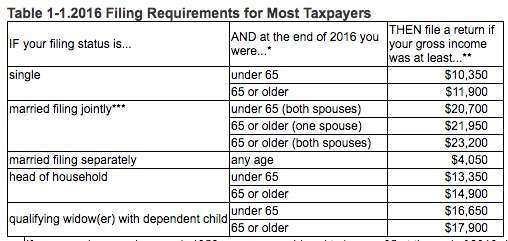
How Much Tax Do I Need To Pay In Australia
How much income tax you pay will depend on your personal situation and criteria such as your residency status, taxable income, and the tax rate and bracket that apply to you based on Australian Taxation Office requirements. If you are an Australian resident for tax purposes with a tax file number, you may be eligible for a tax-free threshold of $18,200. According to the Australian Governments Treasury, the largest amounts of income tax in Australia are paid by high income individuals. OECD figures show Australians had a net average tax rate of 23.6% in a recent year, which was slightly lower than the OECD average at the time of 25.9%.
Adjusting Tax Bracket Parameters
Congress decides how many tax brackets there are and what the rates will be for each bracket. It’s the Internal Revenue Service’s job to adjust income thresholds to keep pace with inflation.
For example, in the 2021 tax year, for a married couple filing a joint return,
- The 10% bracket applied to the first $19,900 in taxable income.
- The 12% bracket went up to $8,050.
- The 22% bracket went up to $172,750, and so on.
- The top rate, 37%, applied when taxable income topped $628,300.
For single taxpayers, the thresholds were lower. The IRS announces the tax brackets for each year before that year begins.
Remember, with TurboTax, we’ll ask you simple questions about your life and help you fill out all the right tax forms. With TurboTax you can be confident your taxes are done right, from simple to complex tax returns, no matter what your situation.
We also offer a handy Tax Bracket Calculator to help you easily identify your tax bracket.
How We Make Money
Bankrate.com is an independent, advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. Bankrate is compensated in exchange for featured placement of sponsored products and services, or your clicking on links posted on this website. This compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear. Bankrate.com does not include all companies or all available products.
Bankrate, LLC NMLS ID# 1427381 |NMLS Consumer AccessBR Tech Services, Inc. NMLS ID #1743443 |NMLS Consumer Access
You May Like: How To Get My Doordash Tax Form
Consequences Of Withdrawing Rrsp Money Early
The biggest consequence of prematurely withdrawing RRSP funds early is certainly the tax penalties. Your tax bill can really suffer, especially if you withdraw a large amount, since in addition to the withdrawal taxes youll also be paying combined income tax.
But another huge consequence of withdrawing funds early? The simple truth is that youre just robbing your future self of money youll need in retirement. An RRSP works its magic when longterm, steady contributions allow funds to grow thanks to the magic of compounding. Withdrawing funds is a huge setback for the progress of your retirement fund, especially since you wont be able to recuperate the contribution room youve lost through early withdrawal.
Keep in mind that withdrawing multiple smaller amounts in a short period of time in an attempt to avoid the higher withholding tax comes with certain disadvantages as well. Your financial institution could still deduct the amount of withholding tax that would apply to the total amount. For example, if you want to withdraw $10,000 but you split it into four monthly withdrawals of $2,500 to avoid the 20% tax withholding rate, your financial institution could still withhold 20% on the last withdrawal if they notice the pattern. The point is: Withdrawals are generally not advisable and you should be exploring other possible avenues before you touch your RRSP.
What Are Some Other Inflation Adjustments I Should Look Out For
We mentioned earlier that the IRSâs tax brackets apply to your taxable income, which is what you get when you apply certain adjustments and deductions to your revenue.
One other way that the IRS helps guard against bracket creep is by adjusting the values of deductions to keep up with inflation. Here are the main ones you should look out for:
Read Also: Doordash Paying Taxes
What Are The 2021 Federal Income Tax Brackets
Which tax bracket you fall into in the United States also depends on your filing status. Here are the 2021 tax brackets according to the IRS. These brackets apply to your 2022 tax filing.
Itâs broken into the four most common filing statuses: individual single filers, married individuals filing jointly, heads of households, and married individuals filing separately:
| Tax rate |
|---|
| $523,600+ |
Tax Rules Are Based On Your Business Structure
Because tax rules differ based on business structure, its important that small businesses consult with an attorney and accountant to determine how their businesses should be classified.
Your business will likely fall into one of four structures:
- Sole proprietorship: A sole proprietor is someone who owns an unincorporated business by him or herself.
- Partnership: In a partnership, individuals are taxed on their share of business net income.
- Limited liability corporation: LLCs are taxed on their share of business net income. Multiple-member LLC’s are taxed as partnerships.
- Corporation: Corporations are the only entities that pay federal taxes on their own based on net earnings. They are currently taxed at a flat 21% rate.
Read Also: Car Sales Tax In North Carolina
Tax As % Of Income : 000
Did you know that you may not pay the same tax rate onall your income? The higher rates only apply to theupper portions of your income.
