Consider The Alternate Valuation Date
Typically the cost basis of property in a decedents estate is the fair market value of the property on the date of death. In some cases, however, the executor might choose the alternate valuation date, which is six months after the date of death.
- The alternate valuation is only available if it will decrease both the gross amount of the estate and the estate tax liability this will often result in a larger inheritance to the beneficiaries.
- Any property disposed of or sold within that six-month period is valued on the date of the sale.
- If the estate is not subject to estate tax, then the valuation date is the date of death.
Other Stronger Reform Options
- Restore the estate tax to what it was under President Clinton a $2.6 million exemption per couple with a 55% top tax rate. This would generate an additional $249 billion over 10 years money that could be used to support popular public services and reduce the deficit. Even with this smaller exemption, the tax would affect fewer than 2 out of 100 estates. Rep. Jim McDermott proposed such legislation in 2011.
- Close the inherited capital gains tax loophole. Wealthy people avoid capital gains taxes by holding onto their assets until they die and bequeathing them to heirs. The increase in value is not taxable when they are sold. This loophole will allow the wealthy to dodge about $650 billion in taxes over the next 10 years.
- Close an estate tax loophole used by the super-rich, known as the Walton grantor retained annuity trust, or GRAT. These specialized trusts allow families like the Waltons to completely avoid paying estate and gift taxes. This loophole may have cost the U.S. Treasury $100 billion since 2000.
What Assets Make Up Taxable Estates
Assets of taxable estates can be classified in one of five categories: financial, real estate, business, retirement, and other .14 As reported on estate tax returns, those asset groupings are similar to the ones used in CBOs estate tax model. Understanding their distribution helps CBO project estate and gift tax receipts more precisely and accurately.
Don’t Miss: How To Avoid Taxes On Bonus Check
Inheritance Tax Vs Estate Tax: Differences
It’s easy to confuse the inheritance tax with the well-known estate tax, but the two are actually quite different. As we discussed, the inheritance tax is one that’s imposed on the individual who inherits assets from someone else. An estate tax, on the other hand, is imposed directly on the decedent’s estate before the assets are distributed to any beneficiaries.
The most prevalent estate tax is the one imposed by the federal government. In 2021, the first $11.7 million of someone’s estate is exempt from the estate tax. Any amount above the exemption is taxed at a rate between 18 and 40 percent, depending on the estate amount.
In addition to the federal estate tax, 12 states and the District of Columbia also charge a state estate tax. Like the federal government, each state allows for an estate tax exemption. Massachusetts and Oregon have the smallest exemption at just $1 million. New York has the largest exemption and allows estates to pass down $5.9 million before paying estate taxes. The estate tax rates vary from one state to the next, but generally range from less than 1 percent to as high as 20 percent, depending on the state and the size of the estate.
Tips For Estate Planning

- Estate planning can be complicated, so it pays to be prepared. A financial advisor can be a solid resource to lean on. SmartAssets free tool matches you with financial advisors in your area in five minutes. If youre ready to be matched with local advisors, get started now.
- Estate planning can be complex, and thats especially true if youre someone with significant wealth. To make sure you have everything you need, read up on the essential estate planning tools for wealthy investors.
- If you want your beneficiaries to avoid a potentially long and costly probate process, consider creating a revocable living trust. This estate planning tool could give you the flexibility that you cannot get from other trusts or wills.
Read Also: How Do You File An Amendment To Your Tax Return
Roughly 2 Of Every 1000 Estates Face The Estate Tax
Today, 99.8 percent of estates owe no estate tax at all, according to the Joint Committee on Taxation. Only the estates of the wealthiest 0.2 percent of Americans roughly 2 out of every 1,000 people who die owe any estate tax. This is because of the taxs high exemption amount, which has jumped from $650,000 per person in 2001 to $5.49 million per person in 2017.
Thus, the estate tax is best characterized as a tax on very large inheritances by a small group of wealthy heirs repeal would amount to a massive windfall averaging more than $3 million apiece for the top 0.2 percent, and more than $20 million for the wealthiest estates. As New York University School of Law professor Lily L. Batchelder explains, it would be more accurate to call wealth transfer taxes silver spoon taxes, not death taxes as their opponents prefer.
Who Is Subject To The Estate Tax
The estates of all U.S. citizens and U.S. residents at the time of death are subject to the federal estate tax, but very few estates actually have to pay it because of the exemption. Only estates whose values exceed the exemption after deductions are made, and credits are taken, are subject to the federal estate tax on the balance.
Don’t Miss: Do I Qualify For Child Tax Credit 2021
How The Estate Tax Works
The total tax due is calculated by adding up the fair market values of all the decedent’s assets as of their date of death. The assets that are part of your estate can include:
- Stock, bonds, and other securities
- Business interests
- Other valuable assets
The total of all these assets is known as your “gross estate.”
