How Can I Avoid Owing Taxes
Why Do I Owe Taxes To The IRS & How To Avoid Them Too little withheld from their pay. You can give yourself a raise just by changing your Form W-4 with your employer. Extra income not subject to withholding. Self-employment tax. Difficulty making quarterly estimated taxes. Changes in your tax return.
File Your Taxes With Confidence
While tax season may never be your favorite time of year, you dont have to do it all on your own. Reach out to a;tax Endorsed Local Provider ;in your area to help you sort out your tax situationtax liabilities and all! Get ready to walk into the next season feeling like a tax boss. Get a tax pro today!
Feel like your taxes are simple enough to do them yourself? With Ramsey SmartTax, you can! Ramsey SmartTax makes it easy to take control of your taxes and file your tax return in a matter of minutes. You wont be surprised by hidden fees and you wont have to make sense of confusing tax jargonwhat you see is what you get!
About the author
Ramsey Solutions
Ramsey Solutions has been committed to helping people regain control of their money, build wealth, grow their leadership skills, and enhance their lives through personal development since 1992. Millions of people have used our financial advice through 22 books published by Ramsey Press, as well as two syndicated radio shows and 10 podcasts, which have over 17 million weekly listeners.
Is The Health Insurance That I Get As A Graduate Assistant Or Graduate Intern Taxable
No.; Graduate Assistants and Graduate Interns receive wages for providing teaching or researching services to the University.; They are offered medical and dental insurance coverage through the Connecticut Partnership Plan.; If GAs elect health insurance coverage under this Plan, they will be required to pay premiums based on their elected coverage level.; As of July 1, 2015, the State of Connecticut established a separate Cafeteria Plan within the meaning of IRC Sec 125 exclusively for Graduate Assistants, Fellows, and Interns at UConn, which allows them to use pre-tax wages to pay for health insurance premiums.
Therefore, the premium amounts will be deducted from the GAs paycheck on a bi-weekly basis and will be excluded from their taxable wages for both federal and state income tax purposes.
For more information about the health and dental benefits provided to Graduate Assistants please visit UConns HR website at .
You May Like: How To Appeal Property Taxes Cook County
What Is The Difference Between A W
A W-4 is filled out by employees to provide their employer with their tax ID number , marital status, number of allowances and dependents, and how much tax to withhold with each paycheck. The W-4 is filled out when an employee is first hired or if any changes must be made to filing status or withholding. The W-2 is filled out by employers at the end of the tax year and sent to employees to input on their tax returns.
Where Can I Get Detailed Information About The Amounts Of My Scholarship Tuition And Fees
The best sources of information will generally be your fee bill and award letter.; Your fee bills will reflect the actual payments you made during the calendar year for tuition and fees. Your fee bills will also reflect when any scholarships, grants, or fellowships were received by the University and applied against the cost of your education.
Another form that may be helpful to refer to is Form 1098-T, which is issued by the University to most students during the first month of each year for the preceding calendar year.; The University is required to send a Form 1098-T to most students that paid for qualified educational expenses in the preceding tax year.; Qualified educational expenses include tuition and enrollment fees as well as books, supplies and equipment that are required for your courses. However, the University is not required to prepare Form 1098-T for every student even if they paid qualified educational expenses.; For example, the University does not have to prepare a Form 1098-T for students who are not United States residents for tax purposes, or for students whose qualified education expenses are waived entirely or paid for entirely with scholarships and/or fellowships.
For more information about Form 1098-T, please refer to and;
Don’t Miss: How Much Tax Do You Have To Pay On Stocks
How To Figure Out Your Tax Rate If Youre Not A C Corp
If your business is not a C corporation, that means itâs a flow-through entity, meaning youâll pay the taxes yourself, instead of the business paying them.
Your tax rate will depend on the amount of the businessâ taxable income and your tax filing status.
If youâre single and:
| Your total taxable income is: | Your taxes are: |
|---|
| $164,709.50 plus 37% of any income you made above $612,350 |
Taxability Of Employee Tuition Benefits
ON THIS PAGE:
Tuition Benefits can be taxable at the federal and/or state level, depending upon a number of factors.
Undergraduate tuition benefits are generally not subject to withholding for employees using the tuition benefit for themselves at the federal level. State taxability of undergraduate tuition benefits is determined by your state of residence.
Graduate tuition benefits for employees using the benefit for themselves are taxable at the federal and local level once you exceed $5,250 in graduate benefits for the calendar year. State taxability of graduate benefits is determined by your state of residence.
The following information provides a summary of how our office handles withholding, but does not attempt to supersede the Division of Human Resources Policy 406 nor does it affect any agreements made by the employee with the Division of Human Resources through tuition benefit payment requests in the Online Tuition Benefit Management System. Its important to review the official policies before using the benefit at;. Benefits are subject to change as are regulations governing the taxability of tuition benefits.
