When Do You Have To Pay Taxes On Social Security Benefits
The majority of beneficiaries do not pay taxes on their Social Security Benefits, but around 40 percent currently do according to the Social Security Administration. That is up from a little over 18 percent in 1993, the last time the taxation rules were adjusted. When the thresholds were initially set for taxing Social Security Benefits they were intentionally not indexed to inflation, meaning they would lose some of their effect over time. Still, Social Security benefits currently enjoy more favorable taxation provisions than income from private pensions.
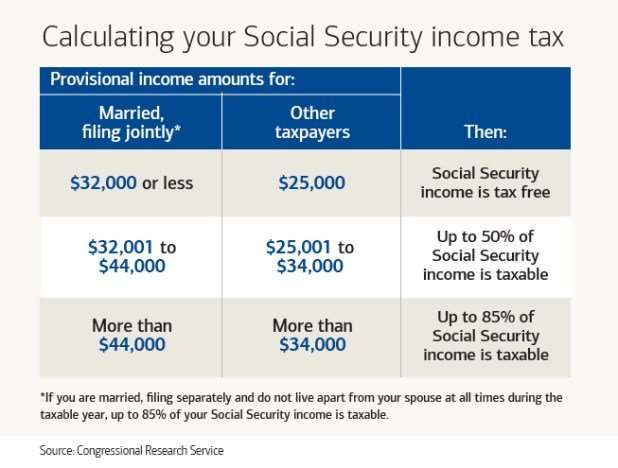
Under current tax law, those with a combined income over $34,000 for individual filers and $44,000 for joint filers will pay tax on up to 85 percent of their benefits. Those with a combined income of less than $25,000 for single filers and $34,000 joint filers will not have a tax liability on their benefits. For those in between the two thresholds they will pay tax on 50 percent of their benefits.
Social Security beneficiaries cross the income thresholds usually when they have other substantial income, be that from work, interest, dividends on investments or other taxable income.
Securing today and tomorrow starts with being informed. Stay up to date with the latest #SocialSecurity news and updates. Subscribe to #SocialSecurity‘s blog today:
Dont Forget Social Security Benefits May Be Taxable
Tax Tip 2020-76, June 25, 2020
Taxpayers receiving Social Security benefits may have to pay federal income tax on a portion of those benefits.
Social Security benefits include monthly retirement, survivor and disability benefits. They don’t include supplemental security income payments, which aren’t taxable.
The portion of benefits that are taxable depends on the taxpayer’s income and filing status.
Your Monthly Benefit Is Less Than The Average Senior’s
Social Security gives out a uniform COLA to all seniors, so no matter what your benefit looks like, you’re entitled to that 5.9% boost in the coming year. But if your benefit is lower than the average, then you won’t see your paycheck from Social Security go up by $92.
Imagine you collect $1,250 a month in benefits now. In that case, after applying a 5.9% COLA, you’d be looking at a raise of about $74 a month, not $92.
Of course, the opposite holds true if your monthly benefit is higher than the average senior’s. In that case, you might see a more sizable raise.
Read Also: Csl Plasma Taxes
What Is The Average Social Security Benefit At Age 62
According to the Social Security Administrations payment statistics as of June 2020, the average Social Security benefit at age 62 is $ 1,130.16 per month or $ 13,561.92 per year.
How much will I get a month if I retire at 62?
If a person of full retirement age received $ 1,000 in benefits per month, a person who retired at age 62 will only receive $ 708 per month in comparison. While those who wait until turn 70 would get $ 1,253 per month.
What is the most you can collect from Social Security at age 62?
In 2021, the maximum amount you can get in benefits if you apply for at the age of 62 is $ 2,324, but if you qualify for the maximum and your full retirement age is 66, then wait until then to start the your benefits entitles you to $ 3,113 per month. Thats a big increase for waiting five years or less to apply for social security.
What Happens If I Inherit Money While On Benefits
If your inheritance is in the form of an annuity , this is treated as income and can affect the amount of your main benefit or your eligibility for benefit. If you have inherited property or money that is paid to you as a one-time payment, these are considered assets.
What happens to your benefits when you inherit money?
