assets To Pay K
Qualified withdrawals from your account can be used to pay for tuition, room and board , books, supplies, fees and equipment required for enrollment or attendance at any eligible educational institution in the United States or abroad, as well as computers or certain peripheral equipment, certain computer software or internet access and related services that are to be used primarily by the Beneficiary during any of the years the Beneficiary is enrolled at an eligible educational institution.
Additionally, qualified withdrawals include fees, books, supplies and equipment required for participation in an apprenticeship program registered and certified with the Secretary of Labor under the National Apprenticeship Act, and amounts paid as principal or interest on any qualified education loan of the beneficiary or a sibling of the beneficiary provided that the total amount that may be used from all accounts for repayment of loans of a beneficiary may not exceed $10,000. You should consult your tax advisor for more information.
Seek 529 Tax Benefits Outside Your State
Some states, including California and North Carolina, dont offer a 529 state tax deduction at all. Then there are states, such as Texas and Florida, which dont levy a state income tax, which means you cant lower a tax burden you dont have.
If youre unlikely to generate much savings by claiming a state 529 tax deduction, it could be a smart move to shop for savings plans outside your state. Here are a few tips to follow when you compare 529 savings plans:
Read Also: How Much Taxes Do I Owe 1099
Who Is Eligible For A 529 Plan State Income Tax Benefit
States typically offer state income tax benefits to any taxpayer who contributes to a 529 plan, including grandparents or other loved ones who give the gift of college. However, in 10 states only the 529 plan account owner may claim a state income tax benefit.
Eligible taxpayers may continue to claim a 529 plan state income tax benefit each year they contribute to a 529 plan, regardless of the beneficiarys age. There are no time limits imposed on 529 plan accounts, so families may continue to make contributions throughout the childs elementary school, middle school, high school, college years, and beyond.
State income tax benefits should not be the only consideration when choosing a 529 plan. Attributes such as fees and performance must always be taken into account before you enroll in a 529 plan. In some cases, better investment performance of another states 529 plan can outweigh the benefits of a state income tax deduction.
How Total Contribution Affects Your 529 Plan Deduction
Tax deductions can potentially lower your taxable state income by excluding the amount of your contribution. So, at a state tax rate of 5%, a $1,000 deduction would save you $50. Keep in mind, this deduction is only available in some states, and is never available federally.
529 plan contributions are made from after-tax income. But depending on your state, you may be able to deduct these contributions from your state taxes. So, the more you contribute, the higher your deduction will be. 529 plan earnings are also exempt from federal taxes. So even if your income is taxed, the earnings in the account will not be.
Also Check: What Is Form 8995 For Taxes
Who Is Eligible For Tax Benefits From A 529 Plan
Anybody can open a 529 account. For the most part, parents or grandparents open these accounts on behalf of a beneficiary child or grandchild. State tax deductions may be available in some jurisdictions for the account holder.
The money in the account grows tax-deferred until it is withdrawn. As long as the money is used to pay for acceptable educational expenses as defined by the IRS, the withdrawals aren’t subject to state or federal taxes.
Students in grades K-12 are limited to $10,000 in tax-free withdrawals each year.
Who Can Open A 529 Plan
A 529 Plan account can be opened by almost anyone, as long as that person is 18 years old and a US resident. It is also not necessary for the account owner to be related to the account beneficiary. These plans are not just a savings tool for parents, they can be opened by grandparents, aunts, uncles, godparents, friends or even the student themselves.
Another key feature of 529 plans is that they are set up to accept third-party contributions, regardless of who owns the account. This means you dont have to open a 529 account to help someone save for college. Anyone can contribute to an existing 529 plan setup for a beneficiary. An added benefit for making a 529 plan contribution is that most states currently offer a state income tax deduction or tax credit. However, in most cases, to get the tax benefit the account must be set up in the taxpayers home states 529 plan.
Also Check: What’s The Last Day To Pay Taxes
Income Tax Treatment Of Nonqualified Withdrawals
If you make a nonqualified withdrawal , the earnings portion of the distribution will usually be taxable on your federal income tax return in the year of the distribution. The earnings are usually taxed at the rate of the person who receives the distribution . In most cases, the account owner will be the distributee. Some plans specify who the distributee is, while others may allow you to determine the recipient of a nonqualified withdrawal.
You’ll also pay a federal 10% penalty on the earnings portion of the nonqualified withdrawal. There are a couple of exceptions, though. The penalty is generally waived if you terminate the 529 account because the beneficiary has died or become disabled, or if you withdraw funds not needed for college because the beneficiary has received a scholarship. A state penalty may also apply.
