From The Encyclopedia Of Taxation And Tax Policy
The Encyclopedia of Taxation and Tax PolicyEncyclopediaclothCD-ROMwww.uipress.org
Document date: October 01, 1999Released online: October 01, 1999 This article was originally published in the , edited by Joseph J. Cordes, Robert D. Ebel, and Jane G. Gravelle. The is available in and editions. Order online at or call toll-free 1-877-847-7377.The nonpartisan Urban Institute publishes studies, reports, and books on timely topics worthy of public consideration. The views expressed are those of the authors and should not be attributed to the Urban Institute, its trustees, or its funders.
This report is available in its entirety in the Portable Document Format .
Treatment of the changes in value of capital assets such as corporate stock, real estate, or a business interest.
Under a pure net accretion approach to income taxes, real capital gains would be taxed each year as they accrued and real capital losses would be deducted. Capital gains are generally taxed only when “realized” by sale or exchange, however, because it would be difficult to estimate the value of many assets, it would be viewed as unfair to tax income that had not been realized, and it could force the liquidation of assets to pay the tax on accruals. Taxation upon realization, however, leads to other problems, which require policy compromises.
Economic issues in capital gains taxation
TABLE 1
Additional readings
This report is available in its entirety in the Portable Document Format .
Capital Gains Tax In The United States
| This article is part of a series on |
|
|
In the United States of America, individuals and corporations pay U.S. federal income tax on the net total of all their capital gains. The tax rate depends on both the investor’s tax bracket and the amount of time the investment was held. Short-term capital gains are taxed at the investor’s ordinary income tax rate and are defined as investments held for a year or less before being sold. Long-term capital gains, on dispositions of assets held for more than one year, are taxed at a lower rate.
Tips For Navigating Tax Planning
- Need help finding a financial advisor? Finding a qualified financial advisor doesnt have to be hard. SmartAssets free tool matches you with up to three financial advisors who serve your area, and you can interview your advisor matches at no cost to decide which one is right for you. If youre ready to find an advisor who can help you achieve your financial goals, get started now.
- You might be interested in signing up for a robo-advisor. Many robo-advisors offer tax-loss harvesting, which sells investments that are hurting your portfolio and helps offset what you earn from the gains. Robo-advisors arent necessarily right for everyone, but if youre starting your investment journey or you dont have complicated assets, you may want to give it a try. If youre unsure, find one that offers you the chance to talk to a financial professional if you have questions about your specific needs. Not all robo-advisors offer this perk, but some do, usually for a fee.
Also Check: Can I Pay Quarterly Taxes Online
How The Tax On Capital Gains Works For Inherited Homes
What if youre selling a home youve inherited from family members whove died? The IRS also gives a free step-up in basis when you inherit a family house. But what does that mean?
Lets say Mom and Dad bought the family home years ago for $100,000, and its worth $1 million when its left to you. When you sell, your purchase price is not the $100,000 your folks paid, but instead the $1 million its worth on the last parents date of death.
You pay capital gains tax only on the difference between what you sell the house for, and the amount it was worth when your last parent died.
How To Know Your Capital Gains Tax Bracket
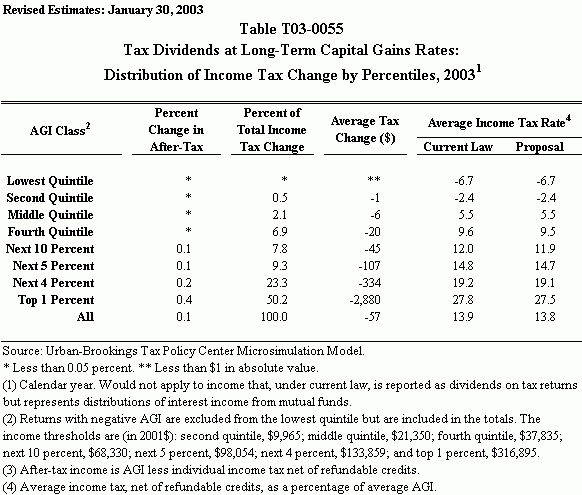
With higher standard deductions and income thresholds for capital gains, it’s more likely you’ll fall into the 0% bracket in 2023, Lucas said.
For 2023, you may qualify for the 0% long-term capital gains rate with taxable income of $44,625 or less for single filers and $89,250 or less for married couples filing jointly.
The rates use “taxable income,” calculated by subtracting the greater of the standard or itemized deductions from your adjusted gross income.
Don’t Miss: What Percentage Of Business Expenses Are Tax Deductible
How To Address Volatility In Capital Gains
Capital gains income and thus capital gains tax revenue can rise or fall rapidly in response to economic changes. States can manage this volatility by, for example, relying on a variety of taxes, some of which respond less dramatically to swings in the business cycle.
The best way to address volatility in capital gains and other taxes is to establish a rainy day fund and make deposits when strong economic growth boosts revenues, so these funds can smooth out revenue downturns. States can tie these provisions directly to capital gains taxes, if desired. For example, Massachusetts deposits all capital gains revenue above a specific threshold into its rainy day fund. Similarly, in Connecticut, when income taxes collected through quarterly payments from taxpayers and at the time of filing exceed a specified threshold, the surplus is deposited into the states reserves. These are mainly taxes on investment income.