The fair market value of your assets is not necessarily what you paid for them. Instead, it’s what they are worth at the time of your death. The executor or administrator of the estate can also elect to have everything valued on an alternate date six months later, provided the assets aren’t “distributed, sold, exchanged, or otherwise disposed of within the six month period,” the IRS notes.
Using the six-month alternate valuation date can be beneficial if an estate is expected to lose value over six months, which would, in theory, lower the estate tax bill.
Only assets that are worth more than a certain threshold are taxed at a percentage of their value. This threshold is known as the “estate tax exemption.” For 2022 , the estate tax exemption is $12.06 million.
The rate at which your estate is taxed depends on how high over the exemption limit your assets are. The rate ranges from 18% for assets that up to $10,000 more than the exemption to 40% for estates that are $1 million or more above the exemption.
President Obama Wants To Strengthen The Estate Tax
The estate tax will currently raise about $225 billion over 10 years. President Obama wants to restore its parameters to 2009 levels a $3.5 million exemption for an individual and a 45% top rate. This reform and others he proposed will raise $131 billion more over 10 years, and affect three estates for every 1,000 deaths.
Read Also: How Are Brokerage Accounts Taxed
Adjustments To Gross Estate
The next step is to calculate any adjustments to the gross estate. Typical adjustments include paying-off the remaining balance on a , or the fees associated with settling the estate. This can include costs such as estate administration fees or payments made to an attorney. Finally, there is also a Marital Deduction that can be taken for property left to a surviving spouse.
How Inheritance Tax Works
Once the executor of the estate has divided up the assets and distributed them to the beneficiaries, the inheritance tax comes into play. The tax amount is calculated separately for each individual beneficiary, and the beneficiary must pay the tax.
- For example, a state may charge a 5% tax on all inheritances larger than $2 million.
- Therefore, if your friend leaves you $5 million in his will, you only pay tax on $3 million, which is $150,000.
- The state would require you to report this information on an inheritance tax form.
Read Also: Where Do I Get Federal Tax Forms
Estate And Inheritance Taxes At The State Level
Currently, fifteen states and the District of Columbia have an estate tax, and six states have an inheritance tax. Maryland has both. Some states exempt estates at the federal level. Other states impose tax at lower levels New Jersey estate tax was abolished for deaths after Jan 1, 2018.
In states that impose an inheritance tax, the tax rate depends on the status of the person receiving the property, and in some jurisdictions, how much they receive. Inheritance taxes are paid not by the estate of the deceased, but by the inheritors of the estate. For example, the Kentucky inheritance tax “is a tax on the right to receive property from a decedent’s estate both tax and exemptions are based on the relationship of the beneficiary to the decedent.”
For decedents dying in calendar year 2014, 12 states and the District of Columbia impose only estate taxes. Delaware and Hawaii allowed their taxes to expire after Congress repealed the credit for state estate taxes, but reenacted the taxes in 2010. Exemption amounts under the state estate taxes vary, ranging from the federal estate tax exemption amount or $5.34 million, indexed for inflation to $675,000 . The most common amount is $1 million . In 2014, four states increased their exemption amounts: Minnesota , Rhode Island , and Maryland and New York . Top rates range from 12 percent to 19 percent with most states, like Minnesota, imposing a top rate of 16 percent.
The Largest Estates Consist Mostly Of Unrealized Capital Gains That Have Never Been Taxed
Much of the money that wealthy heirs inherit would never face any taxation were it not for the estate tax. In fact, thats one reason why policymakers created the estate tax in 1916: to serve as a backstop to the income tax, taxing the income of wealthy taxpayers that would otherwise go completely untaxed.
Under the current tax system, capital gains tax is due on the appreciation of assets, such as real estate, stock, or an art collection, only when the owner realizes the gain . Therefore, the increase in the value of an asset is never subject to income tax if the owner holds on to the asset until death.
These unrealized capital gains account for a significant proportion of the assets held by estates ranging from 32 percent for estates worth between $5 million and $10 million to as much as about 55 percent of the value of estates worth more than $100 million.
The estate tax also serves as a modest corrective to other tax rules that provide massive tax benefits to income from wealth, such as the fact that capital gains are taxed at lower rates than wages and salaries. The top 0.1 percent of taxpayers those with incomes above $3.1 million will receive 56 percent of the benefit of the preferential capital gains rates in 2017, worth more than $600,000 apiece. Other tax rules allow part of the income of the very wealthiest to go completely untaxed, even with the estate tax.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Difference Between Federal And State Taxes
Ways To Protect Your Inheritance
OVERVIEW
Received an inheritance of cash, investments, or property? Here are four ways that can help you keep it from being swallowed up by taxes.
