Use Your Traditional Or Roth Ira To Invest In Crypto And Other Alts
Whether a Roth or traditional IRA is right for you, both offer considerable advantages over taxable investment accounts. For this reason, many investors have both traditional and Roth IRA accounts.
If youre interested in using tax-advantaged retirement funds to invest in non-traditional assets, a self-directed IRA from Alto may be what youre looking for.
Alto offers two different IRAs, both of which are available as traditional, Roth, or Simplified Employee Pension IRAs:
- Alto IRA makes it easy for accredited and non-accredited investors alike to invest in alternative assets through more than 60 partnerships. Examples include AngelList, Masterworks, Grayscale, Fundr, Vint, and more. You can even bring your own investment deal to the table.
- Alto CryptoIRA® lets you buy, sell, and trade more than 100 different crypto assets with low $10 investment minimums, no monthly account fees, and integration with Coinbaseone of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges in the world.
Ready to start investing with a traditional or Roth self-directed IRA, open an Alto account today!
What Is A Non
A non-deductible IRA is a retirement plan you fund with after-tax dollars. You cant deduct contributions from your income taxes as you would with a traditional IRA. However, your non-deductible contributions grow tax free. Many people turn to these options because their income is too high for the IRS to let them make tax-deductible contributions to a regular IRA. This article will explain all you need to know about a non-deductible IRA and whether one is right for you. A financial advisor can also help guide you in making retirement planning decisions for your situation.
Next Steps To Consider
This information is intended to be educational and is not tailored to the investment needs of any specific investor.
Recently enacted legislation made a number of changes to the rules regarding defined contribution, defined benefit, and/or individual retirement plans and 529 plans. Information herein may refer to or be based on certain rules in effect prior to this legislation and current rules may differ. As always, before making any decisions about your retirement planning or withdrawals, you should consult with your personal tax advisor.
The change in the RMD age requirement from 70½ to 72 only applies to individuals who turn 70½ on or after January 1, 2020. Please speak with your tax advisor regarding the impact of this change on future RMDs.
Fidelity does not provide legal or tax advice. The information herein is general and educational in nature and should not be considered legal or tax advice. Tax laws and regulations are complex and subject to change, which can materially impact investment results. Fidelity cannot guarantee that the information herein is accurate, complete, or timely. Fidelity makes no warranties with regard to such information or results obtained by its use, and disclaims any liability arising out of your use of, or any tax position taken in reliance on, such information. Consult an attorney or tax professional regarding your specific situation.
Fidelity Brokerage Services LLC, Member NYSE, SIPC, 900 Salem Street, Smithfield, RI 02917
Don’t Miss: How To Appeal Property Taxes Cook County
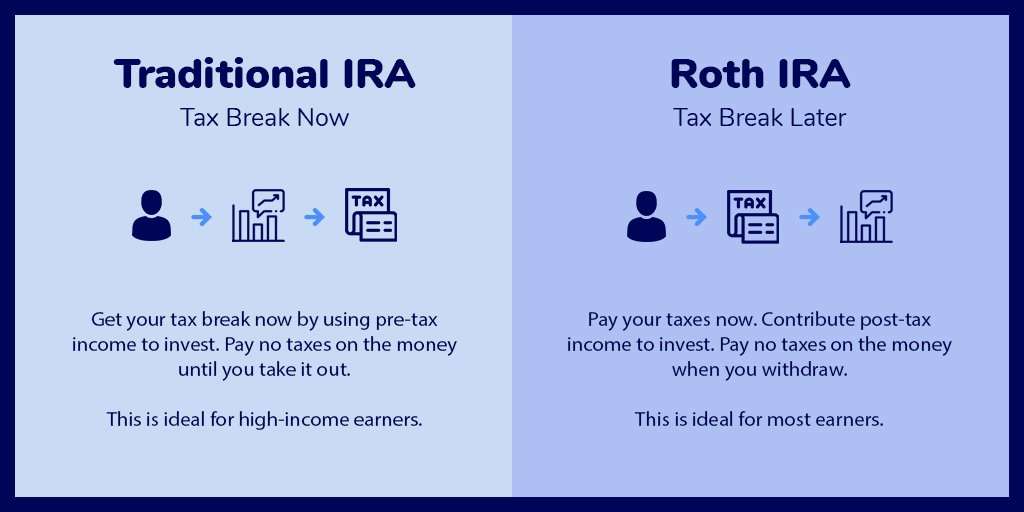
Traditional Vs Roth Ira
The big difference between traditional and Roth IRAs is when you pay taxes.
