Certain State And Local Government Workers
State or local government employees, including those working for a public school system, college, or university, may or may not pay Social Security taxes. If they’re covered by both a pension plan and Social Security, then they must make Social Security contributions. But if they’re covered solely by a pension plan, then they dont have to contribute to the Social Security system.
History Of Social Security Tax Rates
The Social Security tax began in 1937. At that time, the employee rate was 1%. It has steadily risen over the years, reaching 3% in 1960 and 5% in 1978. In 1990, the employee portion increased from 6.06 to 6.2% but has held steady ever sincewith the exception of 2011 and 2012.
The Tax Relief, Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization, and Job Creation Act of 2010 reduced the contribution percentage to 4.2% for employees for those years employers were still required to pay the full amount of their contributions.
The tax cap has existed since the inception of the program in 1937 and remained at $3,000 until the Social Security Amendments Act of 1950. It was then raised to $3,600 with expanded benefits and coverage. Additional increases in the tax cap in 1955, 1959, and 1965 were designed to address the difference in benefits between low-wage and high-wage earners.
The Social Security tax policy in the 1970s saw a number of proposed amendments and re-evaluations. The Nixon Administration was paramount in arguing that tax cap increases needed to correlate with changes in the national average wage index in order to address benefit levels for individuals in different tax brackets. The 1972 Social Security Amendments Act had to be revamped due to problems with the benefits formula that caused financing concerns. A 1977 amendment resolved the financial shortfall and established a tax cap increase structure that correlated with average wage increases.
Do I Have To Pay Taxes On Social Security Benefits
Taxpayers who receive Social Security benefits may be required to pay federal income tax depending on their income and filing status. Those with other income, such as wages from a part-time job, interest, dividends, or other retirement income may have to pay tax on up to 85 percent of their Social Security benefits. Most taxpayers whose only source of income is Social Security, however, will typically not pay taxes on their benefits. As always, its helpful to consult with a tax professional to get a better understanding of your tax liabilities, but this brief overview is a good place to start.
Read Also: What Are Tax Lien Properties
Line 2: Earned Income Tax Credit
The amount of the Earned Income Tax Credit you’re entitled goes on line 27 of your 2020 Form 1040 if you qualify for it. You can complete Schedule EIC to determine the amount of your credit.
Tax credits act just like payments you’ve made. They come off your tax obligation dollar for dollar. Some are even refundable, so the IRS will send you any cash that’s left over after erasing what you owe.
You would enter the amount of a nontaxable combat pay election on line 18a as well.
Recovering Social Security Taxes Withheld By Multiple Employers
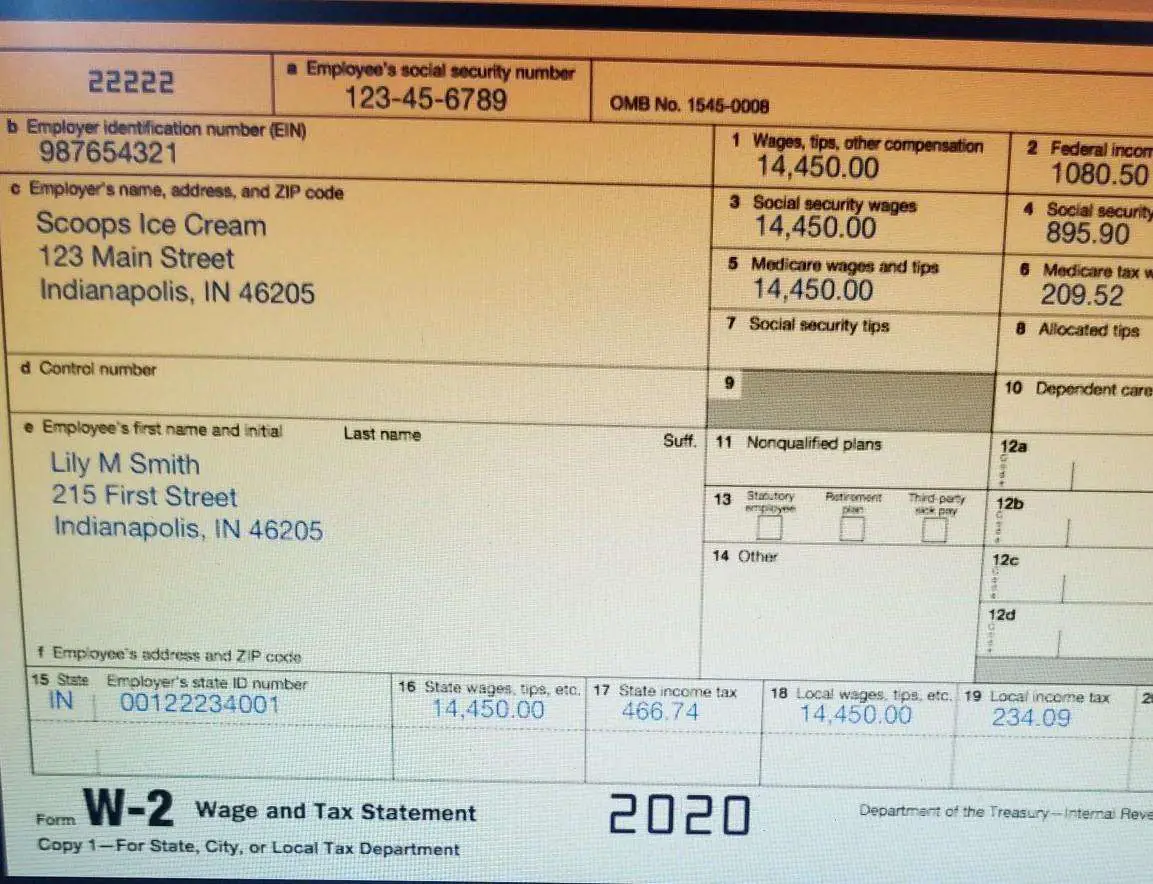
