Payroll Tax Penalties Can Be Severe
There really aren’t too many opportunities for reducing your exposure to payroll taxes. If you hire employees and pay them any kind of compensation, it’s a given that you’re going to have some payroll tax liabilities.It is unwise to try and avoid employment tax liability by classifying your workers as independent contractors. The IRS, the Department of Labor and their state counterparts are aggressively targeting employers to uncover misclassification, and the penalties are severe.
Perhaps your biggest opportunity for realizing any kind of real savings is to make sure you tend to each of your obligations and avoid getting hit with penalties. Many of the potential payroll tax penalties are the same ones you’ll find when you’re dealing with other types of taxes. For example, there are both criminal and civil penalties for failing to timely file payroll tax returns or to timely deposit taxes you owe.
There are, however, a couple of penalties of which you should be particularly mindful as you deal with your payroll tax obligations:
100 percent penalty. The biggest risk you face in administering your payroll tax obligations is that you can be held personally liable for all income and FICA taxes that you willfully either fail to withhold from your employees’ wages or fail to pay to the IRS and your state tax agencies.
In some cases, a reckless disregard of obvious facts will suffice to show willfulness.
Federal Payroll Tax Rates
Following is a summary of the federal 2021 payroll tax changes including Social Security, Medicare, Unemployment Tax, Minimum Wage, 401 limits, and more.
Social Security / Medicare
The wage base increases to $142,800 for Social Security and remains UNLIMITED for Medicare. For Social Security, the tax rate is 6.20% for both employers and employees. . For Medicare, the rate remains unchanged at 1.45% for both employers and employees.
Additional Medicare Tax
A 0.9% additional Medicare tax must be withheld from an individuals wages paid in excess of $200,000 in a calendar year. There is no employer match for the additional Medicare tax.
The wage base remains at $7,000.
The effective tax rate for 2021 is 0.6%.
The federal minimum wage rate per hour for 2020 is $7.25, effective 7/24/09.
Earnings Under Social Security
A social security beneficiary under full retirement age can earn $18,960 before benefits are reduced. For every $2 a person under full retirement age earns over $18,960, $1 is withheld from benefits. In the year an employee reaches full retirement age, $1 in benefits will be withheld for each $3 they earn above $50,520 until the month the employee reaches full retirement age. Once an employee reaches full retirement age or older, their benefits are not reduced regardless of how much they earn.
401 Plan Limits
SIMPLE Plan Limits
Electronic Federal Tax Payment System
Forms W-4, I-9 and W-9
Filing of Form W-2 and 1099
Health Benefits W-2 Reporting
Preventing And Correcting Payroll Tax Mistakes
According to SMB CEO, payroll taxes can be a potential minefield for small businesses. As the largest source of uncollected payroll taxes, small businesses are also under greater scrutiny from the Internal Revenue Service .
While most agencies, including the IRS, will likely work with a business thats made an honest mistake, if theres a willful pattern of errors or overdue amounts, the response tends to be less generous.
Sometimes a mistake is caused by something in your payroll setup. Learn more here.
Don’t Miss: Doordash 1099 Nec
Difference Between Payroll Tax And Income Tax
Payroll tax and income tax are similar concepts because both taxes are based on an employees wages or salary. However, while these terms are used interchangeably, they are different. Since employers are responsible for withholding, reporting, and paying taxes, they need to understand the differences between payroll and income tax to achieve maximum payroll tax compliance.
The payroll tax system usually refers to taxes for Medicare and Social Security that are withheld at essentially a flat rate from employee pay, with a portion also paid by the employer. Income tax is a more complex system because of taxing money earned from sources other than work and employing deductions, exemptions, and credits. Income taxes are mainly used for funding defense and national security programs.
Income taxes are withheld from an employees pay based on projected annual tax. They are deducted from employee wages or salary, based on a Form W-4 that the employee files, showing marital status, a number of exemptions for dependents and other allowances, and any additional amount an employee wants to be withheld. An employee does not have to have tax withheld for all dependents and can add any desired amount to the withholding.
