A Roth Ira Can Be A Great Way To Save For Retirement Since The Accounts Have No Required Minimum Distributions And You Withdraw The Money Tax
Tax-free income is a dream of every taxpayer. And if you save in a Roth account, its a reality. Roths are the youngsters of the retirement savings world. The Roth IRA, named after the late Delaware Sen. William Roth, became a savings option in 1998, followed by the Roth 401 in 2006. Creating a tax-free stream of income is a powerful retirement tool. These accounts offer big benefits, but the rules for Roths can be complex.
Here are 11 things you must know about utilizing a Roth IRA as part of your retirement planning.
Can You Get Around Roth Ira Income Limits
A backdoor Roth IRA may be one way for you to avoid Roth IRA income limits. A backdoor Roth IRA is an IRA funded from a traditional IRA through a “backdoor” route that skirts Roth IRA upper-income limits. This type of backdoor account is funded with savings that are converted or transferred into it from a traditional IRA.
Want to read more content like this? for The Balances newsletter for daily insights, analysis, and financial tips, all delivered straight to your inbox every morning!
General Comments About Roth Iras
1.1 A Roth Individual Retirement Arrangement is an individual retirement plan established pursuant to section 408A of the United States Internal Revenue Code of 1986 . For U.S. income tax purposes, contributions to a Roth IRA are not deductible from income, earnings and gains are exempt from tax, and distributions are generally not included in income. For an overview of Roth IRAs see Internal Revenue Service Publications 590-A, Contributions to Individual Retirement Arrangements and 590-B, Distributions from Individual Retirement Arrangements .
1.2 For Canadian income tax purposes, the income accrued in a Roth IRA is generally taxable on a current, annual basis. An individual resident in Canada who owns a Roth IRA must determine:
- the legal characterization of the Roth IRA and resulting taxation of income accrued in and distributions from the Roth IRA pursuant to the Act and
- whether the relief provided in the Canada-U.S. Treaty for Roth IRAs is available .
Don’t Miss: Is Freetaxusa Legit
Topic No 309 Roth Ira Contributions
A Roth individual retirement arrangement is a tax-favored account or annuity set up in the United States solely for the benefit of you and your beneficiaries. You can contribute to a Roth IRA if you have taxable compensation and your modified adjusted gross income is within certain limitations. Regardless of the amount of your adjusted gross income, you may be able to convert amounts from either a traditional, SEP, or SIMPLE IRA into a Roth IRA. You also may be able to roll over amounts from a qualified retirement plan to a Roth IRA. Contributions made to a Roth IRA may be able to be recharacterized as a contribution made directly to another type of IRA. However, conversions after 2017 from a traditional, SEP, or SIMPLE IRA to a Roth IRA may not be recharacterized. In addition, amounts rolled over after 2017 from a qualified retirement plan to a Roth IRA may not be recharacterized. Refer to Topic No. 413 for information about rollovers. A Roth IRA differs from a traditional IRA in that contributions aren’t deductible and qualified distributions aren’t included in income.
A Traditional Ira Is An

A Traditional IRA is an Individual Retirement Account to which you can contribute pre-tax or after-tax dollars, giving you immediate tax benefits if your contributions are tax-deductible. With a Traditional IRA, your money can grow tax-deferred, but youll pay ordinary income tax on your withdrawals, and you must start taking distributions after age 72. Unlike with a Roth IRA, there are no income limitations to open a Traditional IRA. It may be a good option for those who expect to be in the same or lower tax bracket in the future.
Recommended Reading: Taxes Grieved
If You’re Young Your Income Is Likely To Rise
Generally speaking, the younger you are, the greater the chance that your income will be higher when you retire than it is now. For instance, if you’re under age 30, it’s possible that your income and spending during retirement will be significantly higher than they are now, at the beginning of your career. And the greater the difference between your income now and your income in retirement, the more advantageous a Roth account can be.
What Are Your Plans For Reducing Your Tax Burden Now And In The Future
Schedule a consultation with an Equity Trust Account Executive to discuss your tax-advantaged account options for you or your business.
