Explanation Of Claim Codes
Claim code 0
This code represents no claim amount. If the federal claim code is 0 because the employee is a non-resident, the provincial claim code must also be 0. This code may also be used if the employee indicated they have more than one employer or payer at the same time and have entered 0 on the front page of Form TD1 for 2022.
Claim codes 1 to 10
The claim code amounts do not appear on either the federal or the provincial TD1 form.
You match the “Total claim amount” reported on your employee’s or pensioner’s TD1 forms with the appropriate claim codes. Then, you look up the tax for the employee’s pay under the claim code in the federal and provincial tax tables for the pay period.
Indexing of claim codes amounts
The credits that apply to each federal and provincial claim code have been automatically changed in the tax tables by the indexing factor for the current year. If your employee did not complete the federal and provincial TD1 forms for 2022, you continue to deduct income tax using the same claim code that you used last year.
| Total claim amount |
|---|
| E |
How To Calculate Federal Income Tax Withholding Using The Wage Bracket Method
In IRS Publication 15-A, find the tables marked âWage Bracket Percentage Method Tables.â Use the table corresponding to your employeeâs pay period.
Check form W-4 to determine whether the employee files income tax as married or single and the number of allowances they claim.
Find the employeeâs gross wage for the pay period in columns A and B. The wage should be over the amount found in column A but under the amount found in column B.
Subtract the amount found in Column C.
Multiply the result by the percentage found in Column D.
Check form W-4 to determine if the employee requests additional tax withheld from each paycheck. If they do, add that amount to the final number.
The end result is the amount you should withhold from the employeeâs paycheck for that pay period.
The Percentage Method is much more complicatedânot recommended if youâre doing this alone. If you want to learn more about the Percentage Method, you can read all about both methods in IRS Publication 15-A.
Once youâve figured out how much income tax to withhold from your employeesâ paychecks, your next step is to figure out how much FICA to withhold , and how much youâll be required to pay on their behalf.
How Much Do Employers Pay In Payroll Taxes
So, how much is payroll tax? The cost of payroll taxes largely depends on the number of employees you have and how much you pay your employees. Why? Because payroll taxes are a percentage of each employees gross taxable wages and not a set dollar amount.
Payroll tax includes two specific taxes: Social Security and Medicare taxes. Both taxes fall under the Federal Insurance Contributions Act , and employers and employees pay these taxes.
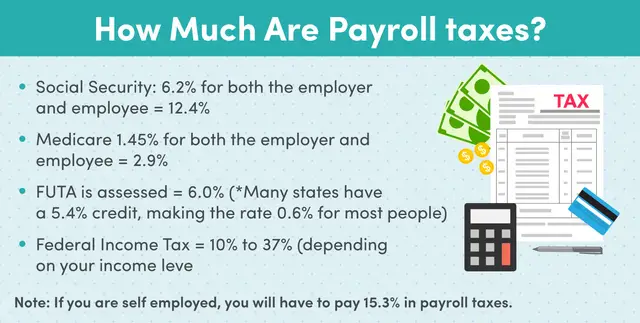
Payroll tax is 15.3% of an employees gross taxable wages. In total, Social Security is 12.4%, and Medicare is 2.9%, but the taxes are split evenly between both employee and employer.
So, how much is the employer cost of payroll taxes? Employer payroll tax rates are 6.2% for Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare.
| Know exactly how much youll pay as the employer without having to do the calculations yourself. Get a FREE trial of Patriots online payroll and skip the calculations! |
If you are self-employed, you must pay the entirety of the 15.3% FICA tax, plus the additional Medicare tax, if applicable .
Read Also: Is Plasma Donation Taxable
What Do I Need To Have In Place Before Issuing Pay Checks
- Establish a standard 7-day workweek for purposes of overtime calculations.
- Many employers choose Monday 12:00 a.m. to Sunday 11:59 p.m.
- Employers cant change their standard work week to avoid paying overtime, but they can change it for business reasons if they provide employees advance notice.
