Additional Resources From The Irs
You should generally increase your withholding if:
- You hold more than one job at a time or you and your spouse both have jobs or
- You have income from sources other than jobs or self-employment that is not subject to withholding ).
If you do not make adjustments to your withholding for these situations, you will likely owe additional tax when filing your tax return, and you may owe penalties. For income from sources other than jobs, you can pay estimated tax instead of having extra withholding.
You should generally decrease your withholding if:
- You are eligible for income tax credits such as the child tax credit or credit for other dependents , and/or
- You are eligible for deductions other than the basic standard deduction, such as itemized deductions, the deduction for IRA contributions, or the deduction for student loan interest ).
The IRS encourages everyone to use their Tax Withholding Estimator to perform a paycheck checkup, and help you make sure you have the right amount of tax withheld from your paycheck. The ISC recommends using this tool beforecompleting your W-4 in Workday.
There are several reasons to check your withholding:
Estimate Your Effective Tax Rate
Important Note: Equitable has designed this material to serve as an informational and educational resource it does not offer or constitute investment advice and makes no direct or indirect recommendation regarding the appropriateness of any particular product or investment-related option. Your unique needs, goals and circumstances require and deserve the individualized attention of your financial professional.
Tax-efficient distributions refers to options where a portion of the distribution is a return of cost basis and thus excludable from taxes.
What is a variable annuity?
A variable annuity is a tax-deferred financial product designed to allow investors to invest for growth potential and provide income for retirement or other long-term life goals. In essence, an annuity is a contractual agreement in which payment are made to an insurance company, which agrees to pay out income or a lump sum amount at a later date. Variable annuities are subject to market risk including loss of principal. There are fees and charges associated with a variable annuity contract, which include, but are not limited to, operations charges, sales and withdrawal charges and administrative fees. The withdrawal charge declines from 6% to 3% over five years for Investment Edge®. Earnings are taxable as ordinary income when distributed and may be subject to an additional 10% federal tax if withdrawn before age 59 ½.
Not every contract is available through the same selling broker/dealer.
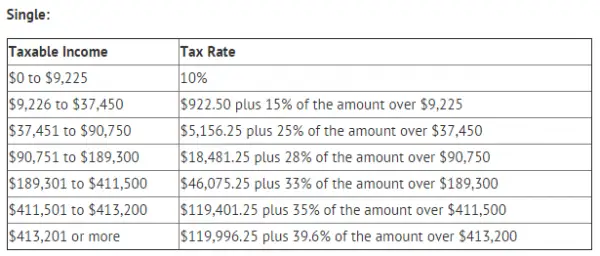
How To Determine Your Tax Bracket
As mentioned above, determining your tax bracket hinges on two things: filing status and taxable income. Here are some useful details:
The IRS recognizes five different filing statuses:
- Single Filing Unmarried, legally separated and divorced individuals all qualify all single.
- A married couple agrees to combine income and deduct the allowable expenses.
- A married couple files separate tax returns to keep an individual income lower. This is beneficial in certain situations like repaying student loans under an income-driven repayment plan.
- Head of Household Unmarried individuals who paid more than half the cost of keeping up a home for the year and have a qualifying person living with them in their home for more than half the year.
- Qualifying Widow A widow can file jointly in the year of their spouses death. A qualifying widow has a dependent child and can use the joint tax rates and the highest deduction amount for the next two years after their spouses death.
Read Also: Property Tax Protest Harris County
Is A Pay Stub The Same As A Paycheck
Although paychecks and pay stubs are generally provided together, they are not one in the same. A paycheck is a directive to a financial institution that approves the transfer of funds from the employer to the employee. A pay stub, on the other hand, has no monetary value and is simply an explanatory document.
Chapter 4 Option 1 Tax Formula
This option determines the federal and provincial or territorial tax deductions on salary, wages, taxable benefits, pension income, commissions, and other periodic payments. This option can also be used to calculate the tax on a bonus or other non-periodic payment.
We use Option 1, with the exception of a few factors, to determine the tax deduction amounts in the publications T4032, Payroll Deductions Tables, and T4008, Payroll Deductions Supplementary Tables, for each province and territory, as well as for Canada beyond the limits of any province or territory and outside Canada.
Outline of Option 1
In general, the Option 1 steps are as follows:
Don’t Miss: Tsc-ind
How Does The Cpp Work
You will contribute towards the CPP from your employment earnings from age 18 to 70. The CPP Investment Board then invests CPP funds. Once you retire, you will then receive a monthly retirement pension that is equal to a certain percentage of your lifetime average earnings.
The base CPP benefit provides a monthly pension of up to 25% of your contributory earnings for the best 40 years of earnings. With changes enhancing CPP contributions, the monthly pension amount can rise to up to 33.33% of your contributory earnings. This pension amount counts as income, and so you must pay income tax on your CPP benefit.
