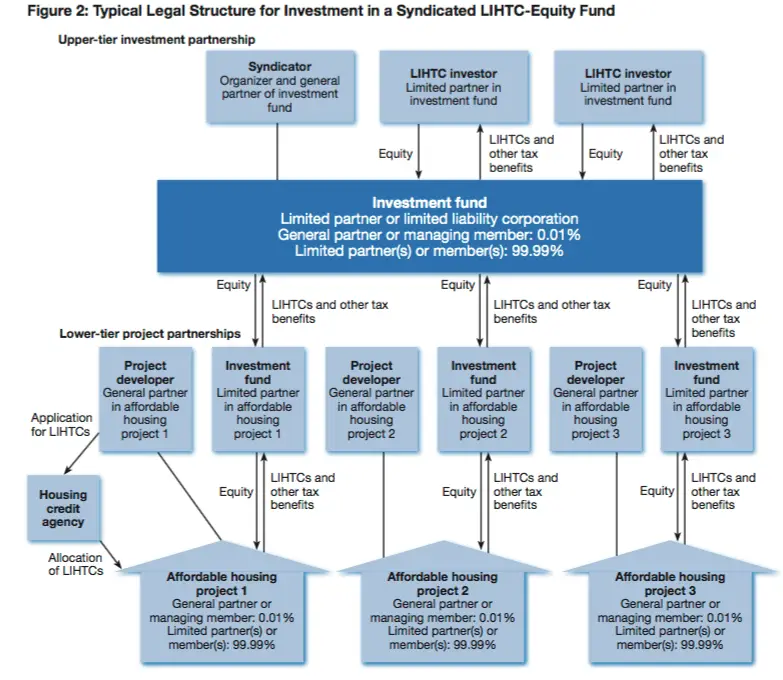
Calculating Costs And Benefits Of Lihtc
It is estimated that the LIHTC costs around $9.5 billion per year in the United States. It is by far the largest federal program that encourages the creation of affordable rental housing for households with low incomes.
Supporters see it as a well-tuned program that increases the affordable housing stock considerably. The LIHTC addresses a major failure in the market, and that is the lack of quality, affordable housing for low-income communities.
Critics will argue that the federal subsidy per unit of new construction is actually higher than it needs to be. This is because of the wide range of intermediaries that are involved in its financing each of which is compensated for their input. As a result of this, a lot of the tax subsidy doesnt go directly into creating new rental housing stock.
The Irs Has Lihtc Forms To Fill Out
- Form 8586 is used to claim the credit on the companys tax return.
- Form 8609 is used to obtain a housing credit allocation for a building.
- Form 8609-A is an annual report showing compliance with the requirements.
You may see these forms described on a search page, but they are not for individuals who want to apply for a low-income housing tax credit. The real estate development companys tax professionals must complete these forms.
What Has Been Liscs Involvement
Since the initiation of Section 4, LISC has invested Section 4 resources to build the capacity of 1,168 CDCs in 299 cities and rural communities across 48 states, the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico.
LISC Section 4 investments have positively impacted communities as diverse as the Mid South Delta small urban communities such as Providence, Rhode Island larger sprawling cities such as Phoenix, Arizona and urban cores such as the Bay Area in California.
From 2009 to 2018, LISCs Section 4 investments in both rural and urban areas have leveraged more than $6 billion in direct real estate investments and have assisted in building, renovating, or preserving approximately 33,099 affordable housing units.
LISC has also invested Section 4 money in programs that address critical national challenges. These initiatives support a wide variety of programs such as green building, the development of healthcare and childcare facilities, the strengthening of neighborhood commercial corridors, job creation, and community safety.
Also Check: Why Do My Taxes Still Say Processing
This Tax Credit Provides Builders Money To Create Affordable Housing
The Low-Income Housing Tax Credit is a tax credit for real estate developers and investors who make their properties available as affordable housing for low-income Americans. Its paid for by the federal government and administered by the states, according to their own affordable housing needs. Since the programs inception, nearly 3 million affordable housing units have been constructed with the help of the tax credit.
