The Roth Ira Advantage
Its not a coincidence that Thiel opted for a Roth IRA to hold his PayPal shares: Investments in a Roth IRA grow tax-free. In Thiels case, ProPublica says that investment has grown to about $5 billion.
Yes, that seems unfair. But typical Americans dont have to be Peter Thiel to take advantage of the Roths tax benefits.
The rules really arent different for Peter, or any wealthy person, and the average person thats out there, says Todd Scorzafava, a certified financial planner and partner at Eagle Rock Wealth Management in East Hanover, New Jersey.
So what are those rules? Among other things, youll have to wait until age 59 ½ to start pulling investment income out of your Roth IRA otherwise, it may be taxed or penalized. The account also has income limits, and an annual contribution limit of $6,000 . Those who follow the rules tech billionaires or otherwise reap the Roths rewards.
Tax Reporting When Making Non
When making after-tax contributions to an IRA, you must inform the IRS that you’ve already paid tax on those dollars. This is done using Form 8606. If you don’t report, track, and file the form, you’ll lose the ability to shield part of your IRA withdrawal from tax when you take the money out. In another words: you’ll pay federal income tax on the same dollar twice. This is the double tax trap.
Who Should Use A Non
A non-deductible IRA isnt the best approach for every investor when planning for retirement. Making non-deductible contributions to an IRA usually only makes sense in one of two scenarios.
There is really no good reason to make an after-tax contribution other than not being able to make either a pretax or Roth IRA contribution, Bergman said. The after-tax contribution does not include a tax deduction and does not have tax-free growth as a Roth IRA.
Making non-deductible IRA contributions could come in handy if youve experienced a life event that changes your tax profile, such as getting a substantial raise at work. You wouldnt be excluded from making IRA contributions based on your income. At the same time, you could further grow your retirement wealth by maxing out your retirement contributions at work.
More importantly, adding money to a non-deductible IRA could be a good choice if youd like to include a Roth IRA in the mix when planning for retirement. Along with tax-free distributions, the other benefit of a Roth is the ability to avoid RMDs. This means that your money can continue growing indefinitely in retirement until you need to begin withdrawing it.
Also Check: What Cars Qualify For Federal Tax Credit
What Are The Limits For Making Contributions To Rollover Iras
The Pension Protection Act of 2006 allows for the consolidation of various types of retirement account balances. However, if you want the option of rolling eligible assets from your IRA into another employer-sponsored retirement plan in the future, you may want to consider keeping separate IRA accounts for each retirement plan type that you are rolling over until the IRS issues further regulations on portability of retirement plan assets. Therefore, you may want to consider making your annual IRA contribution to a separate IRA. Consult your tax advisor.
Note that you cannot make a 60-day direct rollover contribution online. If you are trying to do so, please contact a Fidelity representative at 800-544-6666.
Mechanics Of Making A Backdoor Roth Ira Contribution Via Conversion Of A Non
In addition, under the Tax Increase Prevention and Reconciliation Act of 2005 , there have been no income limits on Roth conversions of traditional IRAs since 2010. As a result, anyone who has funds in a traditional IRA whether originally deductible or not is eligible to do a Roth conversion. In other words, while income limits remain on Roth contributions, there are no income limits for a Roth conversion.
Thus, by putting the two together, those with higher income who are not able to make a Roth IRA contribution are able to effectively work around the income thresholds by making a non-deductible IRA contribution and then converting it to a Roth .
If the IRA contribution is deductible, the end result will be a contribution to an IRA that produces a tax deduction, followed by a Roth conversion that causes the income in the IRA to be recognized for tax purposes. In the end, this means there will be an IRA deduction of up to $5,500 in 2015 , Roth conversion income of up to $5,500 to match it , and since both are above-the-line income/deductions on the tax return, the net result is $0 of Adjusted Gross Income and a $0 tax liability, even while getting the whole $5,500 in a Roth IRA!
Notably, though, while this strategy of making a Roth IRA contribution through the “back door” by making a traditional IRA contribution followed by a Roth conversion seems relatively straightforward, there are some important caveats to consider in executing the strategy.
Don’t Miss: Does New Mexico Have State Income Tax
Exceptions To Ira Limits And Recent Changes
As with all things, there are exceptions to the rules for IRA contributions. In addition, recent changes have altered long-standing rules governing IRA contributions.
Contributions are no longer restricted by age. In 2019 and earlier, people who were 70 ½ or older couldnt make regular contributions to a traditional IRA. Starting in 2020, reforms removed the age limit on who could make contributions to either traditional IRAs or Roth IRAs.
Non-working spouses may contribute to an IRA. If you do not have taxable compensation, but file a joint return with a spouse who works and earns income, you can open up an IRA in your own name and make contributionsthe so-called spousal IRA. The combined IRA contribution limit for both spouses is $12,000 per year, or $14,000 per year if you are both over 50.
Contribution limits dont apply to rollover contributions. If you roll over another retirement plansuch as a 401 from a previous employer into your IRA, the rollover doesnt count toward the annual contribution limit.
What Are The Limits For Making Contributions To Roth Iras
You and/or your spouse may make an annual contribution to a Roth IRA even if you and/or your spouse actively participate in an employer-sponsored retirement plan provided adjusted gross income requirements are met. Annual contributions are not tax deductible and can be made in any year you have compensation equaling the contribution amount after age 18 .
Recommended Reading: How To Pay My Federal Income Taxes Online
Get More With These Free Tax Calculators And Money
-
See if you qualify for a third stimulus check and how much you can expect
-
Know what dependents credits and deductions
-
Know what tax documents you’ll need upfront
-
Learn what education credits and deductions you qualify for and claim them on your tax returnGet started
The above article is intended to provide generalized financial information designed to educate a broad segment of the public it does not give personalized tax, investment, legal, or other business and professional advice. Before taking any action, you should always seek the assistance of a professional who knows your particular situation for advice on taxes, your investments, the law, or any other business and professional matters that affect you and/or your business.
Claiming Roth Ira Losses
Although some taxpayers were once able to develop a workaround to claim Roth IRA losses, this provision was removed as part of the Tax Cut and Jobs Act of 2017. Whether this will become an option again in the future remains unclear.
In the past, while Roth IRA contributions were not tax-deductible, you could claim losses under certain circumstances. These losses were in relation to your original Roth IRA contribution, not simply a declining balance.
For instance, if you contributed $25,000 to your Roth IRA over the years, but your account is now only worth $20,000, then you experienced a $5,000 loss of your original contribution. In this situation, you could claim that loss on your tax return, but only if all of the following applied:
- You closed all of your Roth IRA accounts,
- You claimed your loss on an itemized tax return,
- The loss exceeded 2% of your Adjustable Gross Income , and
- You were not subject to the Alternative Minimum Tax .
Assuming your situation met each of the above factors, you were eligible to claim a loss on your tax return. However, theres another caveat you could only claim the amount that was above 2% of your AGI as a tax deduction.
Since the above provision is no longer in effect, the Savers Tax Credit is likely the next best option.
You May Like: When Was Income Tax Started
There Are Specific Requirements And Limitations For Gifting Ira Contributions
Gifting your children or grandchildren with contributions to an individual retirement account can give them the advantage of a longer period of tax-free savings. It is definitely a gift that keeps on giving.
An IRA is a tax-deferred retirement savings account. It is similar to the employer-sponsored 401 plan because it also allows funds to grow tax free until withdrawn however, it does not require an employer to open the account. Anyone with earned income can open an IRA account, with certain limitations. If you want to contribute to another individuals IRA, it is important to understand the requirements and limitations for doing so.
Find Out If You Can Contribute And If You Make Too Much Money For A Tax Deduction
Traditional IRAs are tax-advantaged retirement savings accounts. Money invested in a traditional IRA can grow tax-free until you begin making withdrawals as a retiree. Withdrawals are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate.
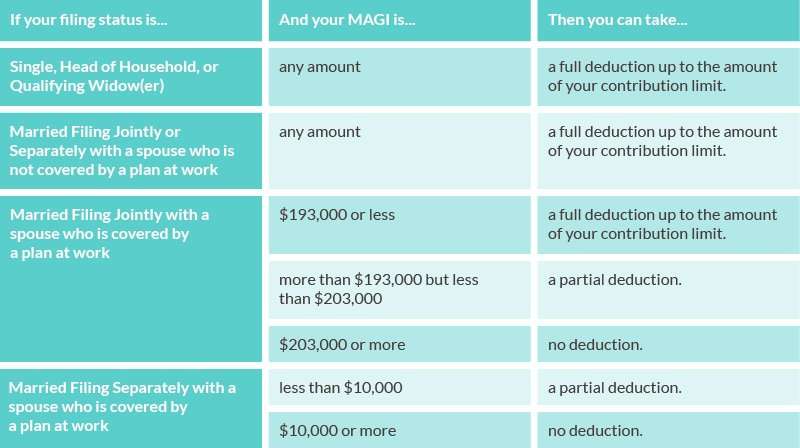
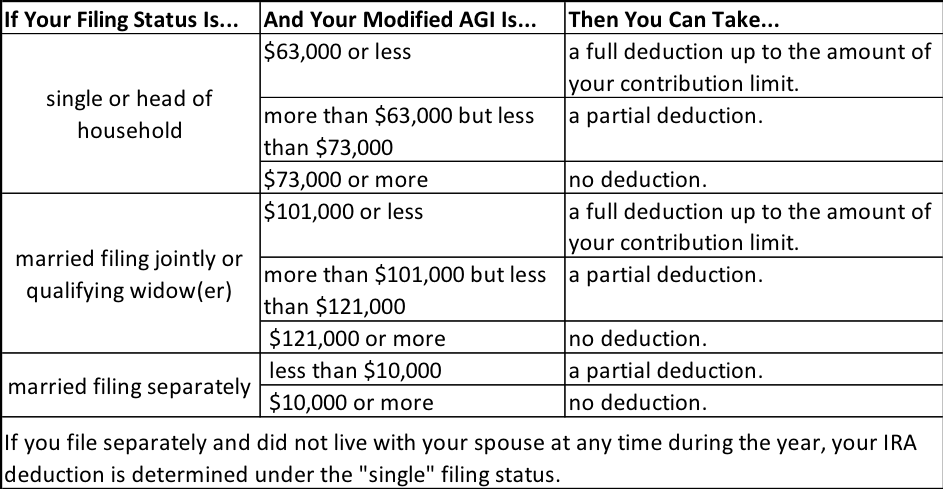
Many, but not all, Americans can invest in a traditional IRA with pre-tax funds, claiming a deduction for their contribution in the year it is made. However, if either you or your spouse is covered by a workplace retirement plan, there are income limits for making tax-deductible contributions to traditional IRAs. If you exceed the income limits, you will not be eligible to contribute to your account with pre-tax funds, but you can still make nondeductible contributions and benefit from tax-free growth. On a related note, there are limits to your IRA contribution as well.
Here’s what you need to know about traditional IRA income limits in 2020 and 2021.
Recommended Reading: What To Do When Taxes Are Late
What To Know About Ira Tax Deductions And Other Tax
Now is the time to think about how you can maximize your retirement account contributions. In addition to boosting your savings, theres another potential benefit to contributing to your IRA during tax season: potential IRA tax deductions.
Roth IRA and Traditional IRA holders can make the most of their contributions at tax time. Assuming you are reporting enough earned income, you can contribute up to $6,000 when under the age of 50 to either a Roth or Traditional IRA. If youre 50 or older, you can contribute up to $7,000 with the $1,000 catch-up contribution.
You cannot exceed $6,000/$7,000 across any combination of Traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs. In other words, you cannot establish multiple accounts to attempt to contribute more than the $6,000/$7,000 limits.
Are you self-employed? Consider the opportunity to contribute up to 20 percent of your self-employment income, up to $57,000, with the SEP IRA . Like the Traditional IRA, this account is tax-deferred, which means the contributions are tax-deductible, making this account attractive to those seeking last-minute tax deductions for 2020 in preparation for return filing.
Can I Roll Over Funds From My Employer
You certainly can! Most employer-sponsored plans, like 401s and 403s, are pre-tax, which means that you have not yet paid taxes on the contributions you made to those plans. You can roll these amounts into your IRA without paying tax or incurring a penalty. Because these amounts have not yet been taxed, they will not affect your IRA basis.
Its less common to roll over retirement plans that consist of after-tax contributions simply because most contributions to employer-sponsored plans are made with pre-tax dollars. But if you do happen to have an employer-sponsored plan that you funded with after-tax dollars like a Roth 401k you can roll those funds into a Roth IRA without incurring taxes or a penalty. A Roth IRA is separate and distinct from a traditional IRA, but the concept of basis is the same you must track the basis in your IRA to ensure the IRS doesnt tax you twice on the same income. Roth IRA basis can also be reported on IRS Form 8606.
Don’t Miss: Where To Find Real Estate Taxes Paid
Additional Tax Traps To Consider Before Making Non
- State tax laws. The focus of this article is on the federal income tax, but it’s important to remember that states can have their own rules. Massachusetts, for example, does not follow the federal rules on tax deductible contributions or recovering âbasisâ on distributions. LeVangie says, “In Massachusetts, all IRA contributions are treated as after-tax additions, which gives you âbasisâ in your IRA that may be different than reported on the federal Form 8606, and your distributions will be completely tax free up until your âbasisâ is recovered for MA purposes . This is completely at odds with the federal reporting and can cause a lot of confusion and extra tax paid if not tracked and reported properly.”
- The same hazards apply to inherited IRAs. If your beneficiaries are unaware that you’ve made non-deductible IRA contributions, or can’t find the records, they have no way of excluding any of the distribution from tax.
Traditional And Roth Ira Contribution Limits For Individuals
Contribution limits are subject to annual cost of living adjustments as set forth in the Pension Protection Act of 2006. If you’re age 50 or older, you may qualify for an additional catch-up contribution.
For 2020 and 2021, the individual contribution limit is the lesser of earned income or $6,000. The catch-up amount for individuals age 50 or older is $1,000.
Recommended Reading: How Much Do I Owe In Property Taxes
How Is A Non
A non-deductible IRA allows you to defer taxes but not escape them completely. After you pay taxes on your income, you can make non-deductible IRA contributions to a Traditional IRA. The contributions will not be taxed when you withdraw them in retirement, since youve already paid income taxes on them. However, you will owe income taxes on the earnings you withdraw from the account.
Because it is a type of contribution, not a type of account, you need to be careful when non-deductible IRA contributions get mixed into an account that previously had tax-deductible contributions in it, Konrad said. Tax-deductible contributions are taxed upon withdrawal on the entire amount, while non-deductible contributions are only taxed on the growth of the contribution.
Can I Make Catch
Individuals who are 50 or older will be allowed to make catch-up contributions to IRAs up to $1,000.
If you currently do not have a date of birth on file with Fidelity, we assume that your IRA contribution includes the applicable catch-up contribution amount. You can update your date of birth online by visiting Accounts & Trade > Update Accounts/Features > Personal Information/Address on Fidelity.com.
You May Like: How Do I Find My Lost Tax Id Number
Income And Tax Deduction Limitations
The IRS limits the amount you can deduct each year, and this amount is subject to change each tax year. This maximum tax deduction may also be subject to a reduction when your MAGI is too high. The IRS provides a worksheet with your tax return instructions to help you calculate your deduction.
If you use tax software, such as TurboTax, you can avoid tedious calculations and let your computer calculate the deduction for you. TurboTax can help you determine whether your IRA contributions are deductible and will calculate exactly how much you can deduct.
Avoiding The Step Transaction Doctrine On Your Roth Ira Backdoor Contribution
So how is the step transaction doctrine avoided? In this context, the step transaction doctrine applies to a series of steps done in quick succession that have the substance of a single whole transaction, such that the court determines by looking at the end result that it was the taxpayer’s intent to do the single-step transaction in the first place.
Accordingly, then, the key to avoiding the intent test of the step transaction doctrine is conceptually simple: put more time and space between the steps, to clearly establish that they were separate and independent decisions, and not part of a single whole. If there is a deliberate time gap between when the non-deductible IRA contribution is made, and when the subsequent Roth conversion occurs, it’s easier to claim that the end result of dollars in the Roth wasn’t part of a sole intent to circumvent the rules. Again, the reality is that each event separately is permissible, but the goal is to clearly establish that each step really is separate.
But perhaps the most important to step avoid the step transaction doctrine is the simplest one: do not, in any notes or records, indicate that you are doing to do a backdoor Roth IRA contribution in the first place! After all, the reality is that the application of the step transaction doctrine is based on the courts determination of intent so when you say you are trying to do a backdoor Roth IRA to bypass the Roth contribution income limits, you are making the case for the IRS!
Also Check: When Will I Get My Federal Tax Refund 2021
Tips For Getting Retirement Ready
- If youre planning for retirement, a financial advisor may be able to help you get ready. Finding a qualified financial advisor doesnt have to be hard. SmartAssets free tool matches you with up to three financial advisors in your area, and you can interview your advisor matches at no cost to decide which one is right for you. If youre ready to find an advisor who can help you achieve your financial goals, get started now.
- Figure out how much youll need to save in order to retire comfortably. An easy way to get ahead on saving for retirement is by taking advantage of employer 401 matching.