- Establish a basis of pay
- Hourly: Paid a set amount for each hour worked
- Salaried: Paid a set amount each pay period
- Salaried as a basis of pay doesnt mean an employee doesnt earn overtime pay when their hours exceed 40 in a workweek. See calculation of overtime below
- If paid twice per month or monthly, overtime calculations may require you to look at the previous payperiod to determine if an employees hours exceeded 40 in a workweek.
So The Cra Groups Income Tax And Payroll Taxes Together
Yes, they do. In Canada, the CRA is the mothership for income taxes and payroll taxes. The Employers Guide to Payroll Deductions and Remittances is a comprehensive reference resource. Within the deduction tables, theres also a payroll deductions online calculator .
Again, this is stuff that’s a ton easier when you use software. Here’s more information on payroll deductions and payroll contributions.
Also Check: Taxes For Doordash
Payroll Taxes: What Are They And What Do They Fund
Payroll taxes fund social insurance programs including Social Security and Medicare and are the second-largest source of revenues for the federal government. In 2019, the most recent year for which data were not affected by temporary distortions resulting from the pandemic, payroll taxes made up 36 percent of total federal revenues. Most working Americans are subject to payroll taxes, which are usually deducted automatically from an employees paycheck. Employers are also often subject to those types of taxes.
The vast majority of federal payroll taxes go towards funding Social Security and Medicare:
- Taxes directed to the Social Security program were created by the Federal Insurance Contributions Act and are levied equally on employers and employees on all wages up to a certain level.
- Medicare taxes for its Hospital Insurance program are also part of FICA and are levied equally on employers and employees on all wages. The HI trust fund also receives inflows from a supplemental tax on high earners.
A few other types of federal payroll taxes also fund smaller programs:
- Employers pay taxes to fund the Unemployment Insurance program.
- Programs to fund retirement for federal employees and railroad workers also receive revenue from payroll taxes.
What Can You Do If You Are Receiving Cash Wages
File Appropriate Tax Documents: Make your best effort to follow the tax laws. Pay your share of income taxes, Social Security taxes, and Medicare taxes. Fill out the appropriate forms so the government knows that you are paying your fair share of taxes, which will help you to preserve the benefits that you deserve.
If You Do Not Receive a W-2: File a Substitute W-2 form that will take the place of a standard W-2. The substitute form is IRS Form 4852 and can be obtained from the IRS website at www.irs.gov/formspubs.
Keep Detailed Records of Your Hours & Pay: Keep track of the number of hours you work and the amounts you are paid. If the employer does not have documentation of your hours and pay, your records will be critical in showing the amount of taxes that your employer owes.
Report Your Employer: If you do not receive a W-2 and believe that your employer is committing tax fraud, report your employer to the three government agencies that collect taxes Californias EDD, the Federal IRS, and the Federal Social Security Administration. See the Remedies section below.
Recommended Reading: Efstatus.taxact.com
Federal Payroll Tax Rates
At the federal level, in addition to income tax, there are two categories of employment taxes: FUTA and FICA. Well cover each briefly as youll process these as tax deductions on employees paychecks. You must also pay these taxes on your employees behalf, regardless of the state in which you operate.
- Income tax: The tax rate is based on withholdings chosen on the employees W-4 form.
- FUTA: This 6% federal tax is to cover unemployment in most cases, youll be credited back 5.4% of this amount for paying your state taxes on time, resulting in a net tax of 0.6%.
- FICA: This 15.3% federal tax is made up of two parts: 12.4% to cover Social Security and 2.9% to cover Medicare. For employees earning more than $200,000, the Medicare tax rate goes up by an additional 0.9% therefore, FICA can range between 15.3% and 16.2%.
Calculating The Withholding And Employer’s Portion Amounts
You simply multiply an employee’s gross wage payment by the applicable tax rate to determine how much you must withhold and how much you must pay in Social Security and regular Medicare taxes.
The Social Security and regular Medicare taxes owed are unaffected by the number of withholding exemptions an employee may have claimed for income tax withholding purposes.