Hunt For 529 Tax Deductions But Plan For Contribution Limits
As you choose a 529 plan, pay attention to the 529 contribution limits. According to the IRS, contributions cannot be more than the amount needed to provide for the student beneficiarys qualified educational expenses.
Each state might interpret this rule differently when it sets 529 contribution limits, so the limits may vary. But typical 529 contribution limits allow savers to accrue up to $300,000 in savings per beneficiary, according to wealth management firm AXA.
Consider limiting annual 529 contributions to $14,000 or less per beneficiary. According to the IRS, a gift tax might apply to any 529 contributions that exceed that amount.
No matter the ways you plan to help your child cover college costs, educational tax deductions and credits can make a big difference. Learning about tax benefits that can help lessen the financial burden of college is one element in deciding how much to save for your childs education.
Andrew Pentis and Marty Minchin contributed to this report.
Recommended Reading: How To File Past Years Taxes
Which States Offer Tax Credits
Indiana, Minnesota, Oregon, Utah, and Vermont provide tax credits, which families can use to offset their state income taxes. These credits, on average, offer greater tax savings to a broader range of families than deductions do. Oregon’s maximum tax credit for joint filers is $300, which can be met with a relatively low contribution of $1,200. For those earning $100,000, the percentage of contribution eligible for tax credit is 25%, but this percentage is higher for families with lower incomes . Minnesota also offers larger benefits to families earning less, as it offers the option of a deduction or a more generous credit. Like Oregon, the tax credit calculation is adjusted by income level. For those earning less than $80,430, the maximum credit of $500 can be earned with a relatively low contribution of $1,000 . The calculations for tax credits in Indiana and Vermont are a little less generous than Minnesota and Oregon, but the dollar amounts are significantly higher than the states with deductions. In Indiana and Vermont, a $3,000 contribution would result in tax credits of $600 and $300, respectively. Indiana has a high $1,000 state tax credit limit, per taxpayer. Vermont’s state tax credit maximum is $500, but this is per beneficiary. Utah employs a relatively low 4.95% of contribution to calculate the tax credit, so a $3,000 contribution would result in a tax credit of $149.
Federal Income Tax Treatment Of Qualified Withdrawals
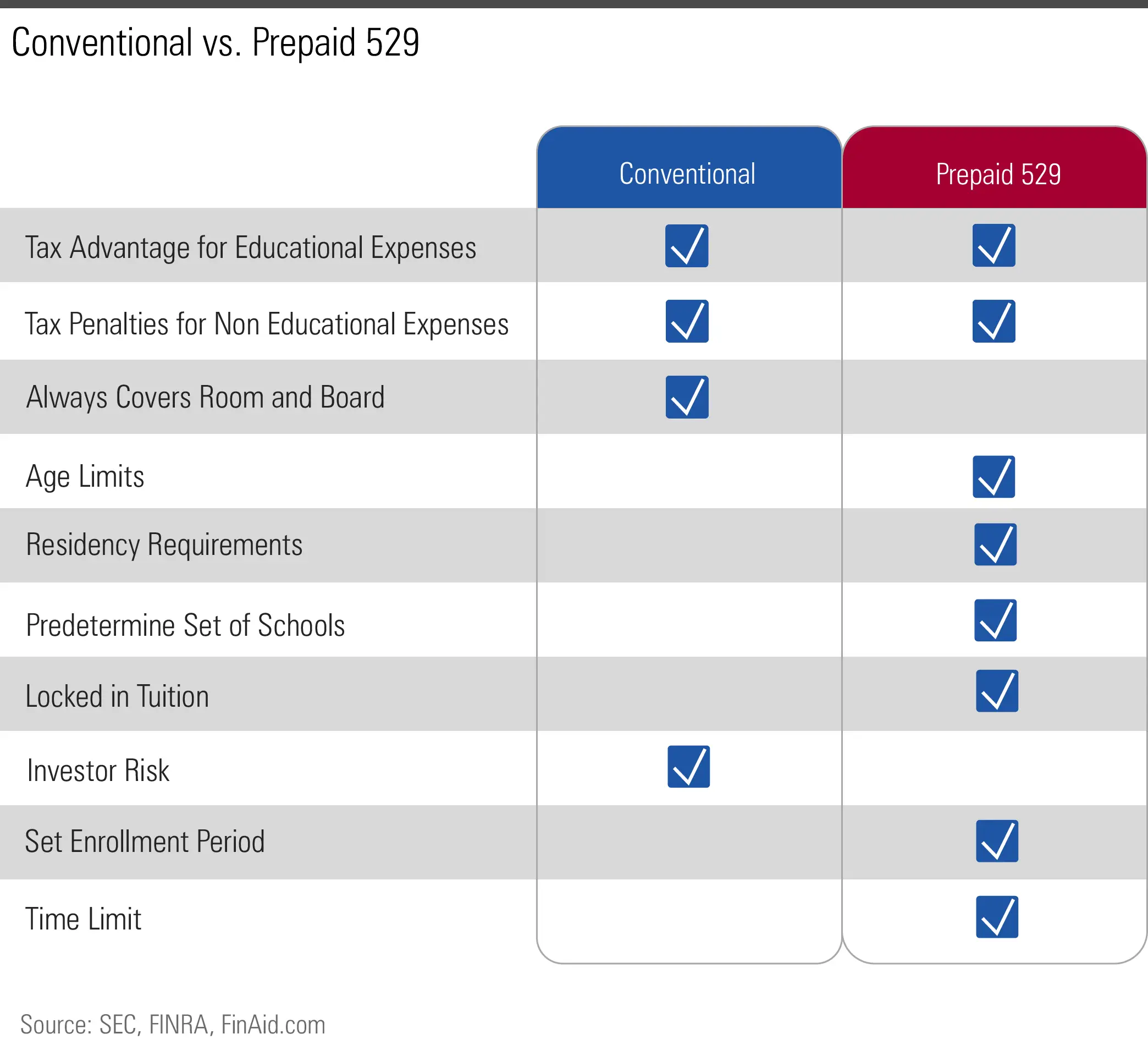
There are two types of 529 plans savings plans and prepaid tuition plans. The federal income tax treatment of these plans is identical. Your contributions accumulate tax deferred, which means that you don’t pay income taxes on the earnings each year. Then, if you withdraw funds to pay the beneficiary’s qualified education expenses, the earnings portion of your withdrawal is free from federal income tax. This feature presents a significant opportunity to help you accumulate funds for college.
