Environment Quality Act Trust
A trust under paragraph 149 of the Act. This is a trust that was created because of a requirement imposed by section 56 of the Environment Quality Act, R.S.Q., c. Q-2. The trust must meet all of the following conditions:
- the trust is resident in Canada
- the only persons that are beneficially interested are one of the following:
- Her Majesty in right of Canada
- Her Majesty in right of a province
- a municipality that is exempt because of subsection 149 from tax under Part 1 on all of its taxable income
Income To Which No Beneficiary Is Presently Entitled
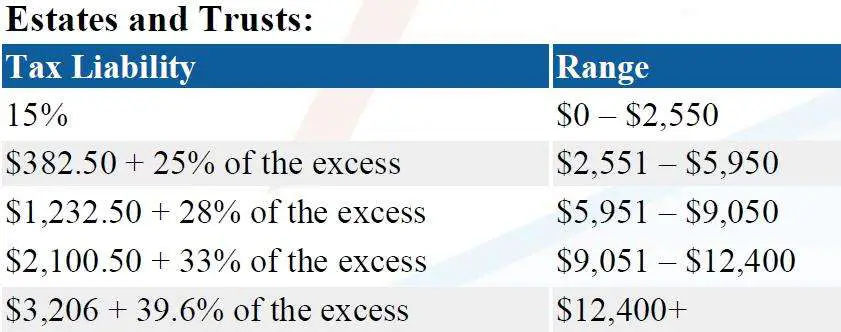
By default the trustee is assessable for tax on trust income for which there is no beneficiary presently entitled, at the top marginal tax rate which is currently 45% unless the Commissioner exercises discretion to apply a concessional tax scale in relation to property of:
- certain compensation claims and death benefits
- or as a result of a family breakdown.
An example of the exercise of the Commissioners discretion in relation to a deceased estate is set out here.
The concessional tax scale applied on the exercise of discretion under Sec 99A is as follows:
| Trust income |
| $21,005 plus 37% of the excess over $80,000 | |
| Over $180,000 | $58,005 plus 47%* of the excess over $180,000 |
* includes Temporary Budget Repair Levy of 2% applicable for 3 years from 1 July 2014 until 30 June 2017
Rules Of Thumb For Trust Income Taxation
Presented by Tim Weller
Rule #1: When in doubt, refer to the trust document an investment policy for a trust cannot be created without it. One advantage of creating a trust is that the grantor can have it tailored to his or her needs therefore, although there may be provisions in common, trust documents vary widely.
The trust document provides instructions to the trustee for managing, investing, and distributing trust assets. It is the primary authority and can supplement or override powers given to the trustee by state law. If the trust document doesnt address an issue, the trustee can refer to state law.
Just as each document is unique, so are each states trust statutes. There has been some effort among states to standardize trust law, but even states that have adopted the Uniform Trust Code have enacted their own version. If state law is silent, the trustee or beneficiaries can ask for interpretation or guidance from state courts.
Managing trust investments follows the same general principles as managing investments for individuals. Factors that must be considered are account risk tolerance, time horizon, long-term goals, and need for current income. Before you and your financial advisor begin a portfolio analysis, read the trust agreement. Here are some important points to consider:
A grantor trust can be either revocable or irrevocable as follows:
An irrevocable trust reports income on Form 1041, the IRSs trust and estate tax return.
Read Also: Protest Property Taxes Harris County
Real Tax Experts On Demand With Turbotax Live Basic
Get unlimited advice and an expert final review. Done right, guaranteed.
-
Estimate your tax refund andwhere you stand
-
Know how much to withhold from your paycheck to get
-
Estimate your self-employment tax and eliminate
-
Know which dependents credits and deductions
-
Estimate capital gains, losses, and taxes for cryptocurrency sales
-
See which education credits and deductions you qualify forGet started
The above article is intended to provide generalized financial information designed to educate a broad segment of the public it does not give personalized tax, investment, legal, or other business and professional advice. Before taking any action, you should always seek the assistance of a professional who knows your particular situation for advice on taxes, your investments, the law, or any other business and professional matters that affect you and/or your business.
Schedule 9 Income Allocations And Designations To Beneficiaries
Complete this schedule if the trust is allocating income to its beneficiaries. You also have to complete T3 slips and a T3 Summary if you are allocating income to resident beneficiaries, and NR4 slips and an NR4 Summary if you are allocating income to non-resident beneficiaries.
Allocations and designations
Generally, you allocate income to the trust’s beneficiaries according to the terms of the will or trust document. Depending on the type of income allocated, you may then designate all or part of the allocated amount. When you designate an amount to a beneficiary, the type of income keeps its identity. This may allow the beneficiary to take advantage of a deduction or credit that applies to that income .See definition of allocate, allocation, and designate, designation.You can choose to designate the following income amounts to a beneficiary:
- net taxable capital gains
- pension income that qualifies for the pension income amount
- pension income that qualifies for acquiring an eligible annuity for a minor beneficiary
- retiring allowances that qualify for a transfer to a registered pension plan or a registered retirement savings plan
Note
An insurance segregated fund trust has to designate all of its capital gains and losses to its beneficiaries.
Income allocated to a beneficiary that is not deductible should not be reported on Schedule 9.
For more information, see the following archived interpretation bulletins:
Recommended Reading: How To Keep Track Of Taxes For Doordash
Benefits Of The Gre Designation
The GRE designation brings with it two key benefits.
For gifts in-kind of publicly traded securities or mutual funds on or after death, a nil capital gains inclusion rate is available however, the exemption is only available if the estate is designated a GRE. This allows a GRE to benefit from the same tax treatment on in-kind donations that living donors enjoy.
The two benefits can only be realized if the executor makes the appropriate designation on the estates first tax return. This is especially important with respect to testamentary donations. The flexibility afforded to the executor in allocating the donation tax credit between the deceased and the estate, along with the tax treatment of in-kind donations, improves the probability that the tax credit gets fully utilized.
Which Estates And Trusts Must File Form 1041
Estates with a gross income of $600 or more for the tax year and those with any beneficiary who’s a nonresident alien are required to file IRS Form 1041.
Trusts that have any taxable income at all, that have a gross income of $600 or more regardless of taxable income, or with any beneficiary who is a nonresident alien are required to file Form 1041 as well.
An estate must request a tax ID number in order to file these documents and to transact other business. The ID number is the employer identification number regardless of whether the estate actually employs anyone. Estate executors can apply to the IRS for an EIN by mail, fax, or online.
Read Also: Do I Have To File Taxes For Doordash If I Made Less Than $600
Income Taxes Aren’t The Same As Estate Taxes
These tax rates and brackets shouldn’t be confused with estate tax thresholds and exemptions. They apply only to income earned by trusts or estates before assets are transferred to beneficiaries. The estate tax applies to the estate’s overall value and requires filing IRS Form 706, the U.S. Estate Tax Return.
Only estates valued at more than $11.7 million were subject to the estate tax in 2021. This threshold is also indexed for inflation. It increases to $12.06 million for deaths that occur in 2022. The TCJA more or less doubled the estate tax exemption when it went into effect in 2018. These values may revert to pre-2018 levels after 2025 when the TCJA expires unless Congress acts to renew its provisions.
Dramatic Differences In Tax Rates
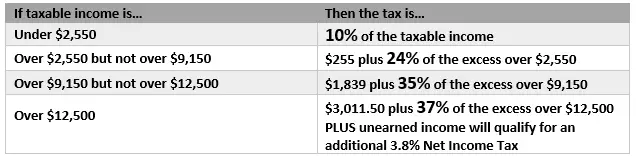
Understanding the income tax treatment of taxable trusts is important because trusts have highly compressed tax brackets. For 2012, trusts reach the highest federal tax bracket of 35% at taxable income of $11,650 . By comparison, the tax rate for single taxpayers on taxable income of $11,650 is only 15%. The highest federal tax bracket of 35% does not apply to most individual taxpayers until their taxable income reaches $388,350. In addition, many states also tax the income of trusts.
Read Also: Doordash Accounting Method
Registered Disability Savings Plan Trust
An RDSP trust has to complete and file a T3 return if the trust has borrowed money and subparagraph 146.4 or 146.4 of the Act applies. If this does not apply and the trust carried on a business or held non-qualified investments during the tax year, you have to complete a T3 return to calculate the taxable income from the business or non-qualified investments, determined under subsection 146.4. If the trust is reporting capital gains or losses, it has to report the full amount on line 1 of the T3 return.
Charitable Trusts Taxability And Tax Return Filing
A charitable trust is a type of entity formed to provide the public with religious or humanitarian facilities. Trusts that are formed for charitable or religious purposes and not intended to do commercial activities are allowed various benefits under the Income-Tax Act. In this article, we look at such benefits and the procedure for filing Trust income tax return.
Read Also: How Do You Pay Taxes With Doordash
Which Tax Package Should You Use
Use the provincial or territorial forms package for the province or territory where the trust was resident on the last day of its tax year.
To get any schedules and forms that you may need, go to Forms and publications, or call 1-800-959-8281. Once you have completed the necessary schedules, forms, and statements, you will be ready to complete the T3 return. Attach all required documents to the return.
Note
The province of Quebec collects its own provincial income tax. Do not calculate provincial income tax on the trust’s federal return if it was resident in Quebec on the last day of its tax year. If the trust had income from a business with a permanent establishment in another province or territory, you have to calculate that province’s or territory’s income tax on the trust’s federal tax return.
I Inherited My Mother’s Traditional Ira Do I Have To Pay Tax On The Full Amount I Receive Each Year From The Account
Actually, when you inherit an IRA, there’s an easily overlooked deduction.
If the estate was large enough to be subject to federal estate tax, you can deduct the portion of the federal estate tax attributable to the IRA. In addition, you dont have to pay tax on the portion of withdrawals attributable to nondeductible contributions that your mother made to the IRA .
Recommended Reading: Buying Tax Liens California
Find Out If This Guide Is For You
This guide provides information on how to complete the T3RET Trust Income Tax and Information Return , the T3 slip, Statement of Trust Income Allocations and Designations, and the T3SUM Summary of Trust Income Allocations and Designations.
Use this guide if you are filing a T3return for either a testamentary trust or an inter vivos trust. For more information, see Types of trusts.
The word “you” throughout the guide refers to the trustee, executor, administrator, liquidator, or anyone preparing the T3 return for a trust. For tax purposes, estates and trusts are treated similarly. In calculating the income of an estate, references in this guide to a trust or trust property include “estate” or “estate property”.
“The Act” refers to the Income Tax Act. Unless otherwise stated, all legislative references within this guide are to the Income Tax Act and the Income Tax Regulations. You can find a list of these references in the Index at the end of the guide.
If you need more information after reading this guide, visit Taxes, or call 1-800-959-8281
What Is The 65
Under the 65-day rule, a trustee can make distributions to trust beneficiaries within 65 days after year-end and treat those distributions as if they were made in the previous tax year. The deadline for the distribution is March 6 . An irrevocable election must be made on the trusts income tax return to treat the distributions made within the 65-day window as made in the prior tax year. For tax year 2020, if trustees make distributions to trust beneficiaries before March 6, 2021, they can elect to treat those distributions as 2020 tax year distributions. The trustee would claim an income distribution deduction for these 65-day rule distributions on the trusts 2020 tax return and shift some of the trusts 2020 income tax burden to the trust beneficiaries, who would be taxed at lower rates than the trust. Trustees may take advantage of the 65-day rule when the trusts distributions to beneficiaries during the calendar year are less than the trusts DNI for that year. If that is the case, the trustee may make 65-day rule distributions up to the trusts DNI to maximize the trusts income distribution deduction and shift the tax liability on those distributions to the beneficiaries.
Wealthspire Advisors LLC is a registered investment adviser and subsidiary company of NFP Corp.
You May Like: 1040paytaxcom
Trusts Are Running Out Of Time To Reduce 2021 Tax Liabilities By Rick Bazzani Cpa
Posted on February 28, 2022 by Rick Bazzani
Under the IRSs 65-day rule, estates and certain complex trusts still have some time to reduce their income-tax liabilities for 2021, but immediate action is required.
Calendar year-end trusts have until Sunday, March 6, to distribute trust income to beneficiaries and treat those payments as if they occurred in 2021. Doing so not only reduces the amount of trust income subject to tax at the highest ordinary income tax rate, but it also reduces the overall tax burdens for both the trust and its beneficiaries. It should be noted that this rule applies only to trusts for which a trustee has the power to distribute income it does not apply to grantor trusts in which grantors report all trust activity nor does it apply to simple trusts that require fiduciary accounting of income to be distributed annually.
For the 2021 tax year, trusts with undistributed income of more than $13,051 are taxed at the highest federal rate of 37 percent plus a 3.8 percent Net Investment Income Tax . By contrast, individual taxpayers do not reach this top tax bracket until their income reaches $523,601 . Consequently, a trust can reduce its taxable income and pay a lower tax rate when it makes distributions to its beneficiaries, especially those in lower tax brackets who will pay far less tax on those amounts than that which the trust would be required to pay, even at the same ordinary income tax rates.
Everything You Need To Know About Graduated Rate Estates
One year later, heres a deep dive
- 00:02
Its been just over a year since the Department of Finance introduced a new income tax term, the Graduated Rate Estate . The GRE has brought with it both advantages and some planning challenges. We will look at each in turn, as well as review, what constitutes a GRE.
Read Also: Csl Plasma Taxes
Taxpayer Bill Of Rights
The Taxpayer Bill of Rights describes and defines 16 rights and builds upon the CRAs corporate values of integrity, professionalism, respect, and collaboration. It describes the treatment you are entitled to when you deal with the CRA. The TBR also sets out the CRA Commitment to Small Business to ensure their interactions with the CRA are conducted as efficiently and effectively as possible.
For more information about your rights and what you can expect when you deal with the CRA, go to Taxpayer Bill of Rights.
Find Out If You Need To Read The Whole Guide
If you are filing a T3 return for an estate that has only pension income, investment income, or death benefits, you do not need to read the entire guide. We have used the symbol to lead you to the information you may need. This symbol appears in the table of contents, in the right margins of the guide, and in the left margins of the return beside the lines that may relate to your situation.
Before you begin, be sure to read:
Read Also: Do You Have To Claim Plasma Donation On Taxes
Does A Trust File Its Own Income Tax Return
Yes, if the trust is a simple trust or complex trust, the trustee must file a tax return for the trust if the trust has any taxable income , or gross income of $600 or more.
For grantor trusts, it depends. A grantor trust may use the grantors Social Security number as its taxpayer identification number, or it may obtain its own taxpayer identification number from the IRS. If a grantor trust uses the grantors Social Security number as its taxpayer identification number, it does not need to file its own income tax return as all tax documents such as 1099s will be issued to the grantor directly to report on the grantors individual income tax return. However, if a grantor trust has its own taxpayer identification number, it may have to file its own tax return for informational purposes only. The pro forma tax return identifies the trust as a grantor trust and includes a grantor trust letter that lists all income items that should be reported on the grantors individual income tax return, so that the grantor can pay the taxes.
