How Is Income From Mutual Funds Taxed
In most situations, income from mutual funds is taxed in two ways:
- While you own the shares or units, you are taxed on the distributions of income that are flowed out to you. If you own units of a mutual fund trust, the trust will give you a T3 slip, Statement of Trust Income Allocations and Designations. If you own shares of a mutual fund corporation, the corporation will give you a T5 slip, Statement of Investment Income. The distributions can be capital gains, capital gains dividends, dividends, foreign income, interest, other income, return of capital, or a combination of these amounts. A return of capital will reduce the adjusted cost base of your units or shares.
- When you sell or redeem the units or shares, you are taxed on the gain, if any. This is usually a capital gain because your mutual fund investment is usually considered capital property for tax purposes. You will receive a T5008 slip, Statement of Securities Transactions, or an account statement from the mutual fund.
Two And Twenty Structure
What gets the most criticism is the other part of the manager compensation schemethe 2 and 20, used by a large majority of hedge funds.
As mentioned above, the 2 and 20 compensation structure means that the hedge funds manager receives 2% of assets and 20% of profits each year. It’s the 2% that gets the criticism, and it’s not difficult to see why. Even if the hedge fund manager loses money, he still gets a 2% AUM fee. A manager who oversees a $1 billion fund could pocket $20 million a year in compensation without lifting a finger. Worse yet is the fund manager who pockets $20 million while his fund loses money. They then have to explain why account values declined while they got paid $20 million. It’s a tough sellone that doesn’t usually work.
In the fictional example above, the fund charged no asset management fee and instead took a higher performance cut25% instead of 20%. This gives a hedge fund manager an opportunity to make more moneynot at the expense of the fund’s investors, but rather alongside them. Unfortunately, this no-asset-management-fee structure is rare in today’s hedge fund world. The 2 and 20 structure still prevails, although many funds are starting to go to a 1 and 20 setup.
How Do Hedge Funds Work
Hedge funds* work in different ways because every hedge fund manager has their own strategy for earning profit. However, there are a few things every hedge fund has in common, including the following:
- Hedge fund managers will use various financial tools, which are known as derivatives, to help them make their decisions.
- When you invest in a hedge fund, youre relying on the fund manager to make good decisions. Even if the hedge fund you choose specialises in a particular asset, theres no guarantee of good performance.
- Most hedge fund managers will charge based on the managers performance fee, and an annual fee based on the value of the hedge fund.
- Hedge funds can specialise in just about any type of asset, as long as the fund manager sees an opportunity to earn a profit.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Payroll Taxes In California
Disadvantages Of Hedge Funds
Hedge funds, of course, are not without risk as well:
- Concentrated investment strategy exposes them to potentially huge losses.
- Hedge funds tend to be much less liquid than mutual funds.
- They typically require investors to lock up money for a period of years.
- The use of leverage or borrowed money can turn what would have been a minor loss into a significant loss.
Some Say It’s A ‘stain’ Others A ‘successful Policy’

Wealthy investors, including Warren Buffett and Bill Ackman, have lambasted the tax treatment of carried interest.
“The carried interest loophole is a stain on the tax code,” Ackman, the chief executive of Pershing Square, wrote July 28 on Twitter.
However, other tax experts and proponents of the current tax structure think a lower rate on carried interest is appropriate, benefiting investors and the economy. Raising taxes on fund profits would be a disincentive for managers to take risk and would reduce investment capital, they said.
“Carried interest is appropriately taxed as a capital gain and a successful policy that incentivizes investment in the U.S. economy,” according to Noah Theran, the executive vice president and managing director of the Managed Funds Association, a trade group.
Higher tax rates could also have “spillover effects” by reducing the rate of return for investors like pension funds and other institutions, said Jennifer Acuna, a partner at KPMG and former tax counsel for the Senate Finance Committee.
“The policies have been going back and forth for many years, on what is the right policy to tax carried interest,” Acuna said. “I don’t think it’s a slam dunk.”