Capital Gains Tax Rate For Collectibles
There are a few exceptions to the general capital gains tax rates. Perhaps the most common exception involves gains from the sale of collectibles that qualify as capital assets. For this special rule, a “collectible” can be a work of art, antique, stamp, coin, bottle of wine or other alcoholic beverage, gold or other precious metal, gem, historic object, or another similar item. If you sell an interest in a partnership, S corporation, or trust, any gain from that sale attributable to the unrealized appreciation in the value of collectibles is also treated as gain from the sale of collectibles.
Instead of a 20% maximum tax rate, long-term gains from the sale of collectibles can be hit with a capital gains tax as high as 28%. If your ordinary tax rate is lower than 28%, then that rate will apply. But if you’re in a higher tax bracket , then the capital gains tax on your collectible gains is capped at 28%.
The 28% limit doesn’t apply to short-term capital gains. So, if you don’t own a collectible for at least one year before selling it, you’ll still be taxed on any gain at your ordinary tax rate .
Also Check: How Can Tax Identity Theft Occur
Stay Invested And Know When To Sell
As weve emphasized, your income tax rate is a dominant factor when considering capital gains. By waiting to sell profitable investments until you stop working, you could significantly decrease your tax liability, especially if your income is low. In some cases, you might owe no taxes at all.
The same could be true if you retire early, leave your job, or your taxable income drastically changes. In essence, you can evaluate your financial situation each year and decide when the optimal time to sell an investment is.
What Is The Capital Gains Rate For Retirement Accounts
One of the many benefits of IRAs and other retirement accounts is that you can defer paying taxes on capital gains. Whether you generate a short-term or long-term gain in your IRA, you dont have to pay any tax until you take money out of the account.
The negative side is that all contributions and earnings you withdraw from a taxable IRA or other taxable retirement accounts, even profits from long-term capital gains, are typically taxed as ordinary income. So, while retirement accounts offer tax deferral, they do not benefit from lower long-term capital gains rates.
Also Check: What Is The Last Day To File Taxes In Texas
How Capital Gains Taxes Work
If you buy $5,000 worth of stock in May and sell it in December of the same year for $5,500, youve made a short-term capital gain of $500. If youre in the 22 percent tax bracket, you have to pay the IRS $110 of your $500 capital gains. That leaves you with a net gain of $390.
Instead, if you hold on to the stock until the following December and then sell it, at which point it has earned $700, its a long-term capital gain. If your total income is $50,000, then youll fall in the 15 percent bracket for that long-term capital gain. Instead of paying $110, youll pay $105, and see $595 worth of net profit instead.
Capital Gains Tax Rates For 2021
The capital gains tax on most net gains is no more than 15% for most people. If your taxable income is less than $80,000, some or all of your net gain may even be taxed at 0%.
As of 2021, the long-term capital gains tax is typically either 0%, 15% or 20%, depending upon your tax bracket. This percentage will generally be less than your income tax rate.
Source: Kiplinger
There are some exceptions to this 0-15-20% rule which allows certain capital gains to be taxed at higher rates.
Higher Capital Gains Tax Rate Exceptions
- Taxable portions of the sale of certain small business stocks are taxed at a 28% maximum rate.
- Net capital gains from selling collectibles such as coins or art are taxed at a 28% maximum rate.
- Certain portions of capital gains from specific real estate sales are taxed at a 25% maximum rate.
Recommended Reading: What Taxes Do You Pay In Texas
How Much Is Capital Gains Tax On Real Estate Plus How To Avoid It
Capital gains tax is the income tax you pay on gains from selling capital assetsincluding real estate. So if you have sold or are selling a house, what does this mean for you?
If you sell your home for more than what you paid for it, thats good news. The downside, however, is that you probably have a capital gain. And you may have to pay taxes on your capital gain in the form of capital gains tax.
Just as you pay income tax and sales tax, gains from your home sale are subject to taxation.
Complicating matters is the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which took effect in 2018 and changed the rules somewhat. Heres what you need to know about all things capital gains.
Qualified Small Business Stock
The tax treatment of a qualified small business stock depends on when the stock was acquired, by whom, and how long it was held. To qualify for this exemption, the stock must have been acquired from a QSB after Aug. 10, 1993, and the investor must be a noncorporate entity that held the stock for at least five years.
A QSB is generally defined as a domestic C corporation with aggregate gross assets that have never exceeded $50 million at any point since Aug. 10, 1993. Aggregate gross assets include the amount of cash held by the company, as well as the adjusted bases of all other property owned by the corporation. Additionally, the QSB must file all required reports.
Only certain types of companies fall under the category of a QSB. Firms in the technology, retail, wholesale, and manufacturing sectors are eligible as QSBs, while those in the hospitality industry, personal services, financial sector, farming, and mining are not.