How The Payroll Process Identifies Tax Addresses
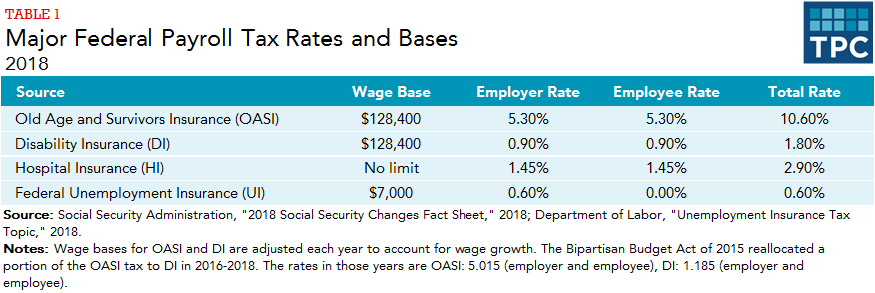
Before the payroll process can begin calculatingtaxes, it has to determine each person’s resident and work defaulttax addresses.
When you perform a payroll run, the process:
Uses the following hierarchy todetermine the person’s work tax addresses.
|
Address source |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Overrides assignment, location address override,and location address |
Use Working at Home on the Employment task. For further info, see Hire an Employee in the HelpCenter. |
|
|
Assignment-level location override |
Overrides location address override and locationaddress |
Use Work Tax Address on the Employment task. |
|
Location override address |
Use the Locations task to define an address of Location override type. |
|
|
Location address |
Use the Locations task to define the main address. |
Uses the following hierarchy todetermine their resident tax address.
|
Address Type |
|---|
Determines the related withholdingstatus and any additional info from the Tax Withholding card.
Based on this info, extracts therelevant regional tax data from the Vertex database.
Calculates the taxes.
Your tax calculations are also impacted by the following.
Wage basis rules determine thetaxable income
For further info, see Tax WageBasis Rules for the US in the Help Center.
Payroll run type
|
How it works |
|
|---|---|
|
Regular |
If the supplemental earnings element run type isset to process separately or pay separately, these elements tax atthe supplemental rate, otherwise they tax at the W-4 rate. |
|
Supplemental |
All earnings are taxed at the supplemental rate. |
Colorado
Recommended Reading: Is Donating Plasma Taxable
Choose Your Calculation Method
Once youve gathered all the W-4 and payroll information you need to calculate withholding tax, you need to choose a calculation method. There are two methods you can choose from:
- The Wage Bracket Method: The wage bracket method of calculating withholding tax is the simpler of the two methods. Youll use the IRS income tax withholding tables to find each employees wage range. The instructions and tables can be found in IRS Publication 15-T.
- The Percentage Method: The percentage method is more complex and instructions are also included in IRS Publication 15-T. The instructions are different based on whether you use an automated payroll system or a manual payroll system. The worksheet walks you through the calculation, including determining the employees wage amount, accounting for tax credits, and calculating the final amount to withhold.
Overview Of Tax Returns And Deposits
Employers have the responsibility to file employment-related tax returns and deposit employment taxes according to set deadlines. If they fail to do so, they may be subject to failure to file and failure to pay penalties. What’s more, “responsible persons” in the company who fail to deposit trust fund taxesamounts withheld from employees’ paychecksmay be subject to a 100% personal liability. This trust fund recovery penalty is triggered when a person with the authority to make payment decisions willfully fails to deposit the taxes. The possibility of these penalties means employers must get things right.
Don’t Miss: Reverse Ein Lookup Irs
What Is Withholding Tax How Does A Withholding Tax Work
A withholding tax is an income tax that a payer remits on a payee’s behalf . The payer deducts, or withholds, the tax from the payee’s income.
Here’s a breakdown of the taxes that might come out of your paycheck.