It is not uncommon to find yourself working for more than one company in a given tax year. Employers are obligated to withhold social security taxes from your wages, regardless of the amount withheld by a previous employer. This will often lead to the amount that is withheld to exceed the maximum amount of tax that can be imposed for the year. $7,254.00 is the maximum amount the IRS can withhold from wages in 2014 .. If this total is exceeded when the withholding from two or more employers exceeds the limit, you can recover this income by claiming a credit for a payment of taxes on your tax return for the year.
Don’t Miss: Where’s My Tax Refund Ga
Line 2: Additional Child Tax Credit
Claiming the Additional Child Tax Credit is a two-step process. You must first make sure you qualify by answering the questions in the Instructions for Form 1040. Your initial Child Tax Credit can be reduced by any tax you might owe, but you might be able to claim the balance as an Additional Child Tax Credit by completing and filing Form 8812.
Complete Form 8812 to find out if you qualify and, if so, how much of a credit you’re entitled to. Enter it on line 28 of your 1040.
Other Payroll Tax Items You May Hear About
-
FUTA tax: This stands for Federal Unemployment Tax Act. The tax funds a federal program that provides unemployment benefits to people who lose their jobs. Employees do not pay this tax or have it withheld from their pay. Employers pay it.
-
SUTA tax: The same general idea as FUTA, but the money funds a state program. Employers pay the tax.
-
Self-employment tax: If you work for yourself, you may also have to pay self-employment taxes, which are essentially the full load of Social Security and Medicare taxes. Thats because the IRS imposes a 12.4% Social Security tax and a 2.9% Medicare tax on net earnings. Typically, employees and their employers split that bill, which is why employees have 6.2% and 1.45%, respectively, held from their paychecks. Self-employed people, however, pay the whole thing. A 0.9% additional Medicare tax may also apply if your net earnings from self-employment exceed $200,000 if youre a single filer or $250,000 if youre filing jointly. Because you may not be receiving a traditional paycheck, you may need to file estimated quarterly taxes in lieu of withholdings.
Read Also: How Do I Paper File My Taxes
Social Security Tax And Withholding Calculator
Enter your expected earnings for 2021 :
Social Security Taxes are based on employee wages. There are two components of social security taxes: OASDI and HI. OASDI and HI program. OASDI has been more commonly be known as Federal Insurance Contributions Act . HI has more commonly known as Medicare. For 2017, the OASDI tax rate is set at 6.2% of earnings with a cap at $127,200 . The HI is rate is set at 1.45% and has no earnings cap. Employers must pay a matching amount for each tax component. Self employed persons must pay an amount equal to the sum of both the employeee and employer portions.
Avoiding Social Security Benefit Taxes
You might be able to tweak your spending if your combined income is close to the taxation thresholds listed above to reduce or avoid taxes on your Social Security benefits. Consider cutting back on spending or withdrawing more money from your Roth savings, if you have any, because this money does not count toward your combined income for the year. Charitable donations will also help reduce your combined income because you can write these off on your taxes.