With a traditional IRA, you contribute pre-tax dollars. While this is better for your immediate cash flow as you’re taking out less from your disposable income now, your money grows tax-deferred and later in retirement you will have to pay income tax on any funds you choose to withdraw. This is a good option if you think you will be in the same or a lower tax bracket when you retire. If you withdraw either your pre-tax contributions or earnings from your traditional IRA before age 59 and a half, you’ll be taxed in addition to incurring a 10% early withdrawal penalty fee.
With a Roth IRA, you pay taxes upfront by contributing after-tax dollars. While this is a bigger hit to your immediate cash flow since you are taking out more from your disposable income now, your money grows tax-free and so in retirement, withdrawals are generally not taxed as long as your account has been open for at least five years. This is a good option if you think you will be in a higher tax bracket when you retire.
You can withdraw your after-tax contributions from your Roth IRA at any age tax- and penalty-free. If you withdraw any earnings you’ve made on your investments before age 59 and a half, you will incur a 10% early withdrawal penalty . Some exceptions to this early withdrawal penalty on Roth IRAs include first-time home purchases, college expenses and birth or adoption expenses.
Convert Earnings On Your After
While converting your after-tax contributions into a Roth account is a good strategy for tax-deferred growth, it bears repeating that the earnings on those contributions are treated differently. Under normal circumstances, they would be taxed. However, you can circumvent that by rolling your after-tax earnings on those contributions into a traditional IRA. You can then convert that IRA to a Roth IRA over time. This allows you to spread the tax hit over a period of years and perhaps avoid being bumped into a higher tax bracket in any one year.
Recommended Reading: Doordash How To File Taxes
How Are After Tax Contributions Taxed
- After-tax contributions are made to retirement plans after taxes have been deducted from the individuals or corporations taxable income.
- The regular after-tax contribution and the Roth 401 after-tax contribution are the two main types of after-tax contributions in the United States.
- The original contribution is not taxed , but the earnings are taxed upon withdrawal in the usual after-tax contribution.
- Some employers offer a Roth 401 after-tax contribution, which means that both the initial investment and the earnings are tax-free when withdrawn after retirement.
A High Percentage Of After
In general, the decision, “To convert, or not to convert,” is one that is driven by the expected change in a clients marginal income tax rate over time. To that end, if marginal tax rates will be lower in the future, it rarely makes sense to pull forward additional income and pay income tax at a higher current tax rate, sooner than otherwise necessary.
That calculus, however, can be changed by the presence of after-tax dollars in an individuals retirement account. Simply put, the greater the percentage of after-tax dollars in the account , the more it makes sense to convert all or a portion of the account now, even if todays marginal tax rate is higher and in some cases, substantially higher than is expected to be the case in the future.
But why? Why pay tax now, at a higher rate, when you can wait and pay taxes in the future, at a lower rate?
In a word earnings.
Recall that while the after-tax dollars in a Traditional IRA are tax-free when distributed, the earnings on those amounts will be taxable in the future. By contrast, if the after-tax amounts are converted to a Roth IRA, the future earnings will be tax-free .
And when a conversion is made from an IRA containing both pre-tax and after-tax dollars, for every $1 of taxable income generated due to the conversion , there is future tax-free growth in the Roth IRA on some amount greater than $1 !