TaxAct Costs Less: 20% less or File for less claim based on comparison with TurboTax federal pricing for paid consumer online 1040 filing products on 10/5/2021. $15 less claim based on comparison with TurboTax federal pricing for paid consumer online 1040 filing products on 10/5/2021.
Maximum Refund Guarantee: If an error in our software causes you to receive a smaller refund or larger tax liability than you receive using the same data with another tax preparation product, we will pay you the difference in the refund or liability up to $100,000 and refund the applicable software fees you paid us. Find out more about our Maximum Refund Guarantee.
$100k Accuracy Guarantee: If you pay an IRS or state penalty or interest because of a TaxAct calculation error, we’ll pay you the difference in the refund or liability up to $100,000. This guarantee applies only to errors contained in our software it doesn’t apply to errors the customer makes. Find out more about our $100k Accuracy Guarantee.
Satisfaction Guarantee: If you are not 100% satisfied with any TaxAct product, you may stop using the product prior to printing or filing your return. We are unable to refund fees after you print or e-file your return.
Over 80 Million Returns Filed: Based on e-filed federal returns through TaxAct Consumer and TaxAct Professional software since 2000.
A Simplified Example Of Brackets
For a simple example of how progressive taxation works, say the government has three , set up like this:
- 10%: $0 to $20,000
- 20%: $20,001 to $50,000
- 30%: $50,001 and above
Now, let’s say your taxable income is $75,000. This would put you in the 30% bracket.
- The first $20,000 of that would be taxed at 10%, or $2,000.
- The next $30,000 would be taxed at 20%, or $6,000.
- The final $25,000 of your income would be taxed at 30%, or $7,500.
- Your total tax would be: $2,000 + $6,000 + $7,500 = $15,500.
In this scenario, even though you’re in the 30% bracket, you would actually pay only about 20.7% of your income in taxes.
Don’t Miss: Pastyeartax Com Reviews
Calculating Taxable Income Using Exemptions And Deductions
Of course, calculating how much you owe in taxes is not quite that simple. For starters, federal tax rates apply only to taxable income. This is different than your total income, otherwise known as gross income. Taxable income is always lower than gross income since the U.S. allows taxpayers to deduct certain income from their gross income to determine taxable income.
To calculate taxable income, you begin by making certain adjustments from gross income to arrive at adjusted gross income . Once you have calculated adjusted gross income, you can subtract any deductions for which you qualify to arrive at taxable income.
Note that there are no longer personal exemptions at the federal level. Prior to 2018, taxpayers could claim a personal exemption, which lowered taxable income. The tax plan signed in late 2017 eliminated the personal exemption, though.
Deductions are somewhat more complicated. Many taxpayers claim the standard deduction, which varies depending on filing status, as shown in the table below.
What Taxes Must Self
Like other taxpayers, self-employed individuals will file an annual return. However, they will usually make tax payments every quarter. Tax payments usually fall into two buckets: self-employment tax and income tax on profits from the business.
For 2022, the self-employment tax rate on net income up to $147,000 is 15.3%. This percentage is broken down into 12.4% for Social Security tax and 2.9% for Medicare tax. Also, if your net earnings exceed $250,000 and youre , $125,000 if youre married but filing separately or $200,000 for all other taxpayers, you must pay an extra 0.9% Medicare tax.
Keep in mind, usually only 92.35% of your net earnings are subject to self-employment tax.
Don’t Miss: Does Doordash Take Taxes Out Of Your Check
How Much Child Tax Credit Can I Get
When it comes to how much child tax credit you can get, theres no single fixed amount as payments are made up from different elements. How much you get depends on your income, the number of children youre responsible for, along with whether any of your children have a disability.
Child tax credit rates for the 2022-23 tax year
| Element |
|---|
Australian Income Tax Calculator
Employment income: Employment income frequency
Enter an income to view the result
The estimated tax on your taxable income is0
| Your income after tax & Medicare levy: |
|---|
| Your marginal tax rate: |
This means for an annual income of you pay:
| No tax on income between $1 – $18,200 | $0 |
| 19c for every dollar between $18,201 – | 0 |
| 32.5c for every dollar between – | 0 |
| 37c for every dollar between – $180,000 | 0 |
| c for every dollar over $180,000 | 0 |
- The rates are for Australian residents.
- Your marginal tax rate does not include the Medicare levy, which is calculated separately.
- The Medicare levy is calculated as 2% of taxable income for most taxpayers. The Medicare levy in this calculator is based on individual rates and does not take into account family income or dependent children.
- The calculations do not include the Medicare Levy Surcharge , an additional levy on individuals and families with higher incomes who do not have private health insurance.
- These calculations do not take into account any tax rebates or tax offsets you may be entitled to.
- For the 2016-17 financial year, the marginal tax rate for incomes over $180,000 includes the Temporary Budget Repair Levy of 2%.
- In most cases, your employer will deduct the income tax from your wages and pay it to the ATO.
- 2020-2021 pre-budget reflects the tax rates prior to those announced in the Budget in October 2020.
Recommended Reading: License To Do Taxes
What Are Qualified Business Income Deductions
You must pay a self-employment tax on your net earnings. This means that you can subtract qualified business income deductions from the mix to lower the amount youre taxed. The IRS allows self-employed individuals and small business owners to deduct up to 20% on their pass-through income.