How Real Estate Developers Receive The Tax Credit

Usually, a group of investors creates a business entity to build or renovate structures to create housing that qualifies as affordable. In order to meet the requirements, the housing project must go through a qualification process, based on the availability of units in the project for use by low-income individuals.
To receive low-income housing tax credits, properties must be qualified. To qualify, a building must:
- Include a specific minimum percentage of affordable units.
- Remain affordable for a minimum of 30 years.
The tax credits come in two types:
- A 4% credit for new construction that involves other government assistance or buying an existing project.
- A 9% credit for new construction with no government assistance.
Also Check: What Home Improvements Are Tax Deductible 2021
The Tax Credit Allocation Process
Each state has an annual tax credit authority equal to $2.00 per state resident. Michigan’s annual authority is approximately $20 million. The process used by MSHDA to evaluate applications and allocate credit is described in Michigan’s Qualified Allocation Plan. Briefly, an application including detailed financial information and various supporting documentation, must be submitted to MSHDA for review and evaluation. The process involves three stages – reservation, commitment, and allocation of credit. The final determination of how much credit will actually be awarded is made at the allocation stage.
Calculating Costs And Benefits
The LIHTC is estimated to cost around $9.5 billion per year. It is by far the largest federal program encouraging the creation of affordable rental housing for low-income households. Supporters see it as an effective program that has substantially increased the affordable housing stock for more than 30 years. LIHTC addresses a major market failurethe lack of quality affordable housing in low-income communities. Efficiencies arise from harnessing private-sector business incentives to develop, manage, and maintain affordable housing for lower-income tenants.
Critics of the LIHTC argue that the federal subsidy per unit of new construction is higher than it needs to be because of the various intermediaries involved in its financingorganizers, syndicators, general partners, managers, and investorseach of whom are compensated for their efforts. As a result, a significant part of the federal tax subsidy does not go directly into the creation of new rental housing stock. Critics also identify the complexity of the statute and regulations as another potential shortcoming. Another downside is that some state housing finance authorities tend to approve LIHTC projects in ways that concentrate low-income communities where they have historically been segregated and where economic opportunities may be limited. Finally, while the LIHTC may help construct new affordable housing, maintaining that affordability is challenging once the required compliance periods are over.
You May Like: Can You Do Your Taxes Late
What Is The Low Income Housing Tax Credit Program
The Low-Income Housing Tax Credit subsidy program allows low and moderate-income renters to pay rent at an affordable rate.
LIHTC participants have a unit assigned to them by a federal housing authority, or private property management company.
The monthly rent is not adjusted by income, but it is lower than the market rate. Low-income renters may not qualify for some LIHTC properties. The frequency of waiting list openings varies, depending on the area.
Read this guide to learn how to apply to the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit program.
Start the guide at Part 1: Who Qualifies for the Low Income Housing Tax Credit Program? or choose a topic from the list below.
Costs And Benefits Of Tax Credit Properties
The LIHTC is estimated to cost around $9.5 billion per year, according to the Tax Policy Center. It is designed to create affordable rental housing for low-income households. Supporters of the program emphasize the lack of quality housing in low-income communities and the need for incentives to encourage property owners to build quality and affordable housing.
Critics of the LIHTC argue that the federal subsidy per unit of new construction is too high because it compensates and finances too many playersâorganizers, syndicators, general partners, managers, and investors.
LIHTC projects are sometimes concentrated in low-income communities where there is limited economic opportunity.
As a result, critics state that a significant portion of the federal tax subsidy does not go directly toward the creation of new rental housing. Critics also state that statute and regulations are overly complex.
Lastly, LIHTC projects tend to be concentrated in areas of limited economic opportunity rather than in more affluent areas where residents have access to better-paying jobs and better schools. This can exacerbate the problem of inequality that exists in society. Finally, it might be difficult for landlords to keep the housing affordable once the required compliance periods are over.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Last Day To File Tax Return
Do Tax Credit Apartments Check Credit
The government looks only at your income and assets to determine whether you qualify for low-income housing or other government benefits, not your credit history. No matter how low your credit score might be, you can get the assistance you need as long as you meet the income requirements.