An inheritance paid in one lump sum would become part of your relatives savings. This means that a lump sum could lead to a reduction in their benefits. Other benefits are not affected by income, savings or other assets under current benefits rules. These are called untested.
Will an inheritance affect my food stamps?
SNAP does not count an inheritance as income, so it will only affect your benefits if you increase your assets beyond the limit.
Don’t Miss: Will A Roth Ira Reduce My Taxes
State Taxation Of Social Security Benefits
In addition to federal taxes, some states tax Social Security benefits, too. The methods and extent to which states tax benefits vary. For example, New Mexico treats Social Security benefits the same way as the federal government. On the other hand, some states tax Social Security benefits only if income exceeds a specified threshold amount. Nebraska, for instance, taxes Social Security benefits only if your income is at least $43,000, or $58,000 if you’re married filing a joint return. Utah includes Social Security benefits in taxable income but allows a tax credit for a portion of the benefits subject to tax.
Three Ways To Reduce The Taxes That You Pay On Benefits
Is Social Security taxable? For most Americans, it is. That is, a majority of those who receive Social Security benefits pay income tax on up to half or even 85% of that money, because their combined income from Social Security and other sources pushes them above the very low thresholds for taxes to kick in.
But you can use some strategies, before and after you retire, to limit the amount of tax that you pay on Social Security benefits. Keep reading to find out what you can do, starting today, to minimize the amount of income tax that you pay after retiring.
Don’t Miss: Wheres My Refund Ga State
One Married Couple’s Tax
The following scenarios illustrate how taking Social Security benefits early versus delaying until age 70 affects the federal taxes of this married couple, who are both age 62.
Scenario 1: Taking benefits at age 62
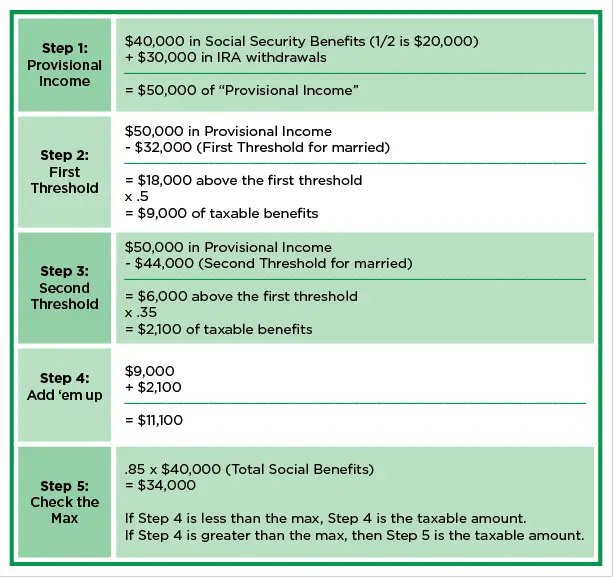
Michael and Patricia anticipate a pre-tax retirement income of $75,000, consisting of $24,000 from their Social Security benefits and $51,000 in taxable distributions from their IRAs.
Based on their earnings history at age 62, 85% of their Social Security benefits would be taxable.
Assuming no other income and using the standard deduction, Michael and Patricia would owe $5,307 in federal taxes. Their after-tax income is $69,693.
Scenario 2: Delaying benefits until age 70
In the years between their retirement and age 70, Michael and Patricia would need to take additional taxable distributions from their IRAs.
But at age 70, they’d receive $42,240 in Social Security benefits, meaning they’d need only $32,760 in IRA withdrawals, including required minimum distributions .
Using the same assumptions , only 34% of the couple’s Social Security benefits would be taxable, and their federal taxes would total $2,086. Their after-tax income would be $72,914.
In this scenario, their total taxes would be slightly higher in the years before they claim Social Security benefits, but lower taxes after age 70 would offset the initial tax cost in less than 2 years.
Social Security claiming strategies at a glance
You’re Enrolled In Medicare
Not everyone who collects Social Security is a Medicare enrollee. Medicare eligibility begins at age 65, whereas you can file for Social Security as early as age 62. Plus, you can collect Social Security even if you’re still working. And if you’re still working, you may still have access to a group health plan that makes enrolling in Medicare unnecessary.