-
Social Security tax: 6.2%. Frequently labeled as OASDI , this tax typically is withheld on the first $137,700 of your wages in 2020 . Paying this tax is how you earn credits for Social Security benefits later.
»MORE:See what the maximum monthly Social Security benefit is this year
-
Medicare tax: 1.45%. Sometimes referred to as the hospital insurance tax, this pays for health insurance for people who are 65 or older, younger people with disabilities and people with certain conditions. Employers typically have to withhold an extra 0.9% on money you earn over $200,000.
-
Federal income tax. This is income tax your employer withholds from your pay and sends to the IRS on your behalf. The amount largely depends on what you put on your W-4.
-
State tax: This is state income tax withheld from your pay and sent to the state by your employer on your behalf. The amount depends on where you work, where you live and other factors, such as your W-4 .
-
Local income or wage tax: Your city or county may also have an income tax. This money might go toward such expenses as the bus system or emergency services.
See what else you can do for your business
-
Learn about coronavirus relief options for small businesses and the self-employed.
|
Employer pays |
What Is Federal Payroll Tax
Every business owner looks for different ways to grow their business. However, while doing this one of the important things that they must do is complying with the tax aspects. They must handle all the activities about their employee payroll properly. Maintaining the payroll system properly is primarily necessary. While doing this, they must accurately handle the federal payroll tax. This can help to maintain the accounting better.
You May Like: How Much Will A Roth Ira Reduce My Taxes
New Hire Reporting Requirements
All employers in the states of New Jersey and Pennsylvania are required to report basic information about employees who are newly hired, rehired, and returning to work after separation of employment or leave of absence, temporary employees, and contracted entities. Employers must report this information within 20 days at www.njcsesp.com and www.cwds.pa.gov. Failure to report a new employee could result in a fine up to $25 per violation. For further information, contact us or call the State of NJ at 1-877-654-4737 or PA at 1-888-PA-HIRES.
Basic employee information which must be provided:
Employees name Employees social security number Employees date of hire and birth Employers name and address Employers federal identification number
For further information contact us or call the State of New Jersey at 1-877-654-4737 or Pennsylvania at 1-888-724-4737 .
What Is The Federal Insurance Contributions Act
As an employer, you have federal payroll tax responsibilities that include withholding taxes from your employees wages and paying an employers contribution to Social Security and Medicare taxes under the Federal Insurance Contributions Act .
The Federal Insurance Contributions Act is the federal law requiring employers to withhold Social Security and Medicare taxes from their employees wages. In addition to withholding these taxes from their employees wages, employers must also match their employees withholdings with an employer portion for the Social Security tax and Medicare tax.
Each paycheck, employers are required to withhold the following three taxes from their employees wages: Social Security, Medicare, andan additional 0.9 percent Medicare surtax for employees earning over $200,000.
FICA taxes fund the two federal programs that provide benefits for retired workers and the disabled Social Security and Medicare. These two federal programs were introduced to provide Americans with savings for the end of their work careers, to provide for Americans with a disabling injury unable to earn an income, to provide for Americans unable to ever work during their lives, and to provide medical care for the elderly. Prior to Social Security being introduced in the 1930s, and Medicare in the 1960s, the federal government had no mandated programs to help provide for these Americans.
Don’t Miss: Appeal Cook County Taxes
What If Your Pay Period Is Not In This Guide
This guide contains the most common pay periods: weekly, biweekly , semi-monthly, and monthly. If you have unusual pay periods, such as daily , or 10, 13, or 22 pay periods a year, go to the Guide T4008, Payroll Deductions Supplementary Tables, or the Payroll Deductions Online Calculator to determine tax deductions.
What Is A Payroll Tax

A payroll tax is a percentage withheld from an employee’s pay by an employer who pays it to the government on the employee’s behalf. The tax is based on wages, salaries, and tips paid to employees. Federal payroll taxes are deducted directly from the employee’s earnings and paid to the Internal Revenue Service .
