Common Deferred Tax Assets
One straightforward example of a deferred tax asset is the carryover of losses. If a business incurs a loss in a financial year, it usually is entitled to use that loss in order to lower its taxable income in the following years. In that sense, the loss is an asset.
Another scenario arises when there is a difference between accounting rules and tax rules. For example, deferred taxes exist when expenses are recognized in a company’s income statement before they are required to be recognized by the tax authorities or when revenue is subject to taxes before it is taxable in the income statement.
Essentially, whenever the tax base or tax rules for assets and/or liabilities are different, there is an opportunity for the creation of a deferred tax asset.
Get Started Today With My Digital Money
If youre looking to make a secure investment in your future, an IRA is one of the safest bets you can make. However, you have many more options than your traditional or Roth IRA these days.
My Digital Money is a leading crypto IRA platform where investors can buy and sell crypto in an IRA or trade in cash. A crypto IRA is a hedge against events like stock market crashes or depressions that traditional IRAs may not be immune to. You can also click here to learn more about what a crypto IRA is and why its beneficial.
If youre interested in learning more about getting started with My Digital Money, contact us today to speak with one of our experienced team members.
What Retirement Accounts Are Not Tax
On the other hand, non-tax-deferred retirement accounts are contributed with after-tax dollars. Meaning, when the person gets paid, taxes are first taken out of their paycheck before putting money away into these accounts. However, those contributions and their growth are then distributed during retirement tax-free.
Employer-sponsored retirement plans can provide non-tax-deferred accounts called Roth 401s. These work in similar ways to traditional 401s however, contributions are made after taxes are taken out of the income. The planâs administrator then automatically contributes the funds into the Roth 401 without the employee ever touching the money. Employers can even match the contributions employees make towards a Roth 401 however, the employerâs matching contributions are tax beforehand. So the employerâs match goes into a traditional 401 and is tax-deferred until retirement.
Another popular non-tax-deferred retirement account is the Roth IRA. Like traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs are held at outside brokerages. Participants receive their paychecks with taxes taken out, and they contribute however much of the leftover amount they want to their Roth IRA. The IRS limits Roth IRAs to $6,000 of annual contributions.
Don’t Miss: Does The Irs Forgive Tax Debt
Earn Now Pay Taxes Later
Just as the IRS gets a share of the income you bring home in your paycheck, so too does it get a share of the gains your investments bring you. But if you save in a tax-deferred retirement account like a traditional IRA or 401, you won’t pay taxes up front as you do in your paychecks, or as you would on investments in traditional brokerage accounts that are sold at a profit. Rather, your investments in a traditional IRA or 401 can continue to grow year after year, and you won’t pay taxes on your gains until the time comes to take withdrawals in retirement.
Imagine you have a year where you make $5,000 in gains in a traditional brokerage account by selling an investment for a price that’s higher than what you paid for it. You’re responsible for paying taxes on that $5,000 when you file that year’s return. With a traditional IRA or 401, however, that won’t happen. Rather, you’ll get the option to reinvest that $5,000 and not pay taxes on it until you’re older and ready to take withdrawals from your account.
What Are The Benefits Of Tax Deferral

The primary benefit of tax deferral is the growth achieved through compounding interest.
As opposed to money market mutual funds, brokerage accounts, and similar financial instruments on which you pay an annual tax on earnings, tax-deferred products allow the full amount of the earned interest to remain in the account and continue to earn interest, which in turn, will not be taxed. And so on until you start taking distributions.
Tax-deferred compound interest can increase the value of an annuity or retirement plan over time.
Its likely that youll be in a lower tax bracket during retirement years, when you have less taxable income and a higher standard deduction than you had during your working years.
For example, the tax code states that only people who have other substantial income in addition to your benefits owe federal income tax on their Social Security benefits.
You may also decide to retire to a tax-friendly state to reduce your tax burden.
Read Also: Are Donations To Nonprofit Organizations Tax Deductible
What Is Tax Deferred Mean
What does tax deferred mean?
taxwalls.blogspot.com
- DEFINITION of TaxDeferred. Taxdeferred status refers to investment earnings such as interest, dividends, or capital gains that accumulate tax-free until the investor takes constructive receipt of the profits. The most common types of taxdeferred investments include individual retirement accounts and deferred annuities.
What Are Retirement Accounts Tax
Not all retirement accounts are equal. The IRS sets different guidelines for retirement accounts depending on whether they are tax-deferred or not or whether they are employer-sponsored or individual accounts.