If you’re still working, consider delaying Social Security until you retire. This could help lower your combined income because you stop getting paychecks, which in turn might help you avoid Social Security benefit taxes. It’ll also help boost your Social Security checks when you do finally begin claiming them. But don’t delay your Social Security benefits past age 70. Your checks won’t increase anymore after this, and avoiding Social Security benefit tax isn’t worth giving up all the money your Social Security checks could provide.
Social Security benefit taxes aren’t the easiest thing to understand, but it’s important that you take the time to learn the rules. It can help you make more educated decisions about your Social Security benefits and your retirement savings so you can hold on to more of your hard-earned cash.
Also Check: Where Do I Get Paperwork To File Taxes
One Married Couple’s Tax
The following scenarios illustrate how taking Social Security benefits early versus delaying until age 70 affects the federal taxes of this married couple, who are both age 62.
Scenario 1: Taking benefits at age 62
Michael and Patricia anticipate a pre-tax retirement income of $75,000, consisting of $24,000 from their Social Security benefits and $51,000 in taxable distributions from their IRAs.
Based on their earnings history at age 62, 85% of their Social Security benefits would be taxable.
Assuming no other income and using the standard deduction, Michael and Patricia would owe $5,307 in federal taxes. Their after-tax income is $69,693.
Scenario 2: Delaying benefits until age 70
In the years between their retirement and age 70, Michael and Patricia would need to take additional taxable distributions from their IRAs.
But at age 70, they’d receive $42,240 in Social Security benefits, meaning they’d need only $32,760 in IRA withdrawals, including required minimum distributions .
Using the same assumptions , only 34% of the couple’s Social Security benefits would be taxable, and their federal taxes would total $2,086. Their after-tax income would be $72,914.
In this scenario, their total taxes would be slightly higher in the years before they claim Social Security benefits, but lower taxes after age 70 would offset the initial tax cost in less than 2 years.
Social Security claiming strategies at a glance
Where To Claim Credit For Excess Social Security Withholding
- If you file Form 1040, enter the excess on line 69.
- If you file Form 1040A, include the excess in the total on line 41. Write Excess SST and show the amount of the credit in the space to the left of the line.
- You cannot claim excess social security tax withholding on Form 1040EZ.
If any one employer withheld too much social security due to an error, you cannot claim the excess as a credit against your income tax. Your employer should make an adjustment of the excess for you. If the employer does not make an adjustment, you can use IRS Form 843Claim for Refund and Request for Abatement, to claim a refund.
The following example uses 2013 numbers $7,049.40 Maximum based on 6.2% of $113,700 base
Example: Tom drew wages from of Acme Widget, Inc. from January through March, 2013, and earns $65,000 during that period. From April through the end of the year he works for Best Widgets, Inc. and earns $60,000 during that period. Acme Widget, Inc. withholds $4,030 in social security taxes from the wages it pays Tom , and Best Widgets, Inc. withholds $3,720 in social security taxes from the wages it pays him. When the calendar year ends, a total of $7,750 withheld, which is $700.60 above the $7.049.40 maximum amount for 2013. On his 2013 individual tax return, Tom will be entitled to a credit for a payment of taxes of $700.60.
Table from IRS website 2013
Recommended Reading: What If I File Taxes Late
How The West Taxes Social Security
Nine of the 13 states in the West don’t have income taxes on Social Security. Alaska, Nevada, Washington, and Wyoming don’t have state income taxes at all, and Arizona, California, Hawaii, Idaho, and Oregon have special provisions exempting Social Security benefits from state taxation. That leaves Colorado, Montana, New Mexico, and Utah, which impose taxes on Social Security for some individuals.
If You Want To Cancel Or Delay Your Old Age Security Payments
If you have been receiving Old Age Security for less than 6 months, you can ask us to cancel or delay your first payment. Write to us within 6 months of receiving your first payment.
From the date your request is granted, you have 6 months to repay any amounts that you received and any related benefits you and/or your spouse or common-law partner received.
You can re-apply at a later date and receive an increased Old Age Security pension.