This exemption originally allowed the taxpayer to exclude 50% of any gain from the sale of QSB stock. However, it was later increased to 75% for QSB stock acquired from Feb. 18, 2009, to Sept. 27, 2010, and then to 100% for QSB stock acquired after Sept. 27, 2010. The gain that is eligible for this treatment has a cap of $10 million, or 10 times the adjusted basis of the stockwhichever is greater.
Read Also: Can I File Taxes Without My Spouse Present
Capital Gains On Sale Of Second Home
If you own multiple homes, it may not be as easy to shelter sale profits as it was in the past.
The Housing Assistance Act of 2008 was designed to provide relief for homeowners on the edge of foreclosure, yet it could cost the owners when they decide to sell.
You used to be able to move into the second property, make it your primary residence, live there for two years, and profit from the gains.
Even when your second piece of real estate is converted into your primary home, you will be taxed on part of the gains based on how long the home was used as a second home and not the primary residence.
Both Capital Gains Rates And The Tax Base Have A Substantial Impact On Revenues
With $1.2 trillion of capital gains and dividends reported in 2018, cutting capital gains tax rates would lose a substantial amount of revenue, while increasing rates would raise a substantial amount of revenue.24 Some economists argue that raising capital gains rates will actually cause a loss in revenue because a higher tax rate would lead more asset holders to avoid realizing their gains by selling.25 But the current maximum capital gains rate of 23.8 percent is below the rate that official estimators believe is revenue maximizing, which is about 30 percent.26 More importantly, new research by Princeton University economists suggests the revenue-maximizing rate is even higher, at 38 percent to 47 percent.27
Another critical point is that those estimates of the revenue-maximizing rate are based on the existing rules for taxing gains, allowing asset holders to defer taxes and avoid capital gains tax entirely by holding assets for their lifetimes. The revenue-maximizing rate would be higher under a system that eliminated stepped-up basis and taxed gains at death. A mark-to-market system that taxed gains annually regardless of whether they are realized would entirely eliminate the ability to defer taxes on gains and allow for even larger revenue increases.
Read Also: Are Campaign Donations Tax Deductible
Ca Capital Gains Rate Vs Previous Years
Since California taxes capital gains as regular income, the tax rates themselves don’t change much. Instead, the criteria that dictates how much tax you pay has changed over the years. For example, in both 2018 and 2022, long-term capital gains of $100,000 had a tax rate of 9.3% but the total income maxed out for this rate at $268,749 in 2018 and increased to $312,686 in 2022.
CA vs. Other Large U.S. States
Now let’s compare the California capital gains tax to the capital gains tax rate of other large states:
- Texas: no state capital gains tax
- New York: 12.70%
- Florida: between 0% and 20%.
It’s important to note that the federal capital gains tax rates are the same in all states.
While California capital gains tax might be easier to understand because it is taxed as regular income, it’s worse on your wallet than other states. In fact, it can be quite expensive for some to pay capital gains on their many investments when compared to a state like Texas.
Capital Gains Tax Rates For 2021 And 2022
The profit on an asset that is sold less than a year after it is purchased is generally treated for tax purposes as if it were wages or salary. Such gains are added to your earned income or ordinary income on a tax return.
The same generally applies to dividends paid by an asset, which represent profit although they aren’t capital gains. In the U.S., dividends are taxed as ordinary income for taxpayers who are in the 15% and higher tax brackets.
A different system applies, however, for long-term capital gains. The tax you pay on assets held for more than a year and sold at a profit varies according to a rate schedule that is based on the taxpayer’s taxable income for that year. The rates are adjusted for inflation each year.
The rates for tax years 2022 and 2023 are shown in the tables below:
| 2022 Tax Rates for Long-Term Capital Gains |
|---|
| Filing Status |
| $44,626 to $276,900 | Over $276,900 |
The tax rates for long-term capital gains are consistent with the trend to capital gains being taxed at lower rates than individual income, as this table demonstrates.
Read Also: What Number Do I Need To File My Taxes
Risks And Rewards Of Bond Funds
Similar to stock ETFs, bond market funds are bundles of bond investments offering easy diversification and exposure to the bond market. Bond funds, like bonds, can have different maturities, risk and yield. Bond funds with longer maturities have higher yields and could be considered a long-term investment, but not for the same reason as stocks. Longer-term bonds pay higher yields because there’s a higher risk of inflation eating into your fixed interest payments.
However, the risk and reward profile of bonds with longer maturities might not stack up with the risks and rewards of investing in stocks:
We’re not interested in long term or high yield , because that offers an element of risk that you’re not necessarily rewarded for. Our attitude is if you’re going to take risk, you’ll be better rewarded for it on the equity side of the portfolio,” says Alexander.
Ultimately, having patience can lead to investing success over time, says Walnut Creek, California-based certified financial planner Mario Hernandez.
Not every asset is going to do well every year. Investments arent meant to. If you bail out and go into cash, youll realize that loss, and you wont be able to participate in the rebound in the market.
|
when you invest in a new Merrill Edge® Self-Directed account. |