When it comes to tax-deferred retirement accounts, none are more popular than the 401. Provided by employers to their employees, a 401 is one the easiest ways to save for retirement. Many companies auto-enroll their new hires, and contributions are made to the account without the employee ever seeing the money. Even better, many employers offer to match employeesâ contributions up to a certain percent. The typical employer match is 3% of the employeeâs salary.
Another common tax-deferred retirement account is a traditional IRA. IRAs are provided by many institutional investment brokers like Vanguard and Fidelity. Usually, IRA account holders get paid and pay taxes first, then contribute to a tax-deferred IRA. These contributions become tax credits that offset the individualâs tax obligation for that tax year.
These tax-deferred retirement accounts are great options for those who plan to save a lot and maximize their retirement savings. This, in turn, allows the account to grow even more as more money is being contributed without taxes being taken out first.
You May Like: How To Check If The Irs Received My Tax Return
Withdrawal Timing To Save Taxes
Using a tax-deferred 401 does not mean you never pay taxes, however. Participants pay taxes when they withdraw their earnings and contributions.
Taxable income often drops in retirement, potentially putting you into a lower tax bracket than you had as an employee. Money you take from a tax-deferred 401 during retirement years therefore, can get taxed at a rate lower than what you pay while fully employed.
- Withdraw money early, though, and you will usually pay taxes plus a 10% penalty.
- The IRS lets you begin to withdraw without a penalty at age 59 1/2, and requires you to begin withdrawing by April 1 the year after you turn 72 or after age 70 1/2 if you attained this age prior to January 1, 2020.
Understanding Deferred Tax Assets
A deferred tax asset is often created when taxes are paid or carried forward but cannot yet be recognized on the company’s income statement.
For example, deferred tax assets can be created when the tax authorities recognize revenue or expenses at different times than those that the company follows as an accounting standard.
These assets help reduce the companys future tax liability.
It is important to note that a deferred tax asset is recognized only when the difference between the loss-value or depreciation of the asset is expected to offset its future profit.
A deferred tax asset might be compared to rent paid in advance or a refundable insurance premium. While the business no longer has the cash on hand, it does have its comparable value, and this must be reflected in its financial statements.
Read Also: What Is Tax Credit Housing
When Your Application Is Approved
If you applied for the first time on your property and your application is approved:
If you renewed your application:
- You will not receive an approval letter
You can check your application status online at any time.
Note: Only property classifications for Residential and Residential and Farm are deferrable. All other property classifications must be paid to your tax office.
Fees
If you applied for or renewed the Regular Program, a fee is added to your account:
- $60 for new applications
There are no fees for the Families with Children Program.
Interest
Simple interest is charged on the deferred tax amount starting from the date your property taxes are due or the date you applied to defer, whichever is later. Find out how interest is applied to your tax deferment loan.
How Is Deferred Tax Liability Calculated
A company might sell a piece of furniture for $1,000 plus a 20% sales tax, payable in monthly installments by the customer. The customer will pay this over two years .
In its financial records, the company will record a sale of $1,000.
In its tax records, it will be recorded as $500 per year for two years.
The deferred tax liability would be $500 x 20% = $100.
Don’t Miss: Where Do I Go For My Taxes
What Is A Deferred Tax Asset Vs A Deferred Tax Liability
A deferred tax asset represents a financial benefit, while a deferred tax liability indicates a future tax obligation or payment due.
For instance, retirement savers with traditional 401 plans make contributions to their accounts using pre-tax income. When that money is eventually withdrawn, income tax is due on those contributions. That is a deferred tax liability.
How Deferred Tax Liability Works

The deferred tax liability on a company balance sheet represents a future tax payment that the company is obligated to pay in the future.
It is calculated as the company’s anticipated tax rate times the difference between its taxable income and accounting earnings before taxes.
Deferred tax liability is the amount of taxes a company has “underpaid” which will be made up in the future. This doesn’t mean that the company hasn’t fulfilled its tax obligations. Rather it recognizes a payment that is not yet due.
For example, a company that earned net income for the year knows it will have to pay corporate income taxes. Because the tax liability applies to the current year, it must reflect an expense for the same period. But the tax will not actually be paid until the next calendar year. In order to rectify the accrual/cash timing difference, tax is recorded as a deferred tax liability.
Don’t Miss: How To Calculate Taxes On Stocks
When You’ve Paid Your Loan In Full
If you pay your account in full, your agreement will close. The Land Title Office or Personal Property Registry will release the tax deferment lien when they receive a Notice of Satisfaction from our office.
Well send the Notice of Satisfaction once your payment has been processed or cleared.
If you repay your loan in full using non-guaranteed funds, such as a personal cheque, it will take at least 30 days to clear your payment. We cant change this clearing time.
We’ll mail your confirmation when your payment has been processed.
It may take several weeks for the lien to be removed after your tax deferment account is paid in full. Contact the Land Title Office to follow up on the status of your lien.
Qualified Tax Deferred Investments
With a qualified tax deferred investment, you can defer the taxes you would normally have to pay on your contributions and earnings on the investment in the current year.
In other words, you invest using pre-taxed income.
A qualified tax deferred investment can be made in tax deferred investment accounts such as an IRA account or 401 plans.
The advantage of a qualified tax deferred investment is that you can avoid paying taxes in the current year by putting pre-tax salary or wages.
The amount of money that you invest in qualified tax deferred investments will help reduce your tax liability in the current year and delay it to a future point in time.
Don’t Miss: How Much Does H& r Block Charge To Do Your Taxes
What Do Deferred Payments Mean
When you make a deferred payment, youre essentially putting off paying for something until a later date. This can be helpful in several situations, such as if you need to make a large purchase but dont have the total amount upfront. It can also be helpful if youre trying to manage your cash flow and want to spread out the cost of something over time.
There are a few things to remember when making a deferred payment. First, youll typically need to pay interest on the borrowed amount, so its essential to factor that into your budget. Youll also need to make sure you can repay the total amount by the deadline, or you may default on the loan. Finally, carefully read the terms and conditions of any deferred payment agreement before signing on the dotted line.
What Is Deferred Income Tax
Deferred income tax can sometimes occur when the calculations to find net income and how much taxes are owed on that net income differ. This can sometimes happen due to a difference in depreciation methods.
Depreciation is how accountants for a company will calculate the value of business assets. There are different ways to calculate these values, which can cause variations in total net income and thus total taxes owed on that income. This is where deferred income tax comes in to help make up for these differences.
You May Like: How To File School District Taxes In Ohio
The Process To Apply Or Renew Your Tax Deferment Application
Ensure you meet all eligibility requirements and have the information you need ready before you apply or renew an application.
You may need to submit supporting documentation with your application if youre applying:
- On behalf of a registered owner
- As a surviving spouse
- As a person with disabilities or as a parent or stepparent of a person with disabilities
When you apply, you may set up automatic renewal for subsequent years.
If you have automatic renewal set up already, you don’t need to submit an application. Our office will determine if you meet the program requirements and may contact you by email or mail requesting additional information. Requested information is due 30 days from the date the email request was sent or when the letter was issued. If the requested information is not received by the due date, your application will be cancelled and late penalties will apply if it’s after your property tax due date.Note: Approved renewals are not issued an approval letter. You can verify your renewal status online, or if you have an eTaxBC logon.Renewal applications will be cancelled and our office will not pay your property taxes if we verify the applicant is no longer eligible for the program. Some examples include:
- Your current year taxes have been paid by you, or your lender
- The applicant has moved off the property
- The applicant has passed away
Find out more about:
What Is A Tax Deferred Account
A tax deferred account is a type of investment account where your investment earnings accumulate in the account on a tax-free basis until you withdraw the funds from your account.
Investment earnings that may accumulate tax-free could be dividend earnings, interest payments, capital gains, or other returns.
One of the most common example of a tax deferred account is a 401 plan.
Recommended Reading: How Much Does It Cost To File Taxes With Taxslayer
Examples Of Deferred Tax Liability
A common source of deferred tax liability is the difference in depreciation expense treatment by tax laws and accounting rules.
The depreciation expense for long-lived assets for financial statement purposes is typically calculated using a straight-line method, while tax regulations allow companies to use an accelerated depreciation method. Since the straight-line method produces lower depreciation when compared to that of the under accelerated method, a company’s accounting income is temporarily higher than its taxable income.
The company recognizes the deferred tax liability on the differential between its accounting earnings before taxes and taxable income. As the company continues depreciating its assets, the difference between straight-line depreciation and accelerated depreciation narrows, and the amount of deferred tax liability is gradually removed through a series of offsetting accounting entries.
What Does Tax Deferred Mean
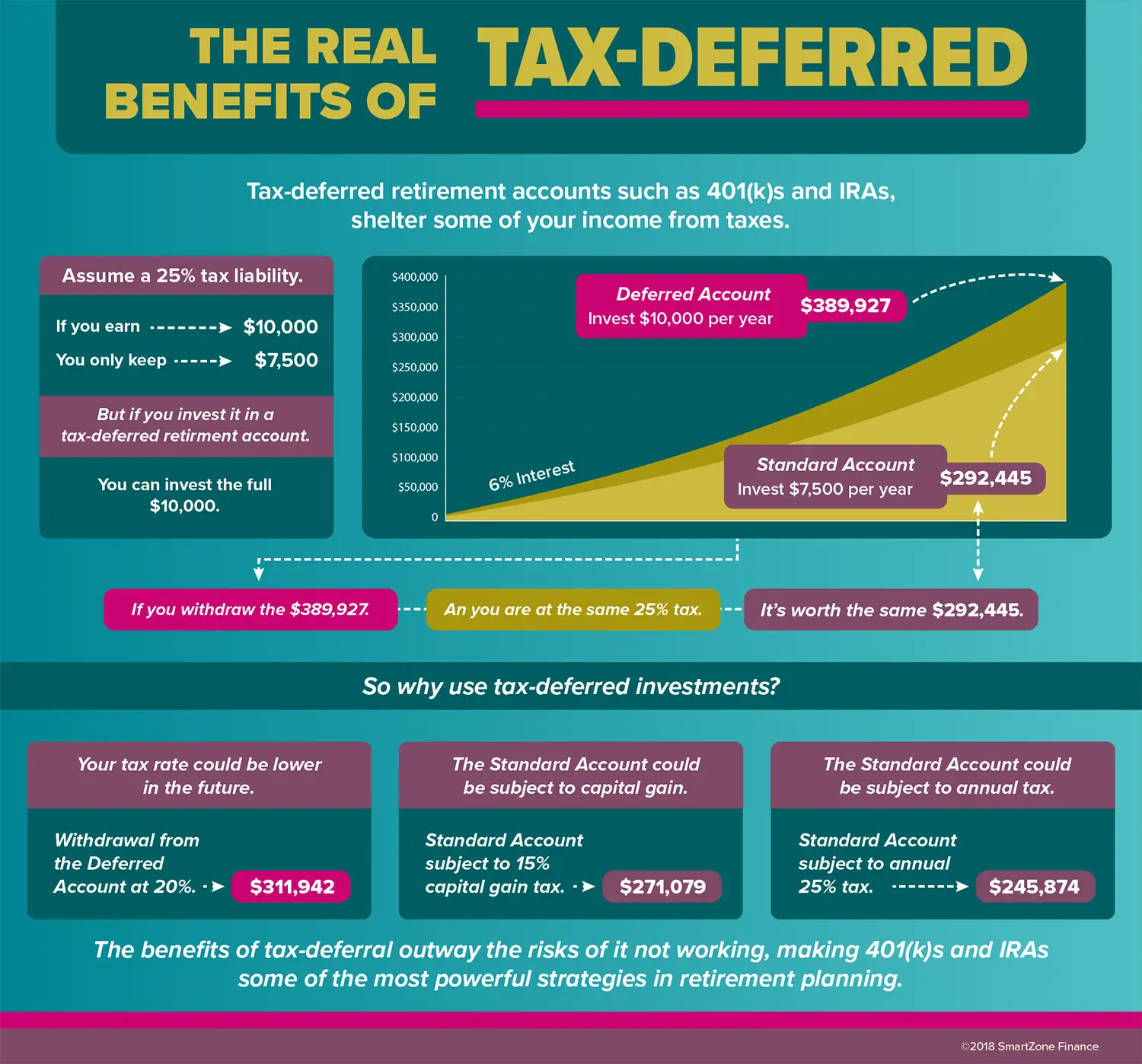
Tax deferred means that the tax that a person or company will need to pay on investments, revenues, or profits will be deferred to a future point in time.
In other words, tax deferral means that the payment of tax obligations is delayed or postponed to the future.
For example, if you invest in a tax deferred account, you will not be taxed for any earnings, dividends, or profits until you withdraw the funds from the said account .
Read Also: Can I File My Taxes Online
Do You Have To Pay Back The Tax Deferral
Q: Will I be required to pay back the Social Security taxes that were deferred? Yes. Per IRS guidance, the Social Security taxes deferred from PP 18 to PP 25, 2020, will be collected from your wages between PP 26, 2020, through PP 25, 2021.
How do I calculate deferred tax?
It is calculated as the companys anticipated tax rate times the difference between its taxable income and accounting earnings before taxes. Deferred tax liability is the amount of taxes a company has underpaid which will be made up in the future.
Do tax deferred investments save you money?
When it comes to tax-deferred accounts, you should save as much as you can comfortably afford . Most experts suggest you need to save at least 10% to 15% of your gross income to maintain the same standard of living in retirement. Tax-deferred accounts make it a lot easier and can save you money along the way.