For information on the third coronavirus relief package, please visit our American Rescue Plan: What Does it Mean for You and a Third Stimulus Check blog post.
Inheritances are not considered income for federal tax purposes, whether you inherit cash, investments or property. However, any subsequent earnings on the inherited assets are taxable, unless it comes from a tax-free source. You will have to include the interest income from inherited cash and dividends on inherited stocks or mutual funds in your reported income. For example:
- Any gains when you sell inherited investments or property are generally taxable, but you can usually also claim losses on these sales.
- State taxes on inheritances vary check your state’s department of revenue, treasury or taxation for details, or contact a tax professional.
Are Estate Taxes And Inheritance Taxes The Same Thing
Estate taxes and inheritance taxes are somewhat different. Anyone in the United States may have to pay estate taxes. Inheritance taxes are state taxes, and only a handful of states take them. A larger number of states collect state estate taxes, but each state offers a tax exclusion on those taxes.
Most people wont have to pay state inheritance taxes because they dont live in the state requiring it. On the other hand, other people can avoid the estate tax because the exclusion is so high. You would have to inherit many millions of dollars to have to pay federal estate taxes.
Recommended Reading: How To Fill Out Taxes For Self Employed
Puerto Rico And Other Us Possessions
A decedent who is a U.S. citizen born in Puerto Rico and resident at the time of death in a U.S. possession is generally treated, for federal tax purposes, as though he or she were a nonresident who is not a citizen of the United States, so the $5 million exemption does not apply to such a person’s estate. For U.S. estate tax purposes, a U.S. resident is someone who had a domicile in the United States at the time of death. A person acquires a domicile by living in a place for even a brief period of time, as long as the person had no intention of moving from that place.
There’s A Lot Of Confusion About How Things Work When You Receive Property After Someone’s Death Get The Facts Here
Follow @DanCaplinger Follow @DanCaplinger
The death of a loved one is always a difficult time. The last thing most people want when they’re grieving is to have to deal with the IRS and state tax officials. Yet unfortunately, estate and inheritance tax rules in many locations require at least some thought to tax planning.
There’s a lot of confusion about how and when people who inherit property from someone have to pay taxes. Below, we’ll go through several key rules to help you determine when you might have to pay taxes on an inheritance.
You May Like: Will The Tax Deadline Be Extended
Only A Handful Of Small Family
Only roughly 80 small business and small farm estates nationwide will face any estate tax in 2017, according to TPC. TPCs analysis defined a small-business or small farm estate as one with more than half its value in a farm or business and with the farm or business assets valued at less than $5 million. Furthermore, TPC estimates those roughly 80 estates will owe less than 6 percent of their value in tax, on average.
These findings are consistent with a 2005 Congressional Budget Office study finding that of the few farm and family business estates that would owe any estate tax under the rules scheduled for 2009, the overwhelming majority would have sufficient liquid assets in the estate to pay the tax without having to touch the farm or business. The current estate tax rules are even more generous than those assumed in this analysis.
Furthermore, special estate tax provisions such as the option to spread payments over a 15-year period and at low interest rates allow the few taxable estates that would face any liquidity constraints to pay the tax without selling off any farm assets.
What Is An Inheritance Tax
Most people think of an inheritance tax as being any tax that is levied on an estate of a deceased person. There are two types of taxes in this category.
- Inheritance Tax. This tax is charged to a person who receives an inheritance. The person who receives the inheritance is responsible for filing the tax return to report what was received.
- Estate Tax. The deceased person’s estate is charged this tax before anything is distributed to the beneficiaries. The personal representative or executor of the estate must file the tax return to report the total value of the estate.
Recommended Reading: Who Can File Ez Tax Form
Federal Inheritance Tax For Expatriates
While there is no New Federal Inheritance Tax for covered transfers, there is IRC Section 2801 along with proposed regulations which expatriates should be aware of. By way of brief background, Expatriation is the formal process of either renouncing US citizenship or relinquishing a green card for a permanent resident that is considered a long-term lawful permanent resident. The tax laws involving expatriation are very complicated and unfortunately, inexperienced attorneys or self-purported tax experts who dabble in this area tend to get the information incorrect and then pass it on to other unsuspecting taxpayers like an adult version of the telephone game. One common misconception is the way inheritance tax works after expatriation. Before expatriating, Taxpayers should consult with a Board-Certified Tax Law Specialist. Lets go through a simple analysis of how and when these types of taxes may kick-in for expatriates.