You May Like: How Do You Find Out If Your Taxes Were Filed
How Do You Calculate Your Acb
Mutual fund units or shares are identical properties because each property in the group is the same as all the others. You may buy and sell several identical properties at different prices over a period of time. This occurs, for example, when you immediately reinvest your distributions in the mutual fund.
To calculate your capital gain from the units or shares you sell or redeem, you first have to calculate your ACB. To calculate the ACB of the units or shares sold or redeemed, multiply the average cost per unit of all units or shares held immediately before the sale or redemption by the number of units or shares redeemed .
The average cost per unit or share of your total investment increases or decreases when you purchase new units or shares, or reinvest your distributions, depending on the price when the transaction occurred. Every time you purchase additional units or shares, or reinvest your distributions, you should recalculate the average cost per unit or share. Do this for each of your mutual funds.
If you receive a T3 slip with an amount in box 42 Amount resulting in cost base adjustment, the ACB of that mutual fund trust identified on the slip will change. If box 42 contains a negative amount, add this amount to the ACB of the units of the trust. If box 42 contains a positive amount, subtract this amount from the ACB of the units of the trust. See the example.
Carried Interest Compensates Investment Executives
Carried interest is a form of compensation paid to investment executives like private equity, hedge fund and venture capital managers.
The managers receive a share of the fund’s profits typically 20% of the total which is divided among them proportionally. The profit is called carried interest, and is also known as “carry” or “profits interest.”
Here’s where the tax controversy lies: That money is considered a return on investment. As such, managers pay a top 20% federal tax rate on those profits, rather than regular federal tax rates of up to 37% that apply to compensation paid as a wage or salary.
That preferential 20% tax rate is the same as “long-term capital gains,” which applies to investments like stocks, bonds, mutual funds and real estate held for more than a year.
You May Like: What Is Federal Withholding Tax
Low Fee Hedge Fund Etf Gives Investors A Bear
The strong dollar has helped Dynamic Beta’s managed futures ETF outperform this year.
Getty
With both stocks and bonds falling sharply this year, investors becoming discouraged by a standard 60/40 portfolio are beginning to pile into one three-year-old ETF that has served as an effective hedge for this years bear market.
New York-based Dynamic Beta Investments managed futures strategy ETF has gained 22% this year, far outperforming the S& P 500 Indexs 10% decline and the Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Indexs 10% drop. Managed futures funds are actively managed portfolios of futures contracts for assets ranging from stock indexes to commodities like oil and gold. Dynamic Betas fund aims to replicate managed futures strategies at 20 other hedge funds and investment firms and charges a mere 0.85% in management fees. Dynamic Betas founder and co-managing member Andrew Beer, who runs the firm with a Paris-based partner Mathias Mamou-Mani, boasts that a podcast recently dubbed him the Jack Bogle of hedge funds.
No one has figured out how to pick which hedge funds going to do well, just like they haven’t figured out how to pick which stock is going to do well, Beer says. The most reliable way to outperform is by cutting fees. Most managed futures hedge funds charge limited partners 20% in performance fees based on profits and 2% administration fees per year.
Certain Key Us Regulatory Matters
There is a myriad of US rules and regulations that impact the formation, operation and sales of hedge funds in the US. This is a short list of the key items to consider:
Recommended Reading: How To Take Taxes Out Of Check
Tax Breaks For Billionaires: Loophole For Hedge Fund Managers Costs Billions In Tax Revenue
Report By Randall Dodd July 24, 2007
Policy Memo #120
This policy memo focuses on the privileged tax treatment given to hedge fund managers that results in a conservative estimate of over $6 billion in forgone tax revenue.
Private investment companies, organized as hedge funds or private equity firms, have recently grown into major economic forces in the U.S. economy. They mobilize capital, and often leverage it with borrowed funds, in order to accumulate a tremendous amount of assets under their management. These investments include leveraged buyouts market-neutral investment strategies in publicly traded stocks and bonds, energy, and other commodities various arbitrage strategies as well as many lesser known and some entirely unreported transactions. Hedge funds are big players in the large corporate take-over activity that reached $3.6 trillion in 2006¸ and they are also responsible for a significant share of trading volume on the major stock exchanges and in some over-the-counter derivatives markets.
