What If You Sell A House Less Than 2 Years After Buying It
You probably cannot qualify for the $250,000 single/$500,000 married-filing-jointly exemption from gains on selling your primary residence. Thats because to qualify for that exemption, you must have used the home in question as your primary residence for at least two of the previous five years, and you generally cant use the exemption twice within two years.
However, there are exceptions for certain circumstances: Military service, death of a spouse, and job relocation are the most common reasons that might allow you to take at least a partial exemption. The IRS has a worksheet for determining an exclusion limit see Topic 701.
Have Investment Income We Have You Covered
With TurboTax Live Premier, talk online to real experts on demand for tax advice on everything from stocks, cryptocurrency to rental income.
-
Estimate your tax refund andwhere you stand
-
Know how much to withhold from your paycheck to get
-
Estimate your self-employment tax and eliminate
-
Know which dependents credits and deductions
-
Estimate capital gains, losses, and taxes for cryptocurrency sales
-
See which education credits and deductions you qualify for
The above article is intended to provide generalized financial information designed to educate a broad segment of the public it does not give personalized tax, investment, legal, or other business and professional advice. Before taking any action, you should always seek the assistance of a professional who knows your particular situation for advice on taxes, your investments, the law, or any other business and professional matters that affect you and/or your business.
How These Strategies Apply To You:
While avoiding the capital gains tax may seem the obvious choice when structuring your estate, there are a few factors you should consider.
Most importantly, we always urge clients to make the right decision based on the totality of their current needs and future goals regardless of the incurrence of any capital gains tax. Some of the things you may want to consider are:
- Do you need the money from the sale of your house in the near future, or can you wait to include it in your estate for heirs?
- Do any of your children want the house, or would they prefer money? Will multiple children be able to work together amicably if gifted property to split?
- Is most of your money tied up in your property, making it the main source of generational wealth transfer?
- Are you single, or is your spouse still living and likely to outlive you?
As mentioned above, there has been some talk about possibly eliminating the step-up in basis. In effect, capital gains would be taxed, even on inherited assets. For now, however, these proposed changes are far from assured in fact, no details on any specific legislation have been released, much less presented or voted on in Congress.
At Cardinal, we emphasize education when it comes to our clients. We make sure you are well informed about all your options before making these important decisions. Laws can change. And even the most straightforward of estates can be made complicated by complex tax codes and opaque rules.
Don’t Miss: Do You Pay Federal Taxes On Unemployment
Take Advantage Of Tax
When you invest your money through a retirement plan, such as a 401, 403, or individual retirement account , it will grow without being subject to immediate taxes. You can also buy and sell investments within your retirement account without triggering capital gains tax.
In the case of traditional retirement accounts, your gains will be taxed as ordinary income when you withdraw money, but by then, you may be in a lower tax bracket than when you were working. With Roth IRA accounts, however, the money you withdraw will be tax-freeas long as you follow the relevant rules.
For investments outside of these accounts, it might behoove investors near retirement to wait until they stop working to sell. If their retirement income is low enough, their capital gains tax bill might be reduced, or they may be able to avoid paying any capital gains tax. But if theyre already in one of the no-pay brackets, theres a key factor to keep in mind: If the capital gain is large enough, it could increase their total taxable income to a level where they would incur a tax bill on their gains.
Capital losses can offset your capital gains as well as a portion of your regular income. Any amount left over after that can be carried over to future years.
Do You Pay Capital Gains If You Lose Money On A Home Sale
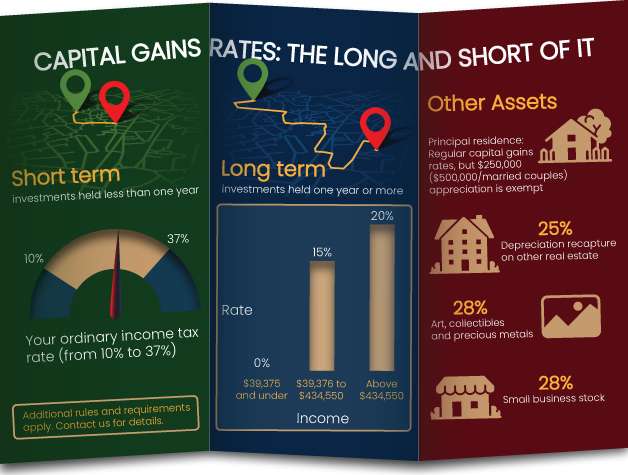
You cant deduct the losses on a primary residence, nor can you treat it as a capital loss on your taxes. You may be able to do so, however, on investment property or rental property. Keep in mind that gains from the sale of one asset can be offset by losses on other asset sales up to $3,000 or your total net loss, and such losses may be eligible for carryover in subsequent tax years.
If you sell below-market to a relative or friend, the transaction may subject the recipient to taxes on the difference, which the IRS may consider a gift. Also remember that the recipient inherits your cost basis for purposes of determining any capital gains when they sell it, so the recipient should be aware of how much you paid for it, how much you spent on improvement, and costs of selling, if any.