Can I roll over a 401 account into a self-directed IRA?
Yes. A self-directed IRA gives you the ability to diversify your portfolio with additional investments that are permitted by the IRS, in a tax-free or tax-deferred environment.
Am I eligible to make a contribution? How much can I contribute?
The IRS publishes maximum IRA contribution limits and catch up provisions each year. Summaries for each type of contribution can be found on Contribution Limits.
Also Check: Does Doordash Do Taxes
How Do You Report An Excess Ira Contribution
You don’t have to report it to the government if you accidentally exceed your IRA contribution limit, and you catch your error before you file your tax return for that tax year. You can simply contact the financial institution that holds your IRA and ask them to withdraw the excess amount. But you’ll have to claim the income on your 1099 if your contributions were invested and gained value while in your IRA. This could come with a 10% penalty tax if you’re younger than age 59 1/2.
Is Charles Schwab Good For Roth Ira
Charles Schwab Schwab shines all around, and it remains an excellent choice for a Roth IRA. Schwab charges nothing for stock and ETF trades, while options trades cost $0.65 per contract. And mutual fund investors can find something to love in the broker’s offering of more than 4,000 no-load, no-transaction-fee funds.
You May Like: Doordash On Taxes
Do I Qualify To Make An Ira Or Roth Ira Contribution
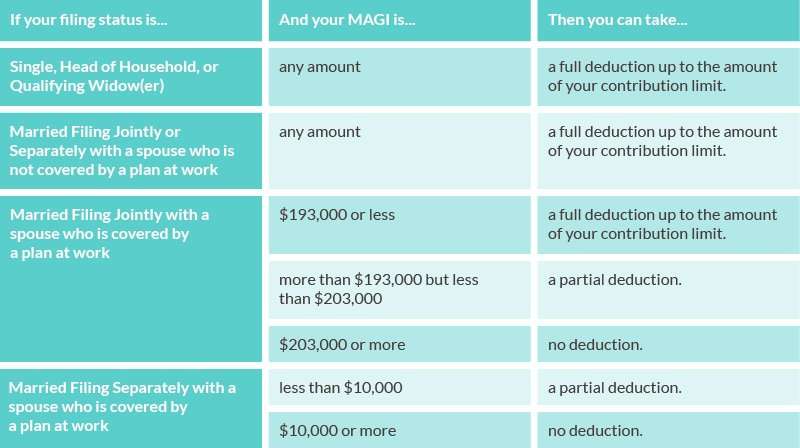
You can contribute to a traditional or Roth IRA whether or not you participate in another retirement plan through your employer or business. However, you might not be able to deduct all of your Traditional IRA contributions if you or your spouse participates in another retirement plan at work. Roth IRA contributions might be limited if your income exceeds a certain level.
Income Rules differ between a Traditional and Roth IRAs:
Traditional IRA: Anyone can make an IRA contribution, but it may not be deductible. Below are the income limits in place for 2022:
-
If married and you and your spouse are not covered by an employer sponsored plan:
-
Full deduction regardless of income
If you are covered by an employer sponsored plan:
Fully deductible if Modified Adjusted Gross Income is less than $68,000 or $109,000
Partially deductible if Modified Adjusted Gross Income is between $68,000 and $78,000 or $109,000 and $129,000
No deduction if Modified Adjusted Gross Income is over $78,000 or $129,000
If you are covered by an employer sponsored plan and your spouse isnt:
Fully deductible if Modified Adjusted Gross Income is less than $204,000
Partially deductible if Modified Adjusted Gross Income is between $204,000 and $214,000
No deduction if Modified Adjusted Gross Income is over $214,000
Roth IRA: You cannot make contributions if your Modified Adjusted Gross Income for 2022 exceed the limits shown below:
What is the benefit of a Roth conversion?
Roth Ira Contribution Limits
Anyone of any age can contribute to a Roth IRA, but the annual contribution cannot exceed their earned income. Let’s say that Henry and Henrietta, a married couple filing jointly, have a combined MAGI of $175,000. Both earn $87,500 a year, and both have Roth IRAs. In 2021, they can each contribute the maximum amount of $6,000 to their accounts, for a total of $12,000.