This policy memo focuses on this special tax break, explaining why it is not economically sound and offering reasonable estimates of what it costs the U.S. Treasury and ultimately other tax payers in terms of lost tax revenue.
Example Of A Hedge Fund At Work
Let’s set up a hypothetical hedge fund called Value Opportunities Fund LLC. The operating agreement states that the fund manager can invest anywhere in the world and receives 25% of any profits over 5% every year.
The fund starts with $100 million in assets$10 from ten different investors. Each investor fills out the investment agreement with a check to the fund administrator. The administrator records each investment on the books, then wires the funds to the broker. The fund manager can then begin investing by calling the broker with attractive opportunities.
The fund goes up by 40% after a year, making it worth $140 million. According to the fund’s operating agreement, the first 5% belongs to the investors. So the capital gain of $40 million is reduced by $2 millionor 5% of $40 millionwhich is distributed evenly among the investors. That 5% is known as a hurdle ratea hurdle the fund manager must reach before earning any performance compensation. The remaining $38 million is split25% to the manager and 75% to investors.
Read Also: Are Home Closing Costs Tax Deductible
Meeting The Needs Of The Investors
From a US perspective, in order to market a hedge fund, it is axiomatic that the sponsor needs to meet the investors needs. Investors come in three varieties:
Each of the foregoing investor types requires a vehicle to suit their particular need. Generally, a one size fits all approach in the US is not suitable for all types of investors. The alternative investment world being as complex and creative as it is, one can never say never but generally speaking two different structures are needed to meet the needs of the foregoing classes of investors.
How Are Hedge Funds Taxed
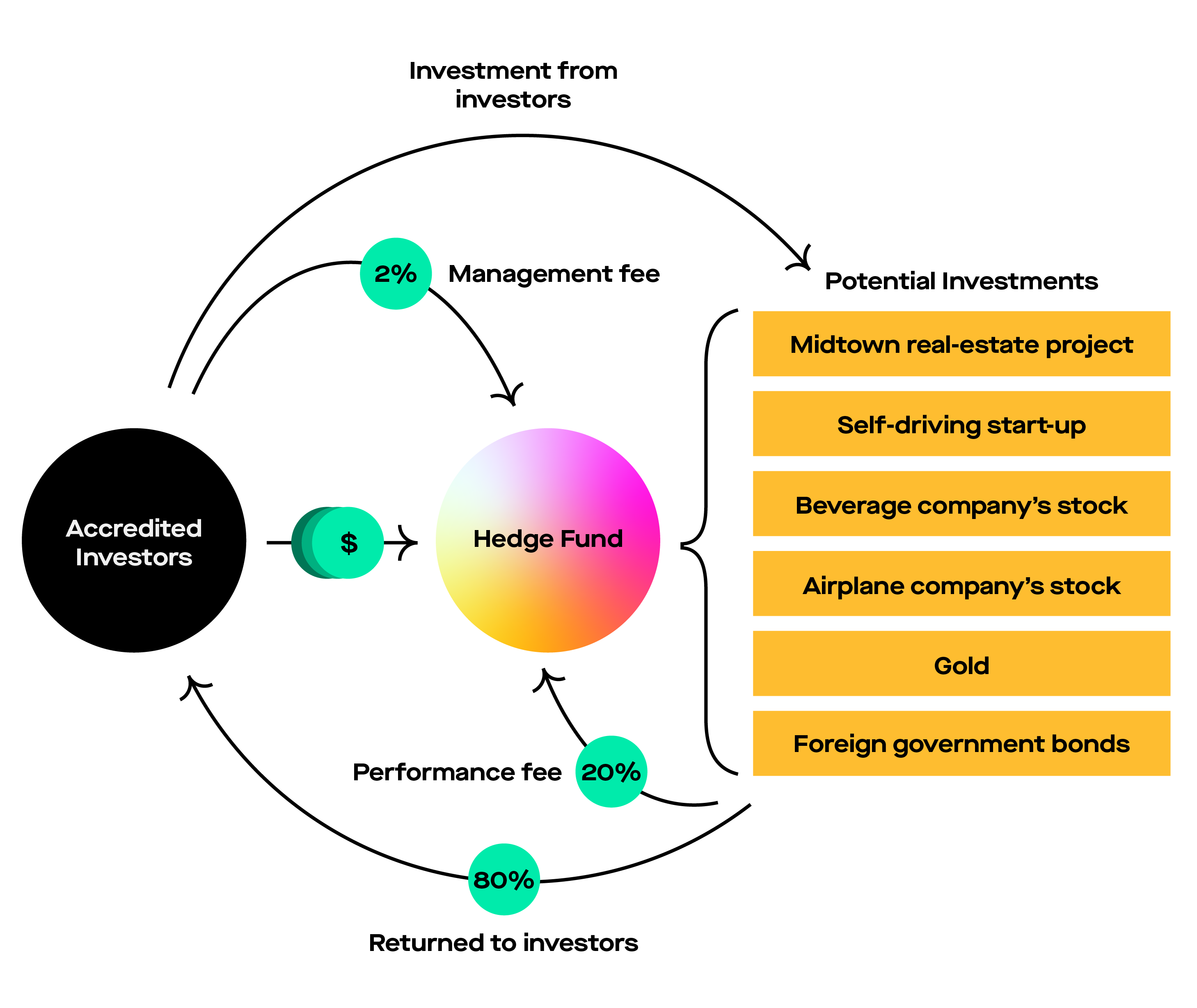
Hedge funds are typically structured as limited partnerships or limited liability companies . Both LPs and LLCs are taxed as partnerships by default, which means that they are pass-through vehicles for tax purposes. This means that there is typically no tax at the entity, or fund, level and investors will be distributed their proportionate share of the funds gains and losses for tax purposes. Investors will report these gains and losses on their individual tax returns and will pay tax on items of income and gain according to the character of the income or gain reported on a K-1 form provided by the fund.
For example, if a hedge fund generates long-term capital gains, by holding an investment for more than one year, investors will pay taxes on such gains at the long-term capital gains rate. The funds manager will generally pay tax on its management fee at ordinary income rates and structure the performance fee as a profit allocation, rather than as compensation for services, in order to receive more favorable tax treatment with respect to assets that are eligible for long-term capital gains.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Do My Tax Return Online
Understanding The Hedge Fund
The term “hedge fund” defines this investment instrument as the manager of the fund often creating a hedged bet by investing a portion of assets in the opposite direction of the fund’s focus to offset any losses in its core holdings.
A hedge fund that focuses on a cyclical sector such as travel, may invest a portion of its assets in a non-cyclical sector such as energy, aiming to use the returns of the non-cyclical stocks to offset any losses in cyclical stocks.
Hedge funds use riskier strategies, leverage assets, and invest in derivatives such as options and futures. The appeal of many hedge funds lies in the reputation of their managers in the closed world of hedge fund investing.
An investor in a hedge fund is commonly regarded as an accredited investor, which requires a minimum level of income or assets. Typical investors include institutional investors, such as pension funds, insurance companies, and wealthy individuals.
Investments in hedge funds are considered illiquid as they often require investors to keep their money in the fund for at least one year, a time known as the lock-up period. Withdrawals may also only happen at certain intervals such as quarterly or bi-annually.
Now That Virtual Assets Are Taxed Will Crypto Be Legalised In India
Trending Now
Hot on Web
In Case you missed it
Top Calculators
Top Searched Companies
Top Prime Articles
Top Slideshow
Top Videos
Popular Articles
Read Also: What Can Be Deducted On Taxes
Tax Implications From A Distribution For An Irrevocable Trust To A
Hedge funds are somewhat akin to mutual funds on steroids, as their limited investment restrictions allow them to pursue high-risk, high-reward scenarios. Typically, you can only invest in a hedge fund if you are an “accredited investor,” meaning you have lots of investment experience, lots of money, or both. However, when it comes time to paying taxes, as an investor you won’t find much difference between a hedge fund and a mutual fund.