Read Also: What Percentage Is Taken Out For Federal Taxes
First How Much Is Your Gain
Many people mistakenly believe that their gain is simply the profit on the sale: “We bought it for $100,000 and sold it for $650,000, so that’s a $550,000 gain, and we’re $50,000 over the exclusion, right?”. It’s not so simple — a good thing, since the fine print can work to your benefit in such instances.
Your gain is actually your home’s selling price, minus deductible closing costs, selling costs, and your tax basis in the property.
Deductible closing costs include points or prepaid interest on your mortgage and your share of the prorated property taxes.
Examples of selling costs include real estate broker’s commissions, title insurance, legal fees, advertising costs, administrative costs, escrow fees, and inspection fees.
So, for example, if you and your spouse bought a house for $100,000 and sold for $650,000, but you’d added $20,000 in home improvements, spent $5,000 fixing the place up for the sale, and paid the real estate brokers at least $25,000, the exclusion plus those costs would mean you’d owe no capital gains tax at all.
For more information, see IRS Publication 551, Basis of Assets, and look for the section on real property.
Exclusion For Sale Of Primary Residence
Special rules apply to the capital gains when you sell your primary residence. If you meet the ownership and use tests, you can exclude up to $250,000 if you are unmarried, or $500,000 if you are married and filing a joint return. The tests mentioned are met if you own and use your house as your primary residence for two out of the five years immediately preceding the date of sale.
You can meet the ownership and use tests for different two-year periods, but both tests must be met within the five years immediately preceding the date of sale. This exclusion of capital gains is sometimes referred to as a Section 121 exclusion.
Recommended Reading: Are Charitable Contributions Still Tax Deductible
Exempt Capital Gains Balance
When you filed Form T664 for your shares of, or interest in, a flow-through entity, the elected capital gain you reported created an exempt capital gains balance for that entity.
Note
Generally, your ECGB expired after 2004. If you did not use all of your ECGB by the end of 2004, you can add the unused balance to the adjusted cost base of your shares of, or interest in, the flow-through entity.
Example
Andrew filed Form T664 for his 800 units in a mutual fund trust with his 1994 income tax and benefit return. He designated the fair market value of the units at the end of February 22, 1994, as his proceeds of disposition. Andrew claimed capital gains reductions of $500 in 1997 and $600 in 1998. At the end of 2003, his exempt capital gains balance was $2,250. In 2004, he had a $935 capital gain from the sale of 300 units. This left him with an unused balance of $1,315 at the end of 2004. In future years, he can only add the unused ECGB to the cost of any remaining units.
1. ECGB carryforward to 2004
6. Unused ECGB at the end of 2004
6
The unused ECGB expired after 2004 so Andrew can add this amount to the adjusted cost base of his shares of, or interest in, the flow-through entity.
Invest In Distressed Communities
The 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act created a new tax benefit allowing investors to defer and minimize capital gains taxes when reinvesting their capital gains into a Qualified Opportunity Fund. QOFs invest in distressed communities throughout the U.S., and this tax break is meant to help create jobs and propel economic growth in these areas.
Some rules do apply. The taxpayer must reinvest capital gains into a QOF within 180 days. The longer the QOF investment is held, the more tax benefits apply:
-
Holding for at least five years excludes 10% of the original deferred gain.
-
Holding for at least seven years excludes 15% of the original deferred gain.
-
Holding for at least 10 years can eliminate most, if not all, of the deferred gains.
Also Check: How Do I Track My Taxes
Remain In Lower Tax Bracket
Capital gain tax rates are charged as per an individuals income tax. Therefore, those in lower tax brackets may pay less.
To avoid being in a higher tax bracket, consider measures such as not selling too many assets a year and making retirement plan payments. In addition, investing in non-taxable incomes like municipal bonds, college savings, and health savings account contributions will ensure you remain in a lower tax bracket.
What Happens If I Inherit Assets
A CGT event is generally only triggered when you sell inherited assets.
If the person who passed away bought the assets after CGT was introduced on 20 September 1985, then the person inheriting the assets will need to determine the cost base. Depending on the asset, the cost base could be:
- The existing cost base of the deceased person who originally bought the assets or
- The market value of the assets at the time of death
If, however, the person who passed away acquired the assets before 20 September 1985, then the person inheriting them is said to have acquired the asset at the time of death. In most cases, the cost base will then be the market value of the assets at that time.
For more information on inherited assets and CGT, visit the ATO website.
Recommended Reading: How To Pay Federal And State Taxes
Chapter 1 General Information
This chapter provides the general information you need to report a capital gain or loss.
Generally, when you dispose of a property and end up with a gain or a loss, it may be treated in one of two ways:
- as a capital gain or loss
- as an income gain or loss
When you dispose of a property, you need to determine if the transaction is a capital transaction or an income transaction. The facts surrounding the transaction determine the nature of the gain or loss.