You May Like: Tax Preparation License
Explanation Of Claim Codes
Claim code 0
This code represents no claim amount. If the federal claim code is 0 because the employee is a non-resident, the provincial claim code must also be 0. This code may also be used if the employee indicated they have more than one employer or payer at the same time and have entered 0 on the front page of Form TD1 for 2022.
Claim codes 1 to 10
The claim code amounts do not appear on either the federal or the provincial TD1 form.
You match the “Total claim amount” reported on your employee’s or pensioner’s TD1 forms with the appropriate claim codes. Then, you look up the tax for the employee’s pay under the claim code in the federal and provincial tax tables for the pay period.
Indexing of claim codes amounts
The credits that apply to each federal and provincial claim code have been automatically changed in the tax tables by the indexing factor for the current year. If your employee did not complete the federal and provincial TD1 forms for 2022, you continue to deduct income tax using the same claim code that you used last year.
Chart 3 2022 Federal claim codes| Total claim amount |
|---|
| E |
Maintaining Payroll Tax Records And Avoiding Penalties
Once you’ve paid over your payroll taxes and filed any necessary returns and reports, your last significant obligation is to maintain records that substantiate the payroll taxes you paid.
For federal tax purposes, you must retain records for at least four years after the due date of the return or the date the taxes were paid, whichever is later. A similar record-keeping requirement exists in each state, with varying time periods.
Types of records. There is no particular form prescribed for properly retaining records. However, the records must be kept in a manner that will enable the IRS and your state tax authorities to ascertain whether any tax liability has been incurred and, if so, the extent of that liability.
The types of information you should retain include:
- the name, address, and Social Security number of each employee
- the total amount and date of each payment of compensation
- the period of service covered by each payment of compensation
- the portion of each payment of compensation that constituted taxable wages
- copies of each employee’s withholding exemption certificate
- dates and amounts of tax deposits you made
- copies of returns you filed
- copies of any undeliverable Form W-2
IRS inspection. You’re obligated to keep all your required records at convenient and safe locations that are accessible to IRS representatives. And, your records must be available at all times for IRS inspections.
Recommended Reading: Plasma Donation Tax
Interplay Between The Erc And Ppp
Eligible businesses can claim the ERC on wages that are not used toward payroll costs when applying for PPP forgiveness. Businesses should analyze their payroll costs in order to obtain 100% PPP loan forgiveness and maximize their ERC. The PPP loan forgiveness program allows businesses to report up to 40% of qualified non-payroll costs on the forgiveness application.
The ERC is claimed on the taxpayers timely filed IRS Form 941. In order to claim the ERC for previously filed quarters, Form 941-X must be filed. An eligible business may reduce its federal employment tax deposits by the allowable ERC amount. If the ERC exceeds the remaining federal employment tax deposits for that quarter, the business may file Form 7200 to claim an advance refund. The ERC provides an unprecedented opportunity for eligible businesses and organizations to offset revenue declines during the COVID-19 pandemic. Every business should evaluate whether it is eligible for the ERC.
What Do Payroll Taxes Fund
In the United States, payroll taxes are social security and medicare taxes. This means federal payroll taxes are used to fund social security and medicare programs across the country. This is intended to ensure a basic level of medical care and social support in old age, disability and various other cases.
Note, in the United States payment of medicare and social security taxes does not negate the need for comprehensive health insurance.
Don’t Miss: Have My Taxes Been Accepted
What Is Payroll Withholding
You pay salaries, bonuses, commissions, vacation pay or tips to your employees. You offer them certain taxable benefits, such as personal use of a vehicle or allowances. You are also required to withhold and remit payroll deductions. Employers are responsible for deducting the following four amounts: federal income tax.
Federal Payroll Return Requirements
Along with actually depositing your federal payroll taxes, you also have an obligation to file periodic returns that show how you computed your tax liabilities. As is true for deposits, the returns you must file for your income and FICA taxes are different from the returns you file for your FUTA taxes.
Recommended Reading: Irs Employee Lookup