How Does The Low
The federal government gives money to every state for low-income housing tax credits, based on population. Each state has a housing agency that awards the tax credit money to groups of developers according to a plan developed by the state. Real estate developers agree to construct buildings that are available to low-income individuals, and in return, the state gives developers tax credits. Developers then sell the credits to investors to raise the money needed to build. The credits can account for as much as 70% of project funding.
State housing agencies handle the granting of tax credits and management of the process. They receive a specified amount of tax credit money each year. A common way to allocate is explained by California the credits go to developers of affordable housing projects. Corporations are set up to get investors and equity to create qualified buildings in return for the tax credits.
Each state handles the requirements for these tax credits differently. Many states, have a developer experience requirement, for example some, like Ohio, may permit newer developers to work with more experienced partners.
The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development provides a list of state housing agencies to help you find the right agency for your state.
Recommended Reading: Where To Report 1042 S On Tax Return
Gst/hst New Housing Rebate
If youre buying a newly-built home or an existing property that has been substantially renovated, you could apply to claim an HST/GST tax rebate.Ouvre un nouveau site dans une nouvelle fenêtre – Souvre dans une nouvelle fenêtre
This could apply if youre purchasing a home directly from the builder or custom building your own property, for example. While the details vary from province to province, you could qualify for a rebate of the provincial tax or the federal tax that you paid on the purchase price .Its worth noting that this rebate is open to all homebuyers, not just those buying for the first time. However, if your first property falls under an eligible category, you can combine this rebate with other programs that are designed exclusively for first-time buyers to maximize your savings.
Are Tax Credit Apartments Free

It is important to remember that tax-credit apartments are not free of charge. The amount you pay will be based on your income.
Each tax credit apartment has a tiered system that determines how much your rent might be each month. Tiers are typically 60%, 40%, and 30%.
For example, if an apartment regularly rents for $1000 a month and you fell in the 60% tier, you would pay $600 a month.
For the 40% tier, youre paying $400 a month. The 30% tier would be $300 a month.
Recommended Reading: How To Know If Your Taxes Are Filed
A Community Reinvestment Opportunity
Corporate investors in this program are able to receive the tax credit and may also get additional tax benefits in the form of losses and depreciation. Furthermore, financial institutions may receive credit under the Community Reinvestment Act for their participation in tax credit developments, while corporate entities will be assisting in the creation of affordable housing in Michigan communities.
Financial Crisis Impact On Lihtc
Under law, the only investors eligible for Low-Income Housing Tax Credit investments are large C corporations. As the financial markets deteriorated in the second half of 2008, so did the C corporations profits that are typically offset by tax credits, like the LIHTC. As a result, the market for LIHTCs was decimated. The development of new tax credit properties and rehabilitation activities for older affordable housing properties froze completely.
Congress took action in February 2009 to help restart the LIHTC market. The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 created two gap-financing programs to help tax credit properties, which were ready to begin construction, get additional financing.
First, Title XII of the Recovery Act appropriated $2.25 billion to the HOME Investment Partnerships Programadministered by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development for a grant program to provide funds for capital investments in LIHTC projects. HUD awarded Tax Credit Assistance Program grants to state housing credit agencies to facilitate development of projects that received LIHTC awards between October 1, 2006, and September 30, 2009. The State housing agencies were allowed to offer the assistance in either a grant or loan form to the properties.
Also Check: How Do I Pay My Arizona State Taxes
Apply For Housing Tax Credits
- During Round 1, known as the annual Consolidated Request For Proposal , when much of our other funding is also available, and
- During Round 2.
Applicants must apply for HTCs using our Multifamily Customer Portal. Some of the documents are listed for reference on the Application Resources webpage.
To receive notification of application updates and reminders, sign up for our eNews list.
- HTC Scoring TIF Resolution and Letter
Income Limits For Tax Credit Apartments In Dallas Texas
To qualify for a Dallas tax credit apartment, you must meet the Area Median Income or AMI. Below is a table that shows you want the income limits to fall below 50% of the AMI in Dallas, Texas. If your household size falls under these numbers, then there is a good chance that you could qualify for a tax credit apartment.