Also Check: Where To File Taxes For Free
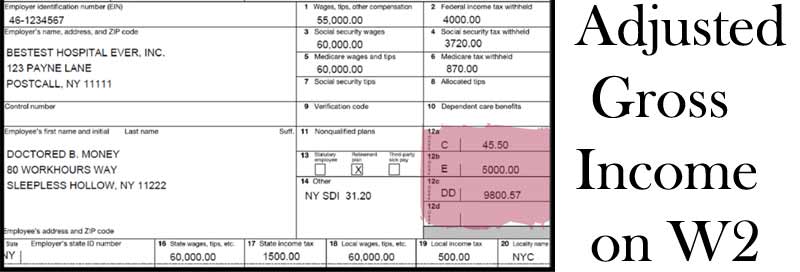
What Is Tax Liabilities On W2
A 20-second summary of how to calculate your tax liability, How to figure out your tax rate if youâre a C corp, How to figure out your tax rate if youâre not a C corp, Reduce your taxes with credits and deductions, The Big List of Small Business Tax Deductions, The Big List of U.S. Small Business Tax Credits, How to Calculate and Pay Estimated Quarterly Taxes, $970 plus 12% of any income you made above $9,700, $4,543.50 plus 22% of any income you made above $39,475, $14,382.50 plus 24% of any income you made above $84,200, $32,748.50 plus 32% of any income you made above $160,725, $46,628.50 plus 35% of any income you made above $204,100, $153,798.50 plus 37% of any income you made above $510,300, $1,940 plus 12% of any income you made above $19,400, $9,086 plus 22% of any income you made above $78,950, $28,765 plus 24% of any income you made above $168,400, $65,497 plus 32% of any income you made above $321,450, $93,257 plus 35% of any income you made above $408,200, $164,709.50 plus 37% of any income you made above $612,350. No pressure, no credit card required. Medicare tax.
To figure out if you are withholding enough federal taxes, follow these steps to estimate your tax liability for 2019: Review last years tax return.
How Capital Gains Are Taxed
When a taxpayer sells an investment, real estate, or any other asset for a gain, that individual owes taxes on the gain.
Assume, for example, that Albert purchases 100 shares of XYZ common stock for $10,000 and sells the securities five years later for $18,000. The $8,000 gain is considered to be the tax base for this taxable event. In this case, the transaction is a long-term capital gain since the stock was held for more than one year.
The tax rate for capital gains can be different from rates for income taxes and other tax calculations. If the tax rate is 10%, the tax liability is $800 and Albert will include this calculation on his individual 1040 tax return.
Read Also: How Much Is New York State Sales Tax
I Won A Contest Or I Was Given A Prize By My Department Why Do I Have To Fill Out Tax Forms
Generally speaking, all prizes and awards are taxable income. This is true regardless of whether the prize is in the form of cash, Husky Bucks or a gift card.; It is the recipients responsibility to report the value of prizes and awards received on his or her tax returns.
As a prerequisite for receiving the prize or award, the University may ask you to complete and sign a;;; Form W-9, Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification. If the recipient properly completes Form W-9, then the University is not required to withhold any taxes on the prize or award.; If the aggregate value of prizes or awards received by any person is less than $600 for a calendar year, then the University has no IRS reporting obligations with respect to those prizes and awards given to that recipient.; If the value of the prize or award is $600 or more, the recipient will receive Form 1099-MISC from the University by January 31st following the close of the calendar year in which the award was received.
If you are not a United States resident for tax purposes, then you will not be able to complete Form W-9.; In this case, the University is required to withhold federal income tax at a rate of 30% on the value of the prize or award and report this event on a Form 1042-S.; An exception exists in very limited circumstances where the student is a resident of a country that has a particular type of tax treaty with the United States.
Who Files Form W
An employer is legally required to send out a W-2 form to every employee to whom they paid a salary, wage, or another form of compensation. This does not include contracted or self-employed workers, who file taxes with different forms. The employer must send the employee the W-2 form on or before Jan. 31 each year, so that the employee has ample time to file income taxes before the deadline .
The 2020 federal income tax filing due date for individuals has been extended from April 15, 2021, to May 17, 2021. Payment of taxes owed can be delayed to the same date without penalty. Your state tax deadline may not be delayed.
If you were affected by the February 2021 snowstorm disaster in Texas, your deadline for filing has been moved to June 15, 2021. If you don’t live in Texas but were affected by the storm, you may still be eligible for the extension.
Employers must also use W-2 forms to report Federal Insurance Contributions Act taxes for their employees throughout the year. By the end of January, employers must file, for the previous year, Form W-2, along with Form W-3, for each employee with the Social Security Administration . The SSA uses the information on these forms to calculate the Social Security benefits to which each worker is entitled.
Tax documents are filed for the previous year. For example, if you receive a W-2 form in January 2021 it reflects your income earned for 2020.
