Example Of Social Security Taxation:
Let’s say a single, 68-year-old retired woman, Susan, receives the average Social Security benefit, totaling $18,516 for the year.
Susan collected $30,000 from other means throughout the year, so her provisional income is $39,258 .
Then, 85% of Susan’s total Social Security benefit, $15,738, is subject to federal income tax.
Every January, the Social Security Administration sends an earnings statement to Social Security recipients Form SSA-1099 showing the amount they were paid in benefits throughout the tax year. The statement is used to fill out their federal income tax return, which will determine whether tax is owed on Social Security benefits. Some states also tax Social Security benefits.
If Social Security recipients anticipate they’ll need to pay federal taxes on their benefit and want to do it ahead of time, they can make estimated quarterly payments or elect to have federal taxes withheld either 7%, 10%, 12%, or 22% of their monthly benefit.
What Is The Social Security Tax Limit
If you earn a high income, you may not have to pay Social Security Tax. Workers contribute to the Social Security system until they reach the Social Security tax limit. The Social Security taxable limit is $142,800 in 2021. This amount is not subject to Social Security taxes and can be factored into Social Security retirement payments.
C Should Benefits Be Subject To Tax And Contributions
The interaction between social security benefits and the income tax and contribution treatment of those benefits involves several complex issues.
1. Making Benefits Subject to Contributions
The first issue is whether benefits are subject to contribution liability. When benefits and contributions are related to the same fund, the simplest approach is to treat benefits as not subject to contributions. The fairness of this policy depends on how the rate of benefits compares with the income being replaced by the benefit. If, for example, the benefit fully replaces the income, the beneficiary will gain by having saved the contribution. The easiest approach to avoid overcompensation is to reduce the level of benefits by the amount saved. If the benefit only partially replaces the income, then exempting the benefit from contribution increases the net value of the benefit.
2. Notional Contributions
3. Imposing Income Tax on Benefits
With respect to the income tax treatment of benefits, there are two issues of principle. The first is whether benefit income should be liable to income tax. The second is the legal nature of the benefit income if it is to be subject to income tax. It is not earnings, although it will normally be of an income nature. It may or may not be paid to replace earnings.
Recommended Reading: How To Buy Tax Lien Certificates In California
E Links Between Contributions And Benefits
There is an inevitable linkage in any social security scheme between contributions to the scheme and benefits paid from the scheme. If contributions to the scheme and the income that the scheme itself generates do not match the total level of benefits that must be paid from the scheme, then the scheme will fail. Either further forms of funding must be found or benefit levels must be reduced. It is impossible, except in the very short term, to have a viable social security scheme if the benefits and contributions are decided independently of each other. In consequence, the level of funding of a scheme must be decided by primary reference either to the intended levels of contribution or to the intended levels of benefit. The method selected will influence the structure of the fund. The existence of the fund does not of itself determine how the contributions of any one contributor relate to the benefits to be received by that contributor unless the fund has only that contributor as a member.
Links between contributions and benefits can be of two kinds, reflecting the differences between funded and unfunded schemes. A funded scheme is a scheme in which the contributions paid in are used to create a fund from which benefits will, in due course, be drawn. If the fund has numerous contributors, the level of contributions required by the fund is based on actuarial advice about the probable pattern of contributions, fund income, and benefits in the predictable future.
When To Claim Your Social Security Limit 2021 Benefits

Even if youve earned your 40 credits, you cant begin collecting retirement benefits until youre 62 years old or older, and the longer you wait, the larger the payment will be.
If you wait until you reach your full retirement age, which is 67 if you were born in 1960 or later and is decided by the Social Security Administration, youll receive your primary benefit amount, which is the entire monthly benefit youre entitled to based on your earnings record.
Your monthly payment would be smaller if you applied for Social Security benefits sooner rather than later.
If your full retirement age is 67 and you choose to claim benefits at 62, you will only receive 70% of your primary insurance coverage.
However, if you collect at 65, you would receive 86.7 percent of your monthly benefit. If you wait past your full retirement age, you can receive delayed retirement credits.
Your eventual payout will grow by 8% for every year you wait to claim Social Security benefits. However, because we cap your benefits at age 70, theres no reason to wait any longer.