Don’t Miss: How To File Hsa On Taxes
How To Calculate Your Social Security Benefit Taxes
Just because you could owe taxes on up to 50% or 85% of your Social Security benefits doesn’t mean you’ll actually owe taxes on that amount. If you fall into the 50% taxation range, the government says you should owe taxes on the lesser of half of your Social Security benefits or half of the difference between your combined income and the taxation threshold set by the IRS for your tax filing status.
Examples make this easier to understand, so let’s consider an individual who receives $12,000 in Social Security benefits annually and has a combined income of $30,000. You’d calculate the amount they’d owe taxes on this way:
Things get even more complicated if you fall into the 85% taxation range. If our individual had a combined income of $40,000 instead and still received $12,000 in annual Social Security benefits, you would calculate how much they would owe in taxes this way:
The Goal Withhold Just The Right Amount
The goal is to withhold enough taxes that you will be about break even .
Some people like to over-withhold taxes, meaning they pay in more taxes than will be owed, so when they file in April, they get a refund. Paying in more taxes than you owe isnt ideal because you are lending your money to the IRS all year. The IRS does not give you any interest on the money that you are lending them.
On the other hand, if you do not have enough money withheld throughout the year , it is likely that you will be under-withheld and will owe the IRS when you file. When this happens, the IRS can charge you an under-withholding penalty tax. Yikes!
Its best if you get your tax withholding as close as possible to your tax liability. Lets look at a few examples to see how you can do this.
Read Also: When Are Irs Taxes Due
How To Calculate The Tax Withholding Rate
Take the $2,587 of total taxes owed divided by the $50,000 pension amount, and you get 5.2%. At the beginning of the year, Sam and Sara should ask their pension to begin withholding about 5% in federal taxes. If they have not considered this until the middle of the year, they could have 10% in taxes withheld from July through December.
If Sam does not want taxes withheld from his pension, instead, he could make quarterly tax payments of $647 on April 15, June 15, September 15 of the 2020 tax year, and January 15 of the following year.
If You Work More Than One Job
Keep the wage base in mind if you work for more than one employer. If you’ve earned $69,000 from one job and $69,000 from the other, you’ve crossed over the wage base threshold. Neither employer should withhold any further Social Security tax from your payor pay half the 12.4% on your behalfuntil year’s end.
It doesn’t matter that individually, neither job has reached the wage base threshold. The wage base threshold applies to all your earned income. But separate employers might not be aware you’ve collectively reached this limit, so you’ll have to notify both employers they should stop withholding for the time being. However, you can always receive reimbursement of any overpayment when you file your taxes.
These are annual figures, so the Social Security tax starts right back up again on Jan. 1 until you hit the next year’s Social Security wage base.
Also Check: When Do We Start Filing Taxes 2021
Consider Having Taxes Withheld From Your Social Security Benefits
Posted on February 05, 2006 on Timesnews.net, by John Vogt, Columnist
The law states that individuals must pay federal taxes on their Social Security benefits if they have total income of more than $25,000, and married couples must pay federal taxes on total income of more than $32,000. People whose only source of income is Social Security generally dont pay taxes. However, if you have other income, such as a pension, wages, interest, dividends or other taxable income, this added to your benefits could render a portion of your benefits taxable.
For individual tax filers, if your income is between $25,000 and $34,000, you may have to pay tax on up to 50 percent of your benefits if your income is more than $34,000, up to 85 percent of your benefits may be taxable.
For couples filing jointly, if your combined income is between $32,000 and $44,000, you may have to pay tax on up to 50 percent of your benefits if your combined income is more than $44,000, up to 85 percent of your benefits may be taxable.
Although you are not required to have federal taxes withheld from your monthly benefits, you may find it easier than paying quarterly estimated tax payments. If you are interested in taking the easy automatic withholding route to paying taxes, here is what you need to know.
Now for a few more answers to questions which rose during talks in our community over the last month:
How The Math Works
The math works like this:
- If your wages were less than $137,700 in 2020, multiply your earnings by 6.2% to arrive at the amount you and your employer must each pay for a total of 12.4%. If you were self-employed, multiply your earnings up to this limit by 12.4% to calculate the Social Security portion of your self-employment tax.
- If your wages were more than $137,700 in 2020, multiply $137,700 by 6.2% to arrive at the amount you and your employer must each pay. Anything you earned over this threshold is exempt from Social Security tax. You would do the same but multiply by 12.4% if you’re self-employed.
For taxes due in 2021, refer to the Social Security income maximum of $137,700 as you’re filing for the 2020 tax year.
Recommended Reading: What Is Schedule D Tax Form