For more information on the difference between capital and income transactions, see the following archived interpretation bulletins:
For information on how to report income transactions, see Guide T4002, Self-employed Business, Professional, Commission, Farming, and Fishing Income.
Invest In An Opportunity Zone

When you invest in an Opportunity Zone fund, you can achieve three substantial tax benefits.
The goal of these funds is to incentivize investments in housing, small businesses, and infrastructure in economically-depressed areas across the US.
Besides capital gains from the sale of stocks, you can also roll the gains from selling other assets, such as real estate and bonds, into an Opportunity Zone investment.
The types of businesses eligible for Opportunity Zone funds are quite wide-ranging, so you can select investments that are low in risk and high in return.
For example, buying older buildings in Opportunity Zones, renovating them at a reinvestment cost, then managing them as rental properties is one of the most high-yielding strategies you can use to take advantage of this new tax bill.
When you purchase real estate in Opportunity Zones, you have the potential to buy properties that are dramatically cheaper than other parts of the the US due to their location.
However, not all opportunity zones are created equal, and there are a number of places, like Puerto Rico for example, that qualify for opportunity zone investing that have huge upside potential as it is a growing tourism destination that commands very high rents.
Recommended Reading: How Much Money To Do Taxes
How To Get The Most Out Of The Capital Gains Exemption
By Jason Heath on May 9, 2017
Not everyone qualifies for the lifetime capital gains exemption, but there are other options
Q: I would be interested in understanding the $500,000 lifetime capital gains exemption and what it can be used for.
Can I chip away at it by applying annual small investment capital gains?
Greg
A: Canada has had different capital gains exemptions over the years. Until 1972, capital gains were completely exempt from tax.
There was a broad $500,000 lifetime capital gains exemption that was introduced in 1985 that applied to any asset. It was subsequently reduced to $100,000 in 1988, Greg. It was wiped out in 1994, but taxpayers were allowed to bump up the cost of capital assets at that time without selling if they filed the appropriate election.
An enhanced lifetime capital gains exemption limit was introduced in 1994 for $500,000, but it only applied to qualified small business corporation shares and qualified farm properties. In 2006, qualified fishing properties became eligible for the exemption. In 2008, it was increased to $750,000 and in 2014, it was set at $800,000 to be indexed every year thereafter with CPI inflation.
Currently, the capital gains exemption is $835,714 for QSBC shares or $1,000,000 for qualified farm or fishing properties.
Qualified small business corporation shares do not include publicly traded shares, mutual funds or exchange-traded funds , so most investors do not own QSBC shares, Greg.
Donate Appreciated Investments To Charity
Investments that have appreciated in value from when you purchased them can be donated to charity. You will receive a charitable donation tax deduction for the fair market value of the investment on the date of the charitable donation and will not pay capital gains tax on the investments donated to the charity.
Read More:Tax-Wise Charitable Giving: Donating Appreciated Assets
You May Like: How Much Tax Do You Pay On Social Security
What Is A Capital Gain
Capital gains are profits you make from selling an asset. Typical assets include businesses, land, cars, boats, and investment securities such as stocks and bonds. Selling one of these assets can trigger a taxable event. This often requires that the capital gain or loss on that asset be reported to the IRS on your income taxes.
How To Avoid Capital Gains Tax On Home Sales
Want to lower the tax bill on the sale of your home? There are ways to reduce what you owe or avoid taxes on the sale of your property. If you own and have lived in your home for two of the last five years, you can exclude up to $250,000 of the gain from taxes.
Adjustments to the cost basis can also help reduce the gain. Your cost basis can be increased by including fees and expenses associated with the purchase of the home, home improvements, and additions. The resulting increase in the cost basis thereby reduces the capital gains.
Also, capital losses from other investments can be used to offset the capital gains from the sale of your home. Large losses can even be carried forward to subsequent tax years. Lets explore other ways to reduce or avoid capital gains taxes on home sales.
Don’t Miss: Is Ny 529 Tax Deductible
What Can I Do If I Make A Loss On An Asset
If you make a profit when selling one item, but a loss when selling another, you can deduct the loss from the gain when working out how much tax you owe.
You can carry forward any losses that havent been used to offset gains for up to four years. Even if you dont owe any CGT, its still important to submit details of losses in your tax return to make it easier to offset them against a potential gain in future years.
You may also be able to reduce your tax bill by deducting any costs related to improving your assets. For example, you could deduct the costs of restoring a valuable painting or making improvements to your holiday home.
Limit On The Deduction And Carryover Of Losses
If your capital losses exceed your capital gains, the amount of the excess loss that you can claim to lower your income is the lesser of $3,000 or your total net loss shown on line 16 of Schedule D . Claim the loss on line 7 of your Form 1040 or Form 1040-SR. If your net capital loss is more than this limit, you can carry the loss forward to later years. You may use the Capital Loss Carryover Worksheet found in Publication 550, Investment Income and Expenses or in the Instructions for Schedule D PDF to figure the amount you can carry forward.
Also Check: How To Retrieve 1040 Tax Return