Still, many seniors on Social Security are Medicare enrollees and therefore have their Part B premiums deducted from their monthly benefits. Next year, Medicare Part B costs are rising substantially. The standard monthly premium is set to increase from $148.50 to $170.10. That’s a jump of $29.60. And that’s also a figure you’ll need to subject from your upcoming COLA.
So, let’s say you collect the average monthly benefit of $1,565. After applying a 5.9% COLA, your benefit rises by $92. But when we subtract $29.60, you’re left with a $62.40 raise instead.
Now to be clear, a $62.40 bump is still pretty significant in the context of Social Security. But unfortunately, much of that remaining money could easily get eaten up by higher food and fuel costs, which consumers of all ages are grappling with now.
Recommended Reading: Www.1040paytax.com
Tips For Saving On Taxes In Retirement
- Finding a qualified financial advisor doesnt have to be hard. Finding a qualified financial advisor doesnt have to be hard. SmartAssets free tool matches you with up to three financial advisors in your area, and you can interview your advisor matches at no cost to decide which one is right for you. If youre ready to find an advisor who can help you achieve your financial goals, get started now.
- What you pay in taxes during your retirement will depend on how retirement friendly your state is. So if you want to decrease tax bite, consider moving to a state with fewer taxes that affect retirees.
- Another way to save in retirement is to downsize your home. Moving into a smaller home could lower your property taxes and it could also lower your other housing costs.
Combined Income Base Amounts In 2020
Single filers with combined incomes of less than $25,000 will not pay taxes on Social Security benefits as of tax year 2020.
- Those with combined incomes between $25,000 and $34,000 will pay taxes on up to 50% of their benefits.
- Those making more than $34,000 will pay taxes on up to 85% of their benefits.
It works a bit differently for married couples who file joint tax returns. In this case, you must add together the income of both spouses, even if one of you isn’t getting Social Security. Couples with combined incomes of less than $32,000 won’t pay taxes on their benefits.
- Those with combined incomes between $32,000 and $44,000 will pay taxes on up to 50% of their benefits.
- Those making more than $44,000 will pay taxes on up to 85% of their benefits.
You May Like: How Much Tax For Doordash
Understanding State Taxes On Social Security Benefits
So far, weve only been discussing the implications of federal income tax. But depending on the state in which you reside, you might be required to pay state taxes on your benefits as well. The majority of states do not tax your Social Security benefits. However, some states tax these benefits following the Federal tax guidelines and others tax them based on their own state-specific rules.
States that follow the Federal tax rules: Vermont, West Virginia, Minnesota, North Dakota. West Virginia has recently begun to phase out state taxation of SS benefits. As of 2021, most residents in the state will now owe any taxes on their benefits.
States that partially tax SS benefits: Kansas, Connecticut, Colorado, Montana, Nebraska, Missouri, Rhode Island, Utah, New Mexico. These states tax benefits at varying levels. You might be entitled to exemptions based on your age and income level in these states. You should contact a tax professional or consult your states specific rules for determining how much tax you will owe if you reside in one of these states.
The remaining 37 states do not place a state income tax on your Social Security benefits at all. You might still owe state taxes on distributions or retirement benefits from your private retirement accounts or other income, but no state taxes will be due on your Social Security benefits.
Is My Social Security Income Taxable The Quick Answer
According to the IRS, the quick way to see if you will pay taxes on your Social Security income is to take one half of your Social Security benefits and add that amount to all your other income, including tax-exempt interest. This number is known as your combined income .
If your combined income is above a certain limit , you will need to pay at least some tax.
The limit is $25,000 if you are a single filer, head of household or qualifying widow or widower with a dependent child. The limit for joint filers is $32,000. If you are married filing separately, you will likely have to pay taxes on your Social Security income.
Don’t Miss: Is Plasma Donation Taxable Income
Taxing Social Security Benefits Is Sound Policy
Social Security beneficiaries with higher incomes pay income tax on part of their benefits. Those with incomes below $25,000 pay no tax on benefits, while those with the highest incomes pay tax on as much as 85 percent of their benefits. This arrangement is sound for several reasons:
- The substantial proceeds from taxing Social Security benefits are credited to the Social Security and Medicare trust funds, strengthening the programs financing.