- 1-person household $34100
- 7-person household $60400
Don’t Miss: Is Health Insurance Tax Deductible
Support For People Looking For Low Income Housing
Low-income housing refers to any housing project or residential building that rents units out to tenants who qualify for reduced rent based on income and family size, or who receive a federal stipend to help make their monthly rental payment. These residential units can either be managed by a housing authority or they can be privately managed by landlords or rental agencies that accept a government-issued payment in conjunction with their tenants rental payment.
While the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit is intended to spur the creation of more low-income housing, there are other types of supports for the people seeking low-income housing. Low-income housing subsidies are offered through the Department of Housing and Urban Development .
The income qualifications can be found on HUDs web site and they are subject to change as wages grow or decline in a given area. A prospective renter must earn less than 50 percent of the median income in their area to qualify. While the aid is available to single renters as well as families, there are qualifications for room counts in prospective homes and single renters may be excluded from a housing project due to lack of availability of properly sized units.
Low-income housing should not be confused with affordable housing, which is for families who are spending more than 30 percent of their income on housing.
U.S. Office of Policy Development and Research. “Low-Income Housing Tax Credit.” Accessed Feb. 8, 2021.
Who Qualifies For The Low
Rental property owners and developers who provide affordable housing that meets the specific qualifications may qualify for the LIHTC program. Many types of properties are LIHTC-eligible, including single-family homes, apartment buildings, townhouses and duplexes.
While low-income families dont qualify for the tax credit, they can qualify to live in a LIHTC program property. They must apply for residence and meet certain requirements to qualify to live there.
Also Check: How Many Years Of Taxes To Keep
Qualifying For The Credit
Many types of rental properties are LIHTC eligible, including apartment buildings, single-family dwellings, townhouses, and duplexes.
Owners or developers of projects receiving the LIHTC agree to meet an income test for tenants and a gross rent test. There are three ways to meet the income test:
The gross rent test requires that rents do not exceed 30 percent of either 50 or 60 percent of AMI, depending upon the share of tax credit rental units in the project. All LIHTC projects must comply with the income and rent tests for 15 years or credits are recaptured. In addition, an extended compliance period is generally imposed.
Qualifications To Live In A Low
If youre in need of affordable housing, an LIHTC property may be a good option for you. However, youll need to meet a few basic requirements and income eligibility as a single person or family. To qualify:
- You must meet the income requirements of the specific property, which typically means you must make below a certain amount of money. Usually, youll need to earn less than 60% of the AMI. However, income requirements depend on the unit and the number of members in the household.
- You can be a single person or a family with or without children.
- There are no citizenship requirements to qualify.
Even if you meet these conditions, you could still be denied. Its important to know the common disqualifiers that make a person ineligible to enroll in the LIHTC program. These include:
Find out how much you can afford.
Your approval amount will give you an idea of the closing costs youll pay.
Also Check: How To Get Stimulus Check On Tax Return
Percent Credit Vs 9 Percent Credit
The LIHTC is composed of two major credit types: the 4 percent credit and 9 percent credit. Credits are redeemable every year for 10 years and calculated as 4 percent or 9 percent of the projects qualified basis, a figure calculated from the gross construction costs of the projects affordable units.
Both credits provide housing tied to the same affordability requirements. The 4 percent credit is awarded non-competitively through the federal government and does not impact a state HFAs annual allocation. In other words, all projects that meet the 4 percent criteria will receive the credit. The 4 percent credit is for projects already receiving most of their funding through tax-exempt bonds or other government subsidies and the acquisition, rehabilitation, and conversion of existing structures to affordable housing.
The 9 percent credit is awarded through a competitive allocation process by state HFAs. States develop a Qualified Allocation Plan , which details the minimum requirements for credit eligibility as well as scoring criteria to compare project applications. The specific criteria of each state are unique. However, there are several general goals that a majority of HFAs seek to incentivize, such as number of affordable units, project cost thresholds, and quality of housing.
To illustrate how these calculations interact, Mark Keightley and Jeffrey Stupak at the Congressional Research Service provide an example in their background primer on the LIHTC:
