What Are The Benefits Of Reinvesting Dividends
The primary reason to reinvest your dividends is that doing so allows you to buy more shares and build wealth over time. If you examine your returns 10 or 20 years later, reinvesting is more likely to increase the value of your investment than if you simply took the cash. Also, reinvesting allows you to purchase fractional shares and get discounted prices.
Certain Investments May Have Special Tax Treatment
Certain types of investments can have special tax treatment. For instance, municipal bonds are normally tax-free for federal income taxes but may be taxable on your state tax return, depending on the state you live in and the state that issued the bond you invested in.
- It’s also possible to trigger special taxes, such as the alternative minimum tax , through instances like exercising incentive stock options. TurboTax can guide you through the process of figuring out if this applies to your situation or not.
- A bigger exception is money in tax-advantaged retirement accounts. Traditional retirement accounts, such as a traditional IRA or traditional 401, may allow you to take a tax deduction today. Then, the investments within the account can grow tax-free. When you withdraw the money in retirement after meeting the age requirements, the money typically counts as ordinary income and you will likely have to pay ordinary income taxes on this income.
- The other main type of tax-advantaged retirement accounts that are treated differently are Roth retirement accounts, such as a Roth IRA or Roth 401. You don’t get a tax deduction for contributing to these accounts. However, the money can grow tax-free and you can withdraw it tax-free, including the investment gains, in retirement after meeting age and other requirements.
There may be other exceptions depending on your specific investments and circumstances as well. TurboTax can help you navigate these more complex areas.
The Importance Of Understanding The Basic Tax Aspects Of Investing
Because we pay so much tax, every precaution we can take to minimize tax counts.
Investment taxation is an often overlooked but very important area of personal tax planning.
Contact your advisor for more information about taxation and investment issues that concern you.
1 Information in this document provides an overview of the taxation of personally owned non-registered investments. Income from registered plans is generally either fully taxable at your marginal tax rate when received or is not taxable .2 The gross-up together with the DTC means that eligible dividends are generally taxed more favourably at the personal level than non-eligible dividends. However, due to the higher grossed-up amount that is included in taxable income, eligible dividends are more detrimental than non-eligible dividends in the calculation for income tested benefits.
Commissions, trailing commissions, management fees and expenses all may be associated with mutual fund investments. Please read the prospectus before investing. Mutual funds are not guaranteed, their values change frequently, and past performance may not be repeated.
Subject to any applicable death and maturity guarantee, any part of the premium or other amount that is allocated to a segregated fund is invested at the risk of the contract holder and may increase or decrease in value according to fluctuations in the market value of the asset in the segregated fund.
Recommended Reading: How To Appeal Cook County Property Taxes
Q: How Do I Calculate Capital Gains Tax
A: Find the basis. In order to find the basis, youll look for the original stock price of the investment, which may also include commissions of other fees.
Figure your actual amount. When figuring the actual, or realized amount, you are looking at the selling price of the stock, without the commissions or other fees.
Subtract the basis from the actual amount. Once you do this, youll have the difference. Keep in mind that if you sold your investments at a higher rate than what you initially paid, youll have a capital gain. On the other hand, if you sold your investments for less, youll have a capital loss.
How To Report Dividend Income On Your Taxes
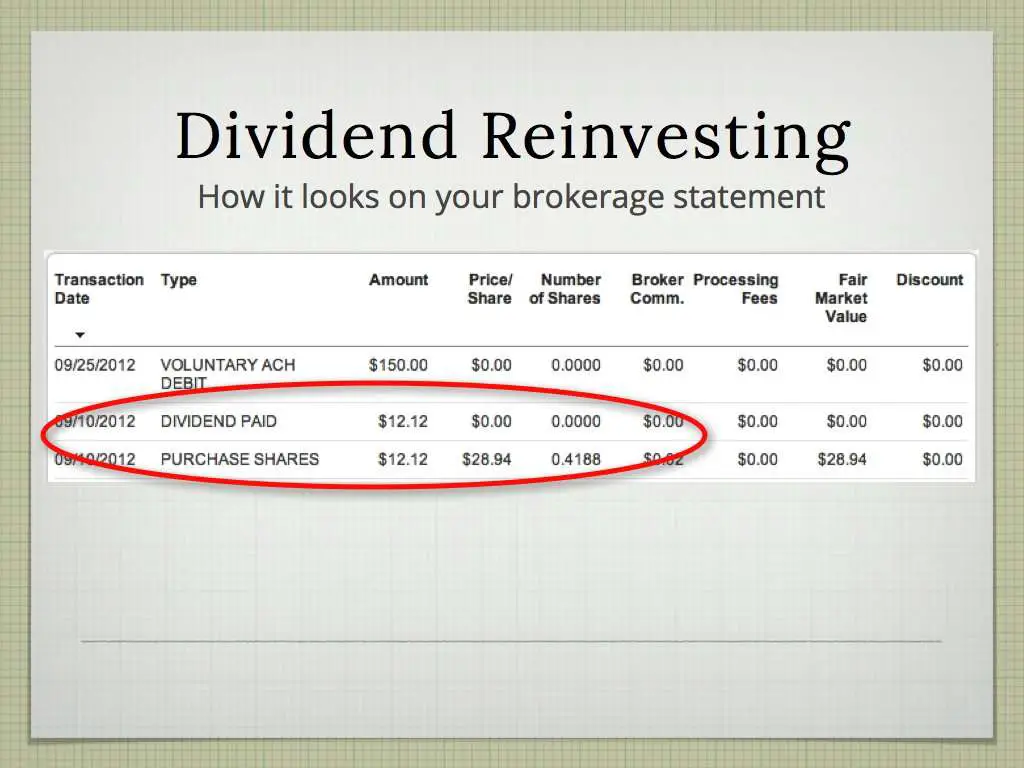
-
After the end of the year, youll receive a Form 1099-DIV or sometimes a Schedule K-1 from your broker or any entity that sent you at least $10 in dividends and other distributions. The 1099-DIV indicates what you were paid and whether the dividends were qualified or nonqualified.
-
You use this information to fill out your tax return. You might also need to fill out a Schedule B if you received more than $1,500 in dividends for the year.
-
Even if you didnt receive a dividend in cash lets say you automatically reinvested yours to buy more shares of the underlying stock, such as in a dividend reinvestment plan you still need to report it.
-
You also need to report dividends from investments you sold during the year.
Also Check: Doordash Taxes California
Is It Possible To Live Off Dividends In Retirement
Living off Dividends in Retirement. Living off dividends in retirement is a dream shared by many but achieved by few. In todays environment marked by rising life expectancies, extremely low bond yields, and the longest bull market in history, retirees face challenges on all fronts to build a consistent income stream that will last a lifetime.
How Are Dividends Taxed In Canada
You may have probably heard that you can earn up to $50,000 in Canadian dividend income, completely tax free if you dont have any other sources of income in certain provinces, for example, here in British Columbia. Amazing isnt it? However not all dividend income is treated equally. Heres the answer to how are dividends taxed in Canada.
Some Canadians are dividend investors, some people are index investors, some are a bit of both. Theres no denying the joy you feel when you get a dividend payment in your account though, its passive income. You have to be a bit careful which accounts you put your income generating assets in to optimize your tax efficient investing, though.
This post will go over how much tax you would pay on dividends in Canada , what the dividend tax credit is, how US dividends are taxed in Canada, and how foreign dividends are taxed in Canada. Basically this post will go over important aspects of investing in Canada and how your investment income is treated differently.
Read Also: Amended Tax Return Online Free
More On Dividend Reinvestment Plans
Most investment brokers make it easy for an investor to reinvest all their dividends by setting up an automatic reinvestment plan. However, investors can also opt to participate in DRIPs offered directly by a dividend-paying company. These programs provide similar benefits to those offered by brokers since many are commission-free and enable investors to buy fractional shares. In addition to that, some companies sell shares via their DRIP program at a discount to the current market price.
However, not all DRIPs offer these benefits, so investors need to read the fine print carefully. For example, some companies have investment minimums such as a requirement to own a certain number of shares or a certain dollar value. Further, some also charge a service fee and a brokerage commission.
Should You Reinvest Dividends
There are many reasons why investors might consider reinvesting their dividends. It’s easy to set up, usually commission-free, typically allows the purchase of fractional shares, and enables investors to put cash to work quickly. However, the best reason to consider automatic dividend reinvestment is to benefit from the miracle of compounding.
That’s evident in the returns a hypothetical investor could have earned in the S& P 500 with and without dividend reinvestment. For example, an investor who put $10,000 into an S& P 500 index fund in 1970 would have more than $350,000 by the end of 2019, according to data from Morningstar and Hartford Funds. That return is the price growth only, as it assumes no dividends.
However, adding in dividends changes the equation dramatically. Investors who reinvested their dividends back into that same S& P 500 index fund would have more than $1.6 million at the end of this 50-year period.
Given that much higher return potential, investors should consider automatically reinvesting all their dividends unless:
- They need the money to cover expenses.
- They specifically plan to use the money to make other investments, such as by allocating the payments from income stocks to buy growth stocks.
- They don’t want to increase their allocation to a particular company or fund.
Recommended Reading: Federal Irs Tax Return
How Does This Affect Me
While paying taxes on the relatively small amount of dividends does seem petty, doing so creates basis in the shares you purchased with what is now considered post-tax money. This is because you paid taxes on the dividends even though they were reinvested. Basis is incredibly important when selling securities. For example, you purchase 10 shares of a stock for $100 and then sell them over a year later for $150. You are taxed at the long-term capital gain tax rate of 15% on the gain, which was $50. This case could be true if you purchased the shares with money through your advisor, or with reinvested dividends. What if you werent taxed on those reinvested dividends though? The entire $150 would be taxable as a capital gain.
Thats all well and good, but lets think bigger for a moment. In one situation I experienced, one of my clients sold hundreds of shares of Exxon stock after having paid thousands of dollars in taxes on reinvested dividends over the years. By paying the tax in smaller increments over the years they averaged out their tax, rather than selling all the shares in one year as they did and having to report significantly higher gains and paying taxes at a much higher tax bracket.
Kevin MolenTax Manager
What Are Qualified And Unqualified Dividends
For dividends to fall in the qualified dividend category, they typically must be paid by a U.S. corporation or a qualifying foreign corporation. Generally, you must also meet the holding period requirement.
The holding period requirement for most types of dividends states you must have held the investment unhedged for more than 60 days during the 121-day period that starts 60 days prior to the ex-dividend date. An ex-dividend date is typically one day before the date of record or record date. If you purchase a dividend generating investment on its ex-dividend date or after, you typically will not receive the next dividend payment. Generally, the holding period doesn’t include the day you purchased an investment, but it does include the day you sold it.
Certain dividend payments aren’t qualified dividends even if they’re reported as such. These are listed in IRS publication 550 under the “Dividends that are not qualified dividends” section, and they typically include capital gains distributions and dividends you receive from a farmers’ cooperative.
Ordinary dividends are the total of all the dividends reported on a 1099-DIV form. Qualified dividends are all or a portion of the total dividends. They’re reported in box 1a on Form 1099-DIV.
While this sounds complicated, your financial institution should clarify which dividends are qualified when they report your dividends to you on Form 1099-DIV. Qualified dividends appear in box 1b.
Recommended Reading: Calculate Doordash Taxes
Have Investment Income We Have You Covered
With TurboTax Live Premier, talk online to real experts on demand for tax advice on everything from stocks, cryptocurrency to rental income.
-
Estimate your tax refund andwhere you stand
-
Know how much to withhold from your paycheck to get
-
Estimate your self-employment tax and eliminate
-
Know which dependents credits and deductions
-
Estimate capital gains, losses, and taxes for cryptocurrency sales
-
See which education credits and deductions you qualify for
The above article is intended to provide generalized financial information designed to educate a broad segment of the public it does not give personalized tax, investment, legal, or other business and professional advice. Before taking any action, you should always seek the assistance of a professional who knows your particular situation for advice on taxes, your investments, the law, or any other business and professional matters that affect you and/or your business.
Dividend Tax Rate 2021
Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This may influence which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list ofour partnersandhere’s how we make money.
Dividends arent free money theyre usually taxable income. But how and when you own an investment that pays them can dramatically change the dividend tax rate you pay. There are many exceptions and unusual scenarios with special rules see IRS Publication 550 for the details but heres generally how dividend tax works.
Recommended Reading: Reverse Tax Id Lookup
What Is Form 1099
Form 1099-DIV Dividends and Distributions is the form financial institutions typically use to report information to you and the IRS about dividends and certain other distributions paid to you.
The financial institutions are required to fill out this form if your total dividends and other distributions for a year exceed $10. It includes information about the payer of the dividends, the recipient of the dividends, the type and amount of dividends paid, and any federal or state income taxes withheld.
Do I Pay Capital Gains Tax On Shares
When you come to sell your shares, you could pay tax on any profits you make. This would be a capital gains tax .
Much like dividends, you get an annual tax-free allowance on capital gains. In 2021-22, this is £12,300 the same as it was in 2020-21.
If the profit you make when selling your shares is below this amount, you won’t have to pay tax.
Above this level, gains are taxed at 10% if you’re a basic-rate taxpayer, or 20% if you’re a higher or additional-rate taxpayer.
Find out more in our guide to capital gains tax on shares.
Read Also: How To Get My Doordash Tax Form
Holding Onto An Asset For More Than 12 Months If You Are An Individual
To qualify for a 50% discount on your CGT, you must meet the following conditions: CGT is only applied to the $1,500 gain on the sale of shares youve held for more than a year, rather than the $3,000 gain you really made.
Assets held for more than a year are eligible for a 33.3 percent discount for SMSFs .
As long as an asset has been in the companys possession for the full twelve-month period, the company is not entitled to any CGT discount and must pay the full 26 percent or 30 percent gain rate.
Next Steps To Consider
Fidelity does not provide legal or tax advice. The information herein is general in nature and should not be considered legal or tax advice. Consult an attorney or tax professional regarding your specific situation.
Votes are submitted voluntarily by individuals and reflect their own opinion of the article’s helpfulness. A percentage value for helpfulness will display once a sufficient number of votes have been submitted.
Also Check: How Do I Get A Pin To File My Taxes
Q: Do I Have To Pay Tax On Stocks If I Sell And Reinvest
A: Yes. Selling and reinvesting your funds doesnt make you exempt from tax liability. If you are actively selling and reinvesting, however, you may want to consider long-term investments. The reason for this is youre only taxed on the capital gains from your investments once you sell them. As a result, the longer you hold on to your shares or funds, the lower your tax liability.
For a married couple with $200k in income, the difference between a short-term and long-term capital gain is nearly 50% more! Short-term gains are taxed at 24%, while long-term capital gains are taxed at 15%. Generating short-term gains five to six times a year will yield more taxes being taken from your gains. This is a more costly option than purchasing your stocks once and holding on to them for twenty or thirty years before selling and reinvesting.
How Is Income From Mutual Funds Taxed
In most situations, income from mutual funds is taxed in two ways:
- While you own the shares or units, you are taxed on the distributions of income that are flowed out to you. If you own units of a mutual fund trust, the trust will give you a T3 slip, Statement of Trust Income Allocations and Designations. If you own shares of a mutual fund corporation, the corporation will give you a T5 slip, Statement of Investment Income. The distributions can be capital gains, capital gains dividends, dividends, foreign income, interest, other income, return of capital, or a combination of these amounts. A return of capital will reduce the adjusted cost base of your units or shares.
- When you sell or redeem the units or shares, you are taxed on the gain, if any. This is usually a capital gain because your mutual fund investment is usually considered capital property for tax purposes. You will receive a T5008 slip, Statement of Securities Transactions, or an account statement from the mutual fund.
Also Check: How To Get Pin To File Taxes
Do I Have To Pay Taxes On Dividends
Dividends are taxed differently depending on their source. Dividends are taxable income by the IRS, so you usually have to pay taxes on them as well. Dividends that are not qualified for tax deductions are taxed according to the regular income tax rates and brackets of the federal government. Dividends that are qualified for capital gains tax treatment are subject to lower rates.