Couples with highly disparate incomes might be tempted to add the higher-earning spouse’s name to a Roth account to increase the amount they can contribute. Unfortunately, IRS rules prevent you from maintaining joint Roth IRAsthat’s why the word “individual” is in the account name. However, you may accomplish your goal of contributing larger sums if your spouse establishes their own IRA, whether they work or not.
How can this happen? To illustrate, let’s go back to our hypothetical couple. Let’s say that Henrietta is the primary breadwinner, pulling in $170,000 a year while Henry runs the house, earning $5,000 annually. Henrietta can contribute to both her own IRA and to Henry’s, up to the $12,000 maximum. In this case, they each have their own IRAs, but one spouse funds both of them.
A couple must file a joint tax return for the spousal IRA to work, and the contributing partner must have enough earned income to cover both contributions.
Recommended Reading: How Much Does H& r Charge
What Is A Roth Ira
A Roth IRA, which stands for a Roth individual retirement arrangement, is a tax-advantaged investment meant for retirement. With a Roth IRA account, you can contribute after-tax funds into the account and withdraw it at retirement age , tax-free.
Roth IRAs are a flexible and liquid investment where you can choose to withdraw any of your funds after at least five years of opening your account without worrying about taxes. However, note that if you withdraw your funds earlier than planned, any profit or growth resulting from the investment will be taxed, and you may have to pay a penalty.
Having access to a Roth IRA is vital for the 33% of private industry workers who have no access to employer-provided retirement plans. It is a convenient way to plan and save for their expenses later in life. Even workers with workplace-based plans can take advantage of this investment, as it can serve as an extra retirement cushion.
How Do I Fix A Roth Ira Contribution
4.8/5There are several ways to correct an excess contribution to an IRA.
Similarly one may ask, how do I withdraw a Roth IRA contribution?
To cancel a Roth IRA contribution, you have to take out what you contributed plus any earnings accrued while the money was in the Roth IRA. If you lost money, you only have to withdraw your contribution minus the losses.
Similarly, do I have to report my Roth IRA contributions? Contributions to a Roth IRA aren’t deductible , but qualified distributions or distributions that are a return of contributions aren’t subject to tax. To be a Roth IRA, the account or annuity must be designated as a Roth IRA when it’s set up.
Simply so, can I recharacterize a Roth contribution in 2019?
As such, you can still contribute to a Roth IRA for 2017 up until Tuesday, April 17, 2018 . You can also contribute to a Roth IRA for 2018 any time in 2018 and up to the tax return date in 2019. However, Roth IRA contributions are phased out if you earn too much money.
How does the IRS know if you contribute to a Roth IRA?
IRS Form 5498 is sent by IRA custodians to the IRS every year. This form has listed the amount you contributed to your IRA and/or Roth IRA, as well as some other information such as amount of rollover contributions and the fair market value of your assets.
Also Check: How To Protest Property Tax Harris County
Taxation Of Roth Iras In Canada
1.3 A Roth IRA does not enjoy the income tax deferral benefits afforded under the Act to Canadian registered plans and traditional IRAs. As a result, the income accrued in a Roth IRA is generally taxable in Canada on a current, annual basis.
1.4 Under the Code, a Roth IRA can take the form of a custodial account, a trust, or an annuity or endowment contract. To determine the Canadian income taxation of a particular Roth IRA, it is necessary to identify its legal characterization. This is fact specific and will depend on the terms of the arrangement. Although providing an exhaustive list of potentially applicable taxing provisions would be impractical, ¶1.5 to 1.7 provide general comments that are intended to assist readers in determining the legal characterization and resulting taxation in Canada of a particular Roth IRA. A tax professional may provide assistance in this regard.
Custodial account
1.5 A Roth IRA that is a custodial account can take various forms. Typically, the CRA understands that a Roth IRA custodial account is a savings or investment account at a financial institution, brokerage firm, or mutual fund company. A common characteristic of such a Roth IRA is that the owner of the Roth IRA is considered to own the assets held in the account by the custodian. In such a case, one must look to the nature of the income and gains derived from the specific assets held in the account to determine the Canadian income tax treatment.