You May Like: Doordash Paying Taxes
You’re Now Leaving Chase
Chase’s website and/or mobile terms, privacy and security policies don’t apply to the site or app you’re about to visit. Please review its terms, privacy and security policies to see how they apply to you. Chase isnt responsible for any products, services or content at this third-party site or app, except for products and services that explicitly carry the Chase name.
A Payroll Tax Definition
Payroll taxes are part of the reason your take-home pay is different from your salary. If your health insurance premiums and retirement savings are deducted from your paycheck automatically, then those deductions can result in paychecks well below what you would get otherwise. When you start a new job and fill out a W-4 tax withholding form, your employer starts deducting state and federal payroll taxes from your earnings to pay for Social Security and Medicare.
Social Security taxes began in 1937, at a modest rate of 2%. Medicare hospital insurance taxes didnt kick in until 1966, at a rate of 0.7%. Rates have climbed since then, of course, with the rate increase for Social Security taxes outpacing the rise in Medicare hospital insurance taxes.
In 2020, payroll taxes only apply to the first $137,700 of income, and in 2021 they will apply to the first $142,800. The income cap on payroll taxes has led some to criticize the payroll tax. Those who want to reform the payroll tax call it a regressive tax one that doesnt require the rich to pay more.
In tough economic times like the Great Recession, Congress cuts payroll taxes to give Americans a little extra take-home pay. Recently, President Trump allowed employers to temporarily suspend withholding and paying payroll taxes in an effort to offer COVID-19 relief. When cuts like these expire, it reignites the debate over how payroll taxes work. President-elect Biden has proposed raising the income cap on payroll taxes.
You May Like: Protest Taxes Harris County
How Do Payroll Taxes Work In Other Countries
Many countries in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development , a group of nations with high-income economies, also fund their social insurance programs with payroll taxes. While the Social Security systems of other countries take different forms, most provide government-financed pensions that provide income assistance for retirees, similar to that of the United States.
Despite that similarity, there is much variation in how other OECD countries impose payroll taxes on their citizens. Countries such as the Netherlands, Sweden, Germany, and Canada have caps on taxable earnings that are lower than in the United States others, such as Norway and Ireland, tax all earnings. Generally, countries with higher payroll tax rates have lower caps, while countries with lower payroll tax rates, like the United States, tend to have higher caps or no caps at all. In some OECD countries, social insurance programs are funded through other sources such as income taxes or excise taxes.
Certain countries, like the United Kingdom and Austria, have a bracketed payroll tax structure that levies the payroll tax at different rates depending on total income, similar to how the United States levies income taxes. In the United Kingdom, that bracketed system is regressive in structure, while in Austria it is progressive.
Social Security Tax Rate Calculation

The Social Security Tax rate is 12.4%, which is split by the employer and the employee equally. The employer pays 6.2% while the employee pays 6.2%. The maximum income amount based on the 2021 tax year that can be subjected to Social security Tax is $142,800. Any earnings above $142,800 are not subject to this tax.
For example, if an employees gross wage is $2,083.33. If the employee wants to find out the Social Security Tax to deduct, he simply multiplies the gross wage by 6.2%. The Social Security Tax to withhold from the employees paycheck is $129.17.
Recommended Reading: Prontotaxclass
Ontario Indexing For 2022
For 2022, the provincial income thresholds, the personal amounts, and the tax reduction amounts have been indexed. They have been changed based on changes in the consumer price index.
The indexing factor for January 1, 2022, is 2.4%. The tax credits corresponding to the claim codes in the tables have been indexed accordingly. Employees will automatically receive the indexing increase, whether or not they file Form TD1ON, 2022 Ontario Personal Tax Credits Return.
What If Your Pay Period Is Not In This Guide
This guide contains the most common pay periods: weekly, biweekly , semi-monthly, and monthly. If you have unusual pay periods, such as daily , or 10, 13, or 22 pay periods a year, go to the Guide T4008, Payroll Deductions Supplementary Tables, or the Payroll Deductions Online Calculator to determine tax deductions.