- The taxation of benefits is broadly progressive, since people with low incomes pay nothing and the tax rate on benefits increases with income.
- As an earned benefit, Social Security should be subject to tax, like other earned benefits, such as employer pensions.
- Social Securitys tax treatment is more favorable than that of private defined-benefit pensions, primarily because of the protections for low-income beneficiaries.
How Does Full Retirement Age Affect Your Social Security Benefits
If you claim your benefits at full retirement age, you will receive your standard Social Security benefit amount. If you claim prior to FRA, you will be subject to early filing penalties that reduce your benefit by the following amounts:
- 5/9 of 1% for each of the first 36 months before FRA
- 5/12 of 1% for each subsequent month before FRA
This amounts to a 6.7% annual reduction for each of the first three years and an additional 5% reduction for each following year before FRA. If you claim benefits at 62 with an FRA of 67, you will face a full 30% reduction in benefits.
By contrast, if you claim benefits after FRA, you receive delayed retirement credits valued at 2/3 of 1% per month. This results in an 8% annual increase to your monthly benefit. Delayed retirement credits can be earned until age 70, after which time there is no financial benefit to delaying your claim. Delayed retirement credits cannot be earned if you are claiming either spousal or survivor benefits.
Read Also: Reverse Ein Lookup Irs
How To Minimize Social Security Taxes
Nobody likes paying taxes, and most people are always looking for ways to minimize the amount of tax that they owe. This is no different for people who receive Social Security benefits. Thankfully, there are some things that you can do to help minimize the amount of tax that you will have to pay while receiving your benefits. We will take a look at a few of those methods here.
How Is Social Security Taxed
A retiree’s provisional income is used to determine the tax owed on their Social Security benefit.
Provisional income is equal to adjusted gross income plus non-taxable interest plus half of annual Social Security benefits.
That total is then applied to the following income limits to determine how much of the Social Security benefit will be taxed at the filer’s marginal tax rate:
| Provisional income for a single, head of household, or qualifying widow filer | Provisional income for a married, joint filer | Amount of Social Security benefit taxed |
| Under $25,000 | ||
| 85% of Social Security benefit taxed at filer’s marginal tax rate |
Also Check: Do I Have To Claim Plasma Donation On Taxes
Please Visit Washington Update For Latest Insights On Tax Proposals And Other Policy Changes That Could Affect The Markets And Your Financial Life
How much of your Social Security income is subject to tax depends on a variety of factors, including your federal income tax filing status and your modified adjusted gross income. But with a little up-front planning, which can include everything from rebalancing your portfolio to structuring certain transactions in the right way, you may reduce the possibility of taxes derailing your plans.
Uncle Sam Can Tax Up To 85% Of Your Social Security Benefits If You Have Other Sources Of Income Such As Earnings From Work Or Withdrawals From Tax
Many people are surprised to learn that Social Security benefits are taxable. But if you look at how the federal tax on Social Security is calculated, you’ll notice that benefits aren’t taxed for most people who only have income from Social Security. For 2021, the estimated average monthly Social Security check is $1,543, which comes to $18,516 per year. That’s well below the minimum amount for taxability at the federal level.
On the other hand, if you do have other taxable incomesuch as from a job, a pension or a traditional IRAthen there’s a much better chance that Uncle Sam will take a 50% or 85% bite out of your Social Security check. Plus, depending on where you live, your state might tax a portion of your Social Security benefits, too.
Recommended Reading: Efstatus.taxact.com
Contributing To Retirement Accounts
Another key advantage of ongoing earned income even after you collect Social Security is that you can keeping contributing to your retirement savings accounts like traditional IRAs, health savings accounts , Roth IRAs, and 401s.
Note: If you are over 72, you will have to take the required minimum distribution from your traditional IRA, except for during the 2020 pause because of COVID-19.
Your traditional 401, or similar employer-based retirement plan, is a different story. In general, you can continue stashing away money in your current employer-provided plan as long as youre still working, even part-time, and you can delay taking your RMD until after you retire.
This additional savings can help, especially if your savings are running a bit behind your goals. The combination of the added savings, tax-deferred growth potential, and the ability to defer tapping into your savings can be powerful, even at the end of your working career.