Example 1
Example 2
Trust
If You Earn Too Much To Contribute
In order to contribute to a Roth IRA, you must have employment compensation, and there are also income limits. If your income is over the IRS limits, the only way you can take advantage of a Roth IRA is by converting money from an existing retirement account, such as a traditional IRA.3 There is a cost, though. You’ll generally need to pay taxes on what you convert, but any after-tax contributions to a traditional account will not be taxable. The rules are complex, so if you have made after-tax contributions to a traditional account and you’re interested in conversion, be sure to consult with a tax advisor.
To learn more, read Viewpoints on Fidelity.com: Do you earn too much for a Roth IRA?
Don’t Miss: Pastyeartax Reviews
What Are The Rules For Obtaining A Roth Ira Account
According to Troy Segal, single filers earning more than $144,000 can’t be part of the Roth IRA.
Married couples earning more than $214,000 filing jointly, can’t contribute to Roth IRA.
People who opened their Roth IRA accounts can deposit $6,000 annually.
If you are 50 or older, you may deposit a maximum of $7,000 a year.
Make sure your IRA account is different than a regular savings bank account.
There’s no robust coverage for IRA accounts. Nevertheless, you still have some options.
“The Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. still offers insurance protection up to $250,000 for traditional or Roth IRA accounts, but account balances are combined rather than viewed individually,” Troy Segal reported.
How Can I Estimate My Tax Liability On An Ira Conversion
Remember, all of the traditional IRAs you own are considered one traditional IRA for tax purposes, not matter how many accounts you have. Your tax liability is based on 2 things: the taxable income generated by the conversion and your applicable tax rate.
To figure out how much of a conversion from a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA may be taxable, youll need to know the types of contributions you made to any one of your traditional IRAs . There are 2 types of contributions.
Estimating the taxable income from a conversion is straightforward if youve never made nondeductible contributions to any traditional IRA. If that is the case, whatever amount you convert will all be taxable income.
Keep state taxes in mind too. A Roth IRA conversion is a taxable event. If your state has an income tax, the conversion will generally be treated as taxable income by your state as well as by the federal government.
Also Check: Is Plasma Donation Taxable Income
Amount Of Roth Ira Contributions For 2022
How much you can contribute to your Roth IRA will depend on your filing status and your MAGI. Review the maximum contribution limits below to determine how much you can give based on your situation.
- Filing StatusModified Adjusted Gross Income Maximum Annual Contribution
-
Up to the limit imposed for 2022:
- $6,000 for under 50 years old
- $7,000 for those 50 and over
and you lived with your spouse at any time during the year
and you lived with your spouse at any time during the year
< $129,000
Up to the limit imposed for 2022:
Single, head of household, separately and you did not live with your spouse at any time during the year
$129,000 but < $144,000
$144,000
Zero
Roth Ira Taxable Distribution Examples
Here are some examples of how Roth IRA distributions may be taxable. First, say that youre 55 years old and opening a Roth IRA for the first time. You make an initial contribution of $7,000 . You also convert $70,000 that you have saved in a traditional IRA to your Roth account.
Once you turn 59½, you decide to withdraw your Roth IRA savings. Because youve reached the age milestone, you wont owe an early withdrawal penalty on the distribution. However, if you havent yet reached the five-year mark since opening the account, then you would have to pay tax on the earnings portion of your withdrawal. This doesnt include earnings from converted amounts, though, since you would have paid taxes on those at the time of the conversion.
Converted amounts may escape income tax, but they still can be subject to the 10% early withdrawal penalty.
Now assume that you opened your Roth IRA at age 54 instead. You made the same initial contribution and rolled over the same amount. Then at age 59½, you withdraw all of the money in your account. The account has been open for five years at this point, so you escape paying any income tax on earnings. You also avoid the 10% early withdrawal penalty, because you meet the age requirement.
Recommended Reading: Does Doordash Tax You