Don’t Miss: Is Doordash A 1099 Job
What Is The Pro
The pro-rata rule is the formula that is used to determine how much of a distribution is taxable when the account owner holds both after-tax and pre-tax dollars in their IRA. For the purposes of the pro-rata rule, the IRS looks at all your SEP, SIMPLE, and Traditional IRAs as if they were one. Even if you have been making after-tax contributions to a separate account for years, and there have been no earnings, you cannot isolate your nontaxable amounts and must take your other IRAs into consideration.
General Guidelines For Investing In A Roth Ira
When does paying taxes now, via investing in a Roth IRA, make more sense than deferring taxes?
Lets look at a few common scenarios:
- If your current marginal tax rate is 15% or less.
- If you expect to have a higher marginal tax rate in the future.
- If you expect to have the same or higher marginal tax rate as you do now after the age of 70½.
- If youre maxing out contributions in all available tax-deferred accounts, leaving you only taxable accounts to invest in.
Beginning Investing Tip
One benefit to a Roth IRA is that youre able to withdrawal contributions any time without taxes or penalty. So, if youre hesitant to start investing because youre afraid youre going to need the cash and dont want to tie it up, Roth IRAs offer more short-term flexibility.
In a sense, they can act as a secondary emergency fund that can provide a bit of peace of mind when youre just starting out.
Also Check: Doordash Income Tax
Results Of Investing In Non Deductible Vs Brokerage Account
Above, you can see the results over time of investing in a non deductible IRA vs a brokerage account.
When she is 65, she has 58k of money in her IRA, of which only 10k is basis . Look at the total and you can see that the account with the TIRA has 14k more due to savings on tax drag over the 25 years. Tax drag is why you would invest in a non deductible IRA vs a brokerage account.
However, once you start taking RMDs at age 72, the money is forced out of a traditional IRA but not a brokerage account. Note at age 90, the TIRA account is still larger due to the continued deferral of taxes in the small non deductible IRA.
What If A Withdrawal Doesn’t Meet These Conditions
Withdrawals that do not meet these conditions are considered nonqualified withdrawals. Nonqualified withdrawals are treated as a prorated return of Roth contributions and earnings. The portion of the distribution that represents earnings will be subject to ordinary income tax and possibly a 10% federal penalty tax for premature distributions. However, the portion of the withdrawal that represents a return of Roth contributions would not be taxed.
Recommended Reading: Pastyeartax
What Are The Key Differences
Knowing the difference between Roth contributions and pretax contributions can help you make confident, informed decisions for your future. Compare the two side-by-side:
|
Pretax: Pay taxes later |
Roth: Pay taxes now |
|---|---|
|
Take home more pay today in exchange for paying taxes on your account when you retire. |
Take home less pay today in exchange for not having to pay taxes on your account when you retire.* |
|
Pay no taxes now on the money you invest, which lowers your taxable income right away. |
Pay taxes now on the money you invest so you can enjoy a tax break later.* |
|
You may pay a penalty if you begin withdrawing money before age 59½. |
You may pay a penalty if you begin withdrawing money before age 59½.You may pay taxes if you withdraw money before it’s been in your account for five years. |
|
In retirement, youll pay taxes on the money you invested and on the earnings. |
In retirement, you wont pay taxes on the money you invested or on the earnings.* |
If your employer matches your Roth contributions, the employer match is considered a pretax contribution. Youll have to pay taxes on that portion when its withdrawn.
Your Qualified Plan Account
The administrator for your qualified retirement plan is responsible for keeping track of which portion of your balance is attributed to after-tax assets and which to pretax assets. However, it helps if you check your statements periodically to ensure that the tabulations match what you think they should be. This will allow you to clarify possible discrepancies with the plan administrator.