For example, you can deduct 50% of your self-employment tax on your income taxes. This means that if your Schedule SE states you owe $4,000 of self-employment tax, you can deduct $2,000 on your Form 1040.
How Much Is The Self
For 2020, the SE tax rate is 15.3% of earnings from your business. That’s a combined Social Security tax rate of 12.4 % and a Medicare tax rate of 2.9%.
For Social Security tax, you pay it on up to a maximum wage base of $137,700. You don’t have to pay Social Security tax on any additional income above this threshold. However, this threshold has been increasing and is likely to continue creeping up in future years.
However, for Medicare, there is no wage base. All your income is subject to the 2.9% Medicare tax.
So, if you’re self-employed with net income less than $137,700, you’d pay SE tax of 15.3% , plus ordinary income tax.
Remember that your future Social Security benefits get reduced if you don’t claim all of your self-employment income.
You May Like: How Much Do You Pay In Taxes For Doordash
What Happens If You Over
While it may seem like a good idea to invest as much money as you can for your retirement, there are consequences to over-contributing. The Canada Revenue Agency limits the investment you can make to your RRSP due to the tax savings. Which means you may have to pay for going over the limit.
If you do go over your contribution on accident, the CRA gives you a free pass for over-contributing $2,000. However, once you use that cushion up, it will cost you for over-contributing. Once you pass the $2,000, they charge a 1% fee every month for your overpayment. Once you withdraw the extra funds, there is no more penalty. However, there are also consequences for early withdrawal .
Do I Need To Do A Tax Return
Generally, if youve met any of these criteria, you need to determine if you may need to lodge an Australian tax return: you have obtained a tax file number , you have worked in or for the benefit of Australia, you have received Australian-sourced investment income that is not subject to withholding. Once youve met one of these criteria, you must either lodge a tax return or advise the ATO one is not required through a non-lodgment advice form every financial year. You should seek professional tax advice if you are unsure whether you should lodge a return.
- Read the full story by Ursula Lepporoli, KPMG
Recommended Reading: Do Doordash Take Out Taxes
You Dont Need To Pay Estimated Taxes If
Youâre an employee If youâre an employee, your employer should be withholding quarterly taxes on your behalf. That being said, sometimes they can get the amounts wrongâfill out Form-W4 and give it to your employer to make sure that theyâre deducting the correct amount.
Youâre a special case If you meet three very specific conditions below, then you donât have to pay estimated quarterly taxes:
- You did not owe any taxes in the previous tax year, and did not have to file a tax return
- You were a US citizen or resident for the entire year
- Your tax year was 12 months long
If you donât meet all of the criteria for non-payment above, then youâre one of the many Americans who needs to pay estimated quarterly taxesâread on!
Want More Tips On Tax
Use our comprehensive tax guides to stay on top of your finances this tax season.
Alison Banney is the banking and superannuation editor at Finder. She has written about finance for over 8 years, with her work featured on sites including Yahoo Finance, Money Magazine and Dynamic Business. She has previously worked at Westpac, and has written for several other major banks including Greater Bank, bcu and Gateway Credit Union. Alison has a Bachelor of Communications from Newcastle University, with a double major in Journalism and Public Relations. She has ASIC RG146 compliance certificates for Financial Advice, Securities and Managed Investments and Superannuation. Outside of Finder, youll likely find her somewhere near the ocean.
-
Do you run a small business? This guide will show you where to begin and what you need to know at tax time, including what you changes have been implemented as a result of COVID-19.
You May Like: Do You Get Taxed For Donating Plasma
Reporting Unemployment Benefits At The Federal Level
For most states, you will receive Form 1099-G in the mail from your state unemployment office. Find out how you can obtain your 1099-G. On Form 1099-G:
- In Box 1, you will see the total amount of unemployment benefits you received.
- In Box 4, you will see the amount of federal income tax that was withheld.
- In Box 11, you will see the amount of state income tax that was withheld.
You dont need to attach Form 1099-G to your Form 1040 or Form 1040-SR.
In certain states, you will not automatically be mailed a Form 1099-G. You will have to access your Form 1099-G online through your unemployment portal or call your state unemployment office to request that they mail your Form 1099-G. In other states, you will only be mailed a Form 1099-G if you selected that as your delivery preference.
| States that will not mail 1099-Gs at all | Connecticut, Indiana, Missouri, New Jersey, New York, and Wisconsin |
| States that will mail or electronically deliver 1099-Gs depending on which option you opted-into | Florida, Illinois, Michigan, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Tennessee, and Utah |
If you received Form 1099-G, but didnt file for unemployment benefits, this may be a case of identity theft and fraud. Contact your state unemployment office immediately for additional information and how to report the potential fraud.
What Is Taxable Income
Income tax is applied to taxable income. So, what is your taxable income? The ATO defines taxable income as follows: Your taxable income is the income you have to pay tax on. It is the term used for the amount left after you have deducted all the expenses you are allowed to claim from your assessable income. Assessable income allowable deductions = taxable income.
Recommended Reading: Florida Transfer Tax Refinance