If youre getting Social Security disability benefits when you reach full retirement age, your disability benefits will convert to retirement benefits automatically, but the amount wont change.
You May Like: How To Buy Tax Liens In California
Buy An Annuity Contract
A qualified longevity annuity contract is a deferred annuity funded with an investment from a qualified retirement plan or IRA.
QLACs provide monthly payments for life and are shielded from the downturns of the stock market. As long as the annuity complies with IRS requirements, it is exempt from the required minimum distribution rules until payouts begin after the specified annuity starting date.
QLAC income can be deferred until age 85. A spouse or someone else can be a joint annuitant, meaning that both named individuals are covered regardless of how long they live.
Keep in mind that a QLAC shouldn’t be bought just to minimize taxes on Social Security benefits. Retirement annuities have both advantages and disadvantages that should be weighed carefully, preferably with help from a retirement advisor.
What’s Included In Social Security Wages And What’s Not
Some common types of compensation payments made to employees are exempt from being included as Social Security wages. They’re not subject to FICA tax.
- Some disabled worker wages paid after the year in which the worker was entitled to collect disability insurance
- Employee business travel expenses reimbursed for amounts not exceeding the specified government rate for per diems or the standard mileage rate
- Compensation paid to family employees under age 18, or age 21 for domestic work
- Some”excess” fringe benefits that are taxable on an excess of the fair market value of the benefit over the sum of an amount paid for it by the employee and any amount that’s excludable by law
- Employee insurance
- Workers compensation benefits
Additionally, earnings are only taxable for the Social Security portion of the FICA tax up to a certain maximum, which changes each year. Earnings begin accumulating again toward this “wage base” on January 1 of the next year.
The Social Security wage base is indexed for inflation so it can be expected to increase a bit annually.
Also Check: Amended Tax Return Online Free
Can You Cut Your Social Security Taxes
There are a few ways you can affect how much tax you pay on Social Security, most of which tie into decisions about taking retirement plan withdrawals as taxable income. Apart from that, though, most older Americans don’t have much flexibility with their tax planning. For them, knowing what tax rate will apply can simply help them prepare for what they’ll have to pay the IRS at tax time.
What You Need To Know About The Social Security Tax
The Social Security tax is a contribution to the overall Social Security system. This ensures that youll receive Social Security payments when you reach retirement age. As an employee, your employer will match what you contribute dollar for dollar.
The idea behind it is that you pay to support the retirees of today, and the next generation will subsequently fund your retirement. The philosophy behind it is to create a self-sustaining retirement plan.
On your paycheck, you may see something called FICA. This stands for the Federal Insurance Contributions Act, and this is the act that Medicare and Social Security Fica limit is taxed under.
This is also why your Social Security payments are higher when you delay claiming your benefits. The longer you pay the tax, the more you receive when the time comes for you to retire.
Working longer is also beneficial for retirees because it means vital extra years of income.
Also Check: Cook County Assessor Deadlines
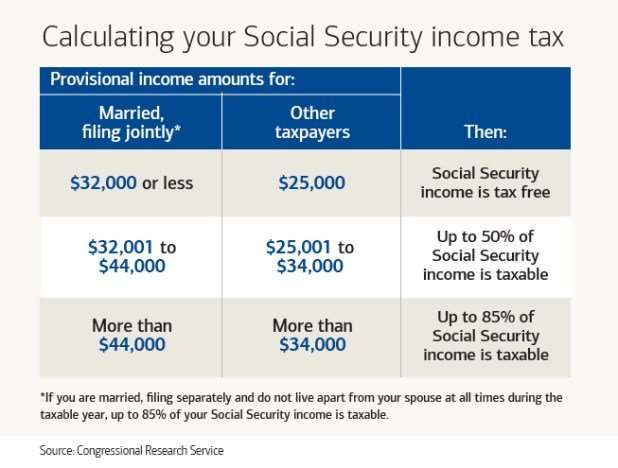
What Percentage Of Social Security Is Taxable
If you file as an individual, your Social Security is not taxable only if your total income for the year is below $25,000. Half of it is taxable if your income is between $25,000 and $34,000. If your income is higher than that, up to 85% of your benefits may be taxable.
If you and your spouse file jointly, you’ll owe taxes on half of your benefits if your joint income is between $32,000 and $44,000. If your income is above that, up to 85% is taxable income.
What Happens If You Stop Contributing To Social Security
Employers match the amount, while workers contribute 6.2% of their annual earnings to Social Security. Social security is 12.4% for self-employed workers. High earners pay into Social Security until their income reaches the Social Security Taxable Maximum, which is $142,800 in 2021.
Earnings above $142,800 do not get taxed by Social Security and are not used to calculate future Social Security benefits. Mike Biggie, a San Francisco-based certified financial planner, says that once you reach the maximum taxable earnings , withholdings will cease from your employer. This will result in a higher paycheck. Your employer payroll will track this maximum and stop withholding Social Security.
Recommended Reading: Can Home Improvement Be Tax Deductible
Does Social Security Income Count As Income
Yes, but you can minimize the amount you owe each year by making some wise moves before and after you retire. Consider investing some of your retirement savings in a Roth account, to shield your withdrawals from income tax. Take out some retirement money after you’re 59½ but before you retire, to take care of the taxes before you need the money. And, you might talk to a financial planner about a retirement annuity.
Are Employer Payroll Taxes Considered Business Expenses

As business expenses, also called deductions, refer to the amount of money a business spends due to factors such as paying salaries or ordering supplies, payroll taxes are considered a business expense on a companys income statement. This is because you as the employer must pay a certain amount of tax for each individual employee and their benefits.
Recommended Reading: Michigan Gov Collectionseservice
Maximum Taxable Earnings Rose To $142800
In 2020, employees were required to pay a 6.2% Social Security tax on income of up to $137,700. Any earnings above that amount were not subject to the tax. In 2021, the tax rate remains the same at 6.2% , but the income cap has increased to$142,800.
The flip side is that as the taxable maximum income increases, so does the maximum amount of earnings used by the SSA to calculate retirement benefits. In 2020, the maximum monthly Social Security benefit for a worker retiring at full retirement age was $3,011. In 2021, the maximum benefit increases by $137 per month to $3,148.
Social Security recipients can receive a 32% larger payment each month if they claim benefits at age 70 instead of at their regular full retirement age.
Withdraw Taxable Income Before Retirement
Another way to minimize your taxable income when drawing Social Security is to maximize, or at least increase, your taxable income in the years before you begin to receive benefits.
You could be in your peak earning years between ages 59½ and retirement. Take a chunk of money out of your retirement account and pay the taxes on it. You can use it later on without pushing up your taxable income.
For example, you could withdraw funds a little earlyor “take distributions,” in tax jargonfrom your tax-sheltered retirement accounts such as IRAs and 401s. You can make distributions penalty-free after age 59½. That means you avoid being dinged for making these withdrawals too early, but you must still pay income tax on the amount you withdraw.
Since the withdrawals are taxable , they must be planned carefully with an eye on the other taxes you will pay that year. The goal is to pay less in tax by making more withdrawals during this pre-Social Security period than you would after you begin to draw benefits. That requires considering the total tax bite from withdrawals, Social Security benefits, and any other sources.
Be mindful, too, that at age 72, you’re required to take minimum distributions from these accounts, so you need to plan for those mandatory withdrawals.
Don’t Miss: Do You Have To Pay Taxes On Plasma Donations
What Is The Social Security Tax
Social Security tax is the tax levied on both employers and employees to fund the Social Security program in the U.S. Social Security tax is collected in the form of a payroll tax mandated by the Federal Insurance Contributions Act or a self-employment tax mandated by the Self-Employed Contributions Act .
The Social Security tax pays for the retirement, disability, and survivorship benefits that millions of Americans receive each year under the Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance Programthe official name for Social Security.
How Fica Tax And Tax Withholding Work In 2021
Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This may influence which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list ofour partnersandheres how we make money.
Payroll taxes, including FICA tax or withholding tax, are what your employer deducts from your pay and sends to the IRS, state or other tax authority on your behalf. Here are the key factors, and why your tax withholding is important to monitor.
You May Like: How Much Social Security Am I Entitled To
Recommended Reading: Is Donating Plasma Taxable
Social Security Wage Base Cola Set For 2022
The maximum amount of an individual’s taxable earnings in 2022 subject to Social Security tax will be $147,000, the Social Security Administration announced Wednesday.
An increase from $142,800 for 2021, the wage base limit applies to earnings subject to the tax, known officially as the old age, survivors, and disability insurance tax. Because the OASDI tax rate is 6.2%, an employee with total wages from an employer at or above the maximum in 2022 will pay $9,114 in tax, with the employer paying an equal amount.
The Medicare hospital insurance tax of 1.45% each for employees and employers has no wage limit and is unchanged for 2022.
Individuals with earned income of more than $200,000 pay an additional hospital insurance tax under Sec. 3103 of 0.9% of wages with respect to employment .
Self-employed individuals pay self-employment tax equal to the combined OASDI and Medicare taxes for both employees and employers, i.e., 15.3%, up to the OASDI wage base and 2.9% in Medicare taxes on net self-employment income above it, with an offsetting above-the-line income tax deduction of half of the OASDI-equivalent component of self-employment tax.
The SSA also announced on Wednesday a cost-of-living adjustment based on an increase in the consumer price index from the third quarter of 2021, applicable to Social Security benefits payable in 2022, of 5.9%, compared with a COLA increase for 2021 of 1.3%.
Paul Bonner is a JofA senior editor.
The Tax Rate On Social Security For Most People: 0%
For the majority of taxpayers, Social Security benefits end up being free of tax. That’s because you’re allowed to have up to a certain amount of income before you have to include any of your Social Security on your tax return.
Specifically, start by taking your income from other sources — wages and salaries, interest and dividend income, and distributions from pension plans, for example — and then add in half of your Social Security benefits for the year. That gives you your countable income, and if it’s less than $25,000 for singles or $32,000 for joint filers, then congratulations! Your tax rate is 0%.
Recommended Reading: When Do We Start Filing Taxes 2021
Just Started Collecting Social Security Here’s How To Know Whether You’ll Owe Taxes On It
Roughly 1 in every 2 older adults will pay federal income taxes on a portion of their Social Security benefits for the 2020 tax year.
To be sure, this usually happens only if you have other substantial income in addition to your Social Security benefits, such as wages, self-employment, interest, dividends and other taxable income that must be reported on your tax return, according to Uncle Sam.
How Has The Social Security Tax Limit Changed Over Time
The Social Security maximum taxable amount is, which is adjusted each year in order to keep pace with the changes in average earnings. The 2021 tax cap is $5,100 higher than the 2020 taxable limit of $137,000. It is also $36,000 more than the 2010 limit at $106,800. In 2000, the taxable maximum was $76,200 and in 1990 it was $51,300.
Also Check: Www.myillinoistax
Delaying Your Social Security Benefit Claim
“The other strategy, says Kumar, involves postponing when you first take Social Security. Both approaches can help shave dollars off your tax bill in retirement every yearit just takes a little forward planning.”
Consider a hypothetical couple named Natalie and Juan: For every year they delay taking Social Security past their full retirement age , they get up to an 8% increase in their annual benefit.
A hypothetical couple claiming Social Security at age 65 vs. age 70
| Natalie and Juan | |
|---|---|
| Net tax savings | $1,904 |
In general, many people would benefit from waiting to age 70 to take Social Security. Others may need the income sooner and may lack the resources necessary to meet expenses during the delay period, or they may not live long enough to reap the rewards of delaying their claim.
Natalie and Juans strategy is to reduce the amount they withdraw from their taxable IRAs over time and make up the difference in income by waiting until age 70 to claim Social Security. This has a big payoff for them because by delaying claiming Social Security until age 70, the percentage of their Social Security income that gets taxed is cut from 85% to 48.33%.
It gets better: While Natalie and Juans retirement paycheck of $70,000 remains the same, they pay approximately 37% less in taxes and withdraw smaller amounts from their respective IRAs each year.
Tip: To learn more about timing and Social Security, read Viewpoints on Fidelity.com: Should you take Social Security at 62?