Also Check: Will I Get Any Money Back From My Taxes
Im A Uconn Student And In Response To The Covid
Starting in April 2020, as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, UConn began issuing various prorated cash refunds and/or fee bill credits to students for previous payments made for:
- Education Abroad Housing and Travel Expenses
- University Provided Housing
- Dining Charges
- Parking Permits
Cash refunds and fee bill credits for these specific expenses are not considered taxable refunds for the 2020 tax year.; The reason the refunds and the fee bill credits are not taxable is because housing, travel expenses, meals plans and parking are not qualified educational expenses as defined below.; As such, payments for these expenses are not eligible for an education tax credit.; Therefore, refunds or credits for these expenses are deemed to be a return of your own money used to pay for personal, nondeductible expenses and, thus, would not be characterized as taxable income for the 2020 tax year.
Qualified educational expenses means 1) required tuition and fees that must be paid as a condition of enrollment; and books, supplies and equipment;required;for your courses.; It does not include room and board, travel, insurance or medical expenses including student health fees.
For more information about refunds and fee bill credits issued to UConn students as a result of COVID-19, please click on the following link:
Examples Of Income Tax Liability
Anytime there is a taxable eventthink earning income, making sales or issuing payrollyou rack up tax liabilities.
Like we mentioned above, the;most common type;of tax liability is;earned income. So, for example, lets say you earn $50,000 in gross income in a year and youre a single filer. If you take the standard deduction of $12,400, that leaves you with $37,600 in taxable incomeputting you in the 12% tax bracket. Wondering where we got that percentage? Lets break it down a bit more.
Your taxable incomeyour gross income after deductions and creditsgets divided into tiers that are each taxed at a certain rate.
Below are the federal income tax rates for the 2020 tax year.1
|
Tax rate |
|
$518,401 or more |
So, to continue with our example above, the first $9,875 is taxed at 10% . The second portion of your taxable incomeanything between $9,876 and $40,125is taxed at 12%.;Since you earn less than $40,125, youll subtract the $9,876 from your total taxable income number to see how much of your income falls into that range. That would look like this: $37,600 minus $9,876 equals $27,724. This is the amount that gets taxed at 12% .
Now we know that your tax liability on that income would be $4,314.50found by adding the first bracket at 10% to the second bracket at 12% .
On top of that, lets say you also had a tax bill of $3,000 from the year before that you didnt pay . Your total tax liability would be $7,314.50 .
Recommended Reading: Can You Change Your Taxes After Filing
Why Its Important To Know Your Tax Liability
If you have a regular job, you should have filled out a W-4 form with your employer. Based on that form, your employer withholds a portion of your income to cover your tax liability and sends it to the government on your behalf.
If youre self-employed or own a small business, youll likely be responsible for calculating your own tax liability and sending in quarterly tax payments throughout the year.
Now, if the amount withheld from your paycheck or the amount you send in for the year is less than your total tax liability, youll have to cut Uncle Sam a check for the difference come tax season. If your total withholding or payment amount is higher than your total tax liability, then youll get a refund.
This is where knowing your tax liability is importantyou want to avoid both of those situations. No one wants to owe more taxes when April rolls around, and a refund only means you overpaid for an entire year. Getting your withholding to line up with your income tax liability is the end goal. You want to break even when tax season arrives!
No one wants to owe more taxes when April rolls around, and a refund only means you overpaid for an entire year. Getting your withholding to line up with your income tax liability is the end goal. You want to break even when tax season arrives!
Why Arent Student Health Fees Considered To Be Expenses That Are Required For Enrollment
The term qualified tuition and related expenses refers to those charges that are required for enrollment, attendance or coursework at the University, and do not include optional charges such as room and board or insurance costs.; IRS Publication 970 explicitly states that medical expenses are not qualified tuition and related expenses.; Even though the University requires all students to maintain health insurance, many students are covered by a personal insurance policy or a plan carried by their parents and, therefore, they do not pay the Student Health Fee.
Also Check: Do You Need To Claim Unemployment On Taxes
Examples Of Tax Liability
The most common type of tax liability for Americans is the tax on earned income. Assume, for example, that Anne earns $60,000 in gross income, which is reported on an IRS W-2 form at the end of the year. With a federal tax rate of 22% for that level of income, Anne’s tax liability would be $8,990 based on 2020 tax brackets.
In particular, Anne would owe 10% on the first $9,875 of income, 12% on the next $30,250, and 22% on the last $19,875.
Assume that Anne’s W-4 resulted in her employer withholding $6,500 in federal taxes and that she made a $1,000 tax payment during the year. When Anne files Form 1040, her individual tax return, the remaining tax payment due is the $8,990 tax liability less the $6,500 in withholdings and $1,000 payments, or $1,490.
Due to Hurricane Ida, some residents and business owners in Louisiana and parts of Mississippi, New York, and New Jersey have been granted extensions on their deadlines for filings and payments to the IRS. Most relate to upcoming due dates for quarterly filings and payments. For details, go to IRS “Tax Relief in Disaster Situations” page and click on “2021.”