Read Also: Payable Doordash 1099
Payroll Taxes Vs Income Taxes
There is a distinction between a payroll tax and an income tax, although both are deducted from paychecks. Payroll taxes are used to fund specific programs. Income taxes go into the general funds at the U.S. Treasury.
Everyone pays a flat payroll tax rate up to a yearly cap. Income taxes, however, are progressive. Rates vary based on an individual’s earnings.
State income tax, if any, goes into the state’s treasury.
When To Get A Payroll Account
Do you need a payroll account with the CRA?
First, determine if youre an employer. According to the CRA youre considered an employer if you pay salaries, wages , bonuses, vacation pay, or tips to your employees. You may also fall under the employer category if you provide specific taxable benefits to staff, such as automobiles or spending allowances. Even if you have no employees or employ seasonal staff, you must still report a nil remittance once per quarter.
Employers must register for a payroll program account with the CRA. To do so, youll need all employees Social Insurance Numbers and have them fill out form TD1 which should be done within seven days of hiring.
Once you register for an account youll be provided with 15-digit payroll account number. The first nine digits are your unique business number. The following two letters are the program code RP for the payroll program and the last four identify each payroll account your business has . Your payroll account number wont change, and can be used to remit all deductions from employees.
Don’t Miss: Is Donating Plasma Taxable
Federal Payroll Return Requirements
Along with actually depositing your federal payroll taxes, you also have an obligation to file periodic returns that show how you computed your tax liabilities. As is true for deposits, the returns you must file for your income and FICA taxes are different from the returns you file for your FUTA taxes.
Your Obligations To Employees
As an employer, you have three payroll obligations to employees:
1) Paying Wages
Employees must be paid on a recurring schedule typically, businesses opt for either monthly or bi-weekly payments.
Wondering how to pay employee salaries? Some SMBs still use physical checks, but this requires manual tracking and entry into payroll systems. Many now opt for direct deposit, which sends wages directly to staff bank accounts. Setting up direct deposit requires you to create a business account with the bank of your choice and then collect employee banking data to ensure funds are sent to the correct accounts. You can choose transfer these funds manually each pay period from your online banking portal, use a payroll system that integrates this function or pay a third-party provider to complete this task.
2) Remitting Deductions
The Canadian Revenue Agency requires you to collect specific deductions from employee pay:
- Employment Insurance
3) Ensuring Compliance
In addition to paying staff on a recurring schedule, the CRA typically requires small businesses to remit all source deductions money taken from employee wages by the 15th of the month after staff are paid. You must also send T4 and T4A tax slips to employees by the last day of February of the calendar year following the deduction period. For example, T4 slips for the 2019 calendar year must be sent out by February 29th, 2020.
Recommended Reading: Www..1040paytax.com
What Is Withholding Tax How Does A Withholding Tax Work
A withholding tax is an income tax that a payer remits on a payee’s behalf . The payer deducts, or withholds, the tax from the payee’s income.
Here’s a breakdown of the taxes that might come out of your paycheck.
-
Social Security tax: 6.2%. Frequently labeled as OASDI , this tax typically is withheld on the first $137,700 of your wages in 2020 . Paying this tax is how you earn credits for Social Security benefits later.
»MORE:See what the maximum monthly Social Security benefit is this year
-
Medicare tax: 1.45%. Sometimes referred to as the hospital insurance tax, this pays for health insurance for people who are 65 or older, younger people with disabilities and people with certain conditions. Employers typically have to withhold an extra 0.9% on money you earn over $200,000.
-
Federal income tax. This is income tax your employer withholds from your pay and sends to the IRS on your behalf. The amount largely depends on what you put on your W-4.
-
State tax: This is state income tax withheld from your pay and sent to the state by your employer on your behalf. The amount depends on where you work, where you live and other factors, such as your W-4 .
-
Local income or wage tax: Your city or county may also have an income tax. This money might go toward such expenses as the bus system or emergency services.
See what else you can do for your business
-
Learn about coronavirus relief options for small businesses and the self-employed.
|
Employer pays |