Qualified education expenses for 529 savings plans include the full cost of tuition, fees, room and board, books, equipment, and computers for college and graduate school, plus K-12 tuition expenses for enrollment at an elementary or secondary public, private, or religious school up to $10,000 per year.
Qualified education expenses for 529 prepaid tuition plans generally include tuition and fees for college only at the colleges that participate in the plan.
Read Also: Where Can I Get Income Tax Forms
Qualified Elementary And Secondary Education Expenses
These are expenses for no more than $10,000 of tuition, incurred by a designated beneficiary, in connection with enrollment or attendance at an eligible elementary or secondary school.
*CAUTION Illinois Qualified Expenses do not include expenses for:
- tuition in connection with the Beneficiarys enrollment or attendance at an elementary or secondary public, private, or religious school. The amount of cash distributions for such expenses from all 529 qualified tuition programs with respect to a Beneficiary shall, in the aggregate, not exceed $10,000 during the taxable year.
- If a withdrawal is made for such purposes it may be a Federal Qualified Withdrawal and not be included in income for federal and Illinois purposes, but if an Illinois income tax deduction was previously claimed for Contributions to the Account all or part of that deduction may be added back to income for Illinois income tax purposes.
Please consult with your tax advisor.
How Your State Of Residence Affects Your 529 Plan Deduction

Each state has its own policy for taxable income deductions. Some states dont have a 529 plan deduction, so you wont be able to deduct any of your state income. Others will allow you to deduct up to $15,000 per year.
If you live in a state with a low 529 plan deduction, make sure to start contributing early so you can space out your contributions. This will maximize your deduction and save you the most money. Its a good idea to try to deduct as much of your college fund as possible from state taxes.
Also read: What are the 529 plan rules?
Also Check: Can You Turn In Taxes Late
What Is Irs Form 1099
IRS Form 1099-Q is a statement issued by a 529 plan or Coverdell ESA administrator that lists the amount of distributions in a given tax year. The Form 1099-Q will be issued to the beneficiary if the 529 distribution was paid to:
- The 529 plan beneficiary
- The college, K-12 school or apprenticeship program the beneficiary attends
- A student loan provider
When the Form 1099-Q is issued to the 529 plan beneficiary, any taxable amount of the distribution will be reported on the beneficiarys income tax return. This typically results in a lower tax obligation than if the Form 1099-Q is issued to the parent or 529 plan account owner.
Form 1099-Q lists the total distributions from a 529 plan or Coverdell ESA during a given tax year, regardless of how the funds were spent. Typically, Box 1 of a Form 1099-Q lists the total distribution, Box 2 includes the earnings portion of the distribution and Box 3 includes the basis, which is the contribution portion of the distribution.
The earnings portion of a non-qualified 529 plan distribution is subject to income tax and a 10% penalty.