The earliest that you can receive your retirement pension is when you turn 60 years of age. If you have a disability, you may receive the CPP disability benefit if you are under the age of 65, or the CPP post-retirement disability benefit if you have already started to receive your CPP retirement pension.
If you start receiving your pension between 60 and before you turn 65, your pension amount will be permanently reduced at a rate of 0.6% for every month before age 65, for a maximum reduction of 36%.
Every month after age 65 permanently increases your pension amount by 0.7%, up to a maximum of 42% when you turn 70.
How To Calculate Federal Income Tax
This article was co-authored by Cassandra Lenfert, CPA, CFP®. Cassandra Lenfert is a Certified Public Accountant and a Certified Financial Planner in Colorado. She advises clients nationwide through her tax firm, Cassandra Lenfert, CPA, LLC. With over 15 years of tax, accounting, and personal finance experience, Cassandra specializes in working with individuals and small businesses on proactive tax planning to help them keep more money to reach their goals. She received her BA in Accounting from the University of Southern Indiana in 2006.There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 94,081 times.
Sometimes, you might need to predict how much you will owe in taxes before the end of a calendar year. It might seem intimidating to try to calculate your federal income tax, but it’s not necessarily as complicated as you might think. You’ll need to know the amount of the wages you’ve earned for the year, along with any deductions and tax credits you may be eligible for. However, keep in mind that it’s still helpful to consult a tax professional if you have any questions or concerns.
Read Also: Doordash Tax Deduction
Calculating Your Tax Refund
Whether or not you get a tax refund depends on the amount of taxes you paid during the year. This is because they were withheld from your paycheck. However, it also depends on your tax liability and whether or not you received any refundable tax credits.
When you file your tax return, if the amount of taxes you owe is less than the amount that was withheld from your paycheck during the course of the year, you will receive a refund for the difference. This is the most common reason people receive a tax refund.
If you paid no taxes during the year and owe no taxes, but are eligible for one or more refundable tax credits, you will also receive a refund equal to the refundable amount of the credits.
Will I Get A 2021 Tax Refund
Typically, you receive a tax refund after filing your federal tax return if you pay more tax during the year than you actually owe. This most commonly occurs if too much is withheld from your paychecks. Another scenario that could result in a refund is if you receive a refundable tax credit that is larger than the amount you owe. Life events, tax law changes, and many other factors change your taxes from year to year. Use our tax refund calculator to find out if you can expect a refund for 2021 .
Read Also: Will A Roth Ira Reduce My Taxes
Anything Else That You Need To Know For 2021
To be eligible for the full solar investment tax credit, you must be able to pass one of two tests to ascertain when the construction started:
Physical Work Test, which means proof that the construction was underway as explained by the Internal Revenue Service Five Percent Test, that shows that you had sustained at least 5% of the total project costs before the deadline. These are permits, site assessments, plans, environmental impact studies all of these expenditures are eligible under this test.
As a result, many businesses are now pushing forward on some projects, especially those who are funded by Power Purchase Agreements . This is due to the fact that the step-down percentage can negatively affect financing by as much as 10 percent for projects that are pushed back till 2023 or beyond.
It goes without saying that the ITC can be a helpful financial incentive for many commercial businesses implementing solar energy . Unfortunately though, not everyone is eligible for it. Thats why we have compiled the following useful FAQ guide to the solar federal ITC.
Payroll Deductions Online Calculator
For verifying your payroll deductions, you can use the Payroll Deductions Online Calculator . The calculator includes an option to help you make sure that enough Canada Pension Plan contributions and employment insurance premiums have been withheld for full-year employees.
It calculates payroll deductions for the most common pay periods, as well as the applicable province or territory. The calculation is based on exact salary figures.
Effective January 1, 2022, PDOC users may choose to calculate personal tax credits by either entering the Total Claim value manually or by selecting the corresponding claim code.
PDOC is available at canada.ca/pdoc.
Also Check: Tax Deductible Home Improvements
Formula To Calculate Annual Taxable Income
A = Projected annual taxable income= + B1 HD F1If the result is negative, A = $0.
S1 = This is a set of two numbers: the number of total pay periods divided by the applicable number of the current pay period, as in the chart below. Also, see the information under Special situations.
Table 5.1 S1 Examples| 24/24 | 12/12 |
I = Gross pay for the pay period. This includes overtime earned and paid in the same pay period, pension income, qualified pension income, and taxable benefits, plus IYTD, but does not include amounts in factor B.
F = Payroll deductions for the pay period for employee contributions to a registered pension plan for current and past services, a registered retirement savings plan , or a retirement compensation arrangement plus FYTD.
Note
For full details, see the description under Option 1.