Who Has To Pay An Inheritance Tax
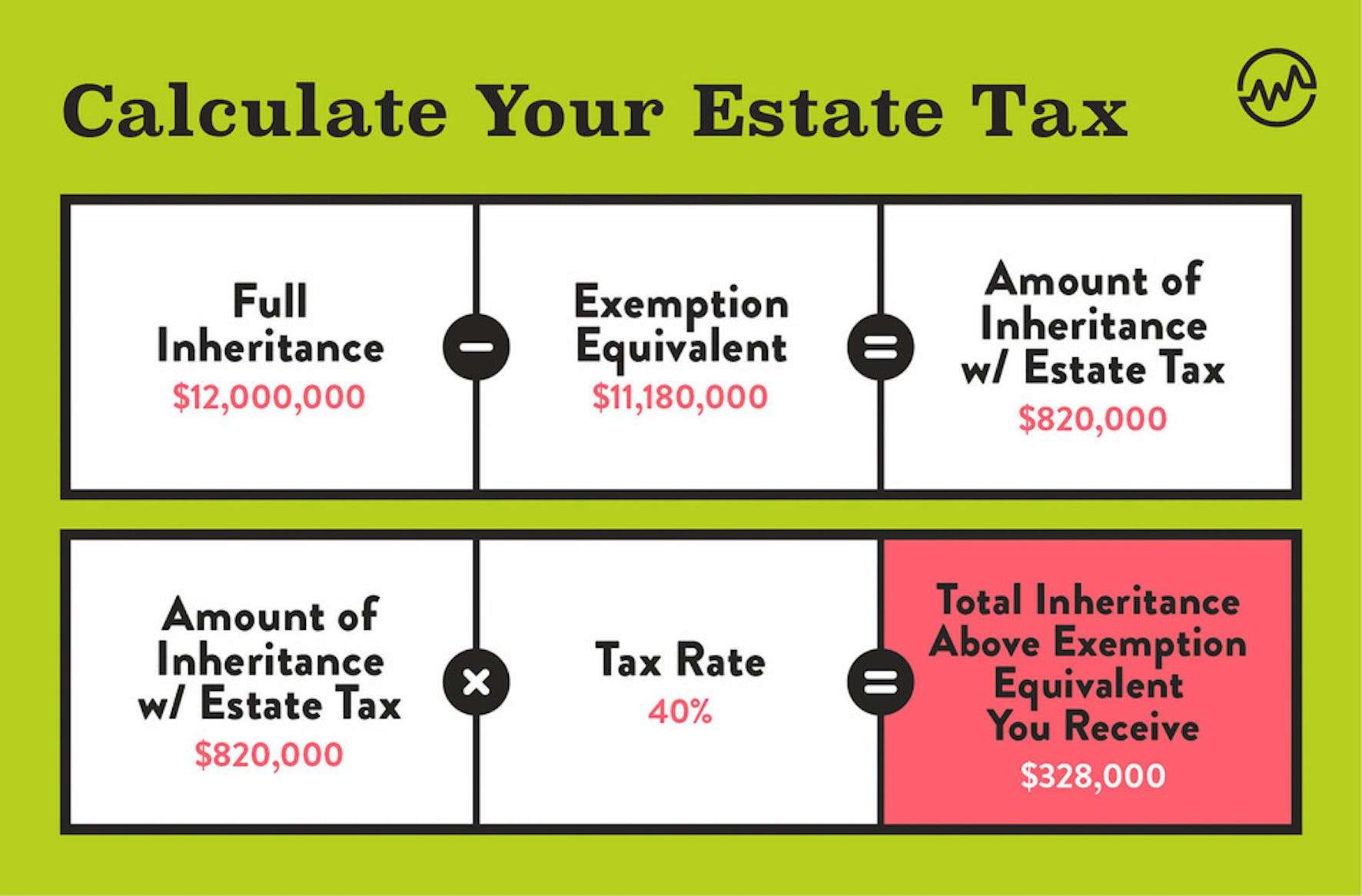
As you can see, there are only six states with inheritance taxes. Overall, inheritance tax rates vary based on the beneficiarys relationship to the deceased person.
Spouses are automatically exempt from inheritance taxes. That means that if your husband or wife passes away and leaves you a condo, you wont have to pay an inheritance tax at all even if the property is located in one of the states mentioned above. Since the Supreme Courts ruling, the same rule applies to same-sex spouses.
Children and grandchildren who receive an inheritance arent taxed either if the deceased person lived in any of these four states: New Jersey, Kentucky, Iowa or Maryland. The bad news then is that all other relatives and kids and grandkids receiving property from Pennsylvania and Nebraska may have to pay up.
Don’t Miss: Do Not For Profits Pay Property Taxes