Recommended Reading: Doordash Driver 1099
Doesnt Always Make Sense To Pay No Taxes
Making use of your deductions and exemptions in retirement are very important. A married couple in 2019 could have at least $24,400 in income and pay no-taxes. This is because the current standard deduction is $24,400 in 2019 for a married couple filing a joint tax return. Current tax rules also state that if you are in the 10% or 12% tax bracket, long-term capital gains are taxed at 0%! For retirees that have multiple types of accounts the first few years of retirement offer an unbelievable opportunity to take advantage of the lower tax brackets that you may experience compared to when you were working. Below are a few examples of situations in which you should be taking full advantage of these potential lower tax brackets in retirement:
Can I Roll Over Just The After
No, you cant take a distribution of only the after-tax amounts and leave the rest in the plan. Any partial distribution from the plan must include some of the pretax amounts. Notice 2014-54 doesnt change the requirement that each plan distribution must include a proportional share of the pretax and after-tax amounts in the account. To roll over all of your after-tax contributions to a Roth IRA, you could take a full distribution , and directly roll over:
- pretax amounts to a traditional IRA or another eligible retirement plan, and
- after-tax amounts to a Roth IRA.
Read Also: How To Pay Doordash Tax
Tax Tips To Help You Manage Retirement More Effectively
One goal of tax planning is to reduce your taxable income and your effective tax rate. There are a number of tax strategies to consider:
The tax landscape changes frequently as rates, limits and thresholds adjust, and provisions are introduced or expire. An Ameriprise financial advisor, working with your tax professional, can recommend tax-efficient strategies that are customized to your individual situation, whether your assets are still growing or are already generating retirement income.
Related information
Or, request an appointment online to speak with an advisor.
There’s a sense of confidence that comes from feeling in control of your finances – and working with a financial advisor can help you get there. Please share your experience and tell your friends and family about me.
Background and qualification information is available at FINRA’s BrokerCheck website.
Be Sure Your Ira Rollover Is Tax Free
getty
Though the rollover is the most frequent IRA transaction, most people do only a few rollovers during their lifetimes. Because of this inexperience, mistakes are made and people pay unnecessary taxes and penalties on their retirement nest eggs.
There are more than 30 types of rollovers, though taxpayers often know them by different names. A conversion of a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA, for example, is a rollover.
A rollover done correctly is tax free.
But an attempted rollover done incorrectly usually is included in gross income and taxed as ordinary income, except for any portion that was after-tax or nondeductible contributions. There also might be a 10% early distribution penalty added if youre under age 59½. Plus, there could be a 6% penalty for making an excess contribution to an IRA.
Fortunately, we know the most likely rollover mistakes and how you can avoid them.
The 60-day rollover trap. The most frequent rollovers are to move money from a 401 plan to an IRA or from one IRA custodian to another.
The best way to do these rollovers is to have the custodians handle the transfers. But some people want to use the 60-day rule that allows them to take a distribution from an IRA or 401 and deposit the money in another retirement account within 60 days. When done correctly and within the 60-day deadline, this is a tax-free rollover.
But there are tricks and traps in the 60-day rollover.
Read Also: Plasma Donation Earnings
How Much Does Contributing To An Ira Reduce Taxes
You can put up to $6,000 in an individual retirement account and avoid paying income tax on it. If a worker in the 24 percent tax bracket contributes the maximum amount to this account, his federal income tax payment will be reduced by $1,440. The money will not be subject to income tax until it is removed from the account. Because IRA contributions arent due until April, you can throw in an IRA contribution when calculating your taxes to see how much money you can save if you put some money into an IRA.
Taxes On Earnings From After
After-tax contributions to a 401 or other workplace retirement plan get a different tax treatment than their earnings. Since you’ve already paid taxes on the contributions, those withdrawals are tax-free in retirement. But the IRS considers the earnings to be pre-taxso they would be treated as pre-tax and you would owe income tax when you withdraw the earnings from the plan.
Earnings in Roth IRAs, however, aren’t subject to income tax as long as all withdrawals from the account are qualified withdrawals. So rolling after-tax money from a workplace plan to a Roth IRA means you can avoid taxes on any future earnings.
Recommended Reading: Efstatus.taxact.com 2019