F2 = Alimony or maintenance payments required by a legal document dated before May 1, 1997, to be deducted at source from the employees salary for the pay period plus F2YTD. The legal document could be a garnishment or a similar order of a court or competent tribunal.
Note
For full details, see the description under Option 1.
U1 = Union dues for the pay period, plus U1YTD.
B1 = Year-to-date non-periodic payments such as bonuses, retroactive pay increases, vacation pay when vacation is not taken, and accumulated overtime. Since tax on a current non-periodic payment is calculated separately, do not include the current non-periodic payment in calculating A.
Note
Calculating Employer Payroll Taxes

In addition to the taxes you withhold from an employees pay, you as the employer are responsible for paying certain payroll taxes as well:
- FICA Matching: You are required to match the employees FICA tax withholding, which means your company will pay 6.2% tax for Social Security and 1.45% tax for Medicare. Using our example employee, you as the employer would pay a matching $129.17 for Social Security and $30.21 in Medicare, resulting in a $159.38 FICA obligation.
- Unemployment Taxes: You will also have to pay federal and state unemployment tax. Unemployment taxes are paid only by the employer, not the employee.
- Federal Unemployment Tax is 6.0% of the first $7,000 in wages you pay each employee each year. If your company is subject to state unemployment, you can receive a federal tax rate credit of up to 5.4%, which makes the effective tax rate 0.6%. Once an employee earns more than $7,000 in a calendar year, you stop paying FUTA for that employee in that tax year. Federal Unemployment: $2,083.33 x 0.6% = $12.50
- State Unemployment Tax varies by state. Consult with your states Department of Labor or Unemployment Revenue for tax rates, wage bases, and filing requirements. For this example, we will assume the employee has not yet been paid $7,000 year-to-date. We will use Floridas unemployment tax rate of 2.7%. State Unemployment: $2,083.33 x 2.7% = $56.25
You May Like: Tsc-ind Ct
Your Federal Tax Refund
Many people probably file their federal income tax returns hoping for a tax refund. Typically, you pay your federal income tax throughout the year, either through the payroll withholdings your employer takes out of your paycheck or through estimated tax payments if youre self-employed. Pay too little, and you could owe Uncle Sam on Tax Day. Pay too much, and you could get an IRS refund of the amount you overpaid.
Tax calculators can help you estimate your tax refund, but when will your federal refund arrive? The IRS says most people can expect their refunds in less than 21 days, and e-filing and choosing to have your refund directly deposited into your financial account can be the fastest way to get your refund. Direct deposit is not only faster than waiting for a paper check to arrive in the mail, its more secure direct deposit means you wont have your refund check get lost in the mail.
If you want to track your refund, you can use the IRSWheres My Refund? tool.
Is This Guide For You
Use this guide if you are a payroll software provider or a company which develops its own in-house payroll solution.
This guide has the formulas you need to determine federal, provincial , and territorial income taxes, Canada Pension Plan contributions, and employment insurance premium deductions. The formulas also let you calculate payroll deductions for income sources such as commission, pension, bonuses, and retroactive pay increases.
The formulas used in this guide to calculate statutory deductions have been approved for purposes of the Income Tax Act, the Canada Pension Plan, and the Employment Insurance Act, as well as their related regulations and any amendments proposed to these acts.
For more information on income amounts that are subject to payroll deductions, see the publication T4001, Employers Guide Payroll Deductions and Remittances.
If you have questions about the formulas in this guide, contact your tax services office or tax centre. For the address and telephone numbers of your tax services office or tax centre, see the listings in the government section of your telephone book or visit canada.ca/taxes.
Don’t Miss: Taxes On Plasma Donation
How To Calculate Federal Tax Credits
Unlike adjustments and deductions, which apply to your income, tax credits apply to your tax liability, which means the amount of tax that you owe.
For example, if you calculate that you have tax liability of $1,000 based on your taxable income and your tax bracket, and you are eligible for a tax credit of $200, that would reduce your liability to $800. In other words, you would only owe $800 to the federal government.
Tax credits are only awarded in certain circumstances, however. Some credits are refundable, which means you can receive payment for them even if you dont owe any income tax. By contrast, nonrefundable tax credits can reduce your liability no lower than zero. The list below describes the most common federal income tax credits.
- The Earned Income Tax Credit is a refundable credit for taxpayers with income below a certain level. The 2021 credit can be up to $6,728 for taxpayers with three or more children, or lower amounts for taxpayers with two, one or no children.
- The Child and Dependent Care Credit is a nonrefundable credit of up to $4,000 or $8,000 related to childcare expenses incurred while working or looking for work.
- The Adoption Credit is a nonrefundable credit equal to certain expenses related to the adoption of a child.
- The American Opportunity Tax Credit is a partially refundable credit of up to $2,500 per year for enrollment fees, tuition, course materials and other qualified expenses for your first four years of post-secondary education.
