State Income Tax Vs Federal Income Tax: An Overview
The United States has a multitiered income tax system under which taxes are imposed by federal, state, and sometimes local governments. Federal and state income taxes are similar in that they apply a percentage rate to taxable incomes, but they can differ considerably with respect to those rates and how they’re applied, as well as to the type of income that is taxable and the deductions and tax credits that are allowed.
Whats The Purpose Of Tax Ids
Essentially, tax IDs are social security numbers for businesses. They serve the same function SSNs do for individuals.
Each business receives a unique number from both federal and state governments, which act as their tax IDs. Primarily, you need a tax ID to file your businesss taxes, including income and payroll taxes.
However, other essential business operations require a tax ID, as well. Therefore, once youve determined your businesss legal structure, its a good idea to obtain relevant tax IDs as soon as possible.
Start with making sure you understand the difference between federal and state tax systems.
Differences Between Book And Taxable Income For Businesses
In the United States, taxable income is computed under rules that differ materially from U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Since only publicly traded companies are required to prepare financial statements, many non-public companies opt to keep their financial records under tax rules. Corporations that present financial statements using other than tax rules must include a detailed reconciliation of their financial statement income to their taxable income as part of their tax returns. Key areas of difference include depreciation and amortization, timing of recognition of income or deductions, assumptions for cost of goods sold, and certain items the tax deduction for which is limited.
You May Like: How Does H And R Block Charge
What Is The Federal Gasoline Excise Tax
Excise taxes are imposed on the sale of specific goods, from indoor tanning facilities to gasoline. These taxes are passed on to consumers because theyre built into the purchase price of the product. Gasoline would cost you less without this tax padding the per-gallon cost.
The federal gasoline excise tax is actually a combination of two taxes. It includes a 0.1 cent per gallon leaking underground storage tank fee, which is added to the tax-per-gallon rate on both gasoline and diesel fuel.
The LUST fee goes into a trust fund that was created in 1986. Its intended to prevent petroleum leaks from federally regulated underground storage tanks. It also funds the oversight and enforcement of petroleum leak cleanups. It pays for cleanup when the responsible party isnt known and funds inspections.
Federal Income Tax Bracket For 2020
| Single | |
| $311,026+ | $518,401+ |
In rare cases, such as when one spouse is subject to tax refund garnishing because of unpaid debts to the state or federal government, opting for the Married filing separately tax status can be advantageous. Typically, though, filing jointly provides a tax break.
Only single people should use the single filing status. Single taxpayers who have dependents, though, should file as Head of household. To qualify for this filing status, you must pay more than half of household expenses, be unmarried and have a qualifying child or dependent.
Also Check: Prontotaxclass
Case Law Prior To The Sixteenth Amendment
Article I, Section 9 of the U.S. Constitution states: “No Capitation, or other direct, Tax shall be laid, unless in Proportion to the Census or enumeration herein before directed to be taken.” In 1894, Congress passed the Wilson-Gorman Tariff, which created an income tax of 2% on income of over $4,000. Charles Pollock contested that the tax was unconstitutional under Article 1, Section 9. As such, the Supreme Court granted certiorari to hear this issue in Pollock v. Farmers Loan and Trust Company, 157 US 429 .
In Pollock, the Court held that the Wilson-Gorman Tariff was unconstitutional under Article I, Section 9 of the Constitution, as the act created a direct taxation on property owners, not a tax apportioned among the states.
Previous Years Tax Brackets
Taxes were originally due April 15, but as with a lot of things, it changed in 2020. The tax deadline was extended to July 15 in order to let Americans get their finances together without the burden of a due date right around the corner.
Here is a look at what the brackets and tax rates were for 2019:
2019 Tax Brackets| Tax rate |
|---|
Also Check: Where’s My Tax Refund Ga
How To Calculate Federal Tax Credits
Unlike adjustments and deductions, which apply to your income, tax credits apply to your tax liability, which means the amount of tax that you owe.
For example, if you calculate that you have tax liability of $1,000 based on your taxable income and your tax bracket, and you are eligible for a tax credit of $200, that would reduce your liability to $800. In other words, you would only owe $800 to the federal government.
Tax credits are only awarded in certain circumstances, however. Some credits are refundable, which means you can receive payment for them even if you dont owe any income tax. By contrast, nonrefundable tax credits can reduce your liability no lower than zero. The list below describes the most common federal income tax credits.
- The Earned Income Tax Credit is a refundable credit for taxpayers with income below a certain level. The credit can be up to $6,660 per year for taxpayers with three or more children, or lower amounts for taxpayers with two, one or no children.
- The Child and Dependent Care Credit is a nonrefundable credit of up to $3,000 or $6,000 related to childcare expenses incurred while working or looking for work.
- The Adoption Credit is a nonrefundable credit equal to certain expenses related to the adoption of a child.
- The American Opportunity Tax Credit is a partially refundable credit of up to $2,500 per year for enrollment fees, tuition, course materials and other qualified expenses for your first four years of post-secondary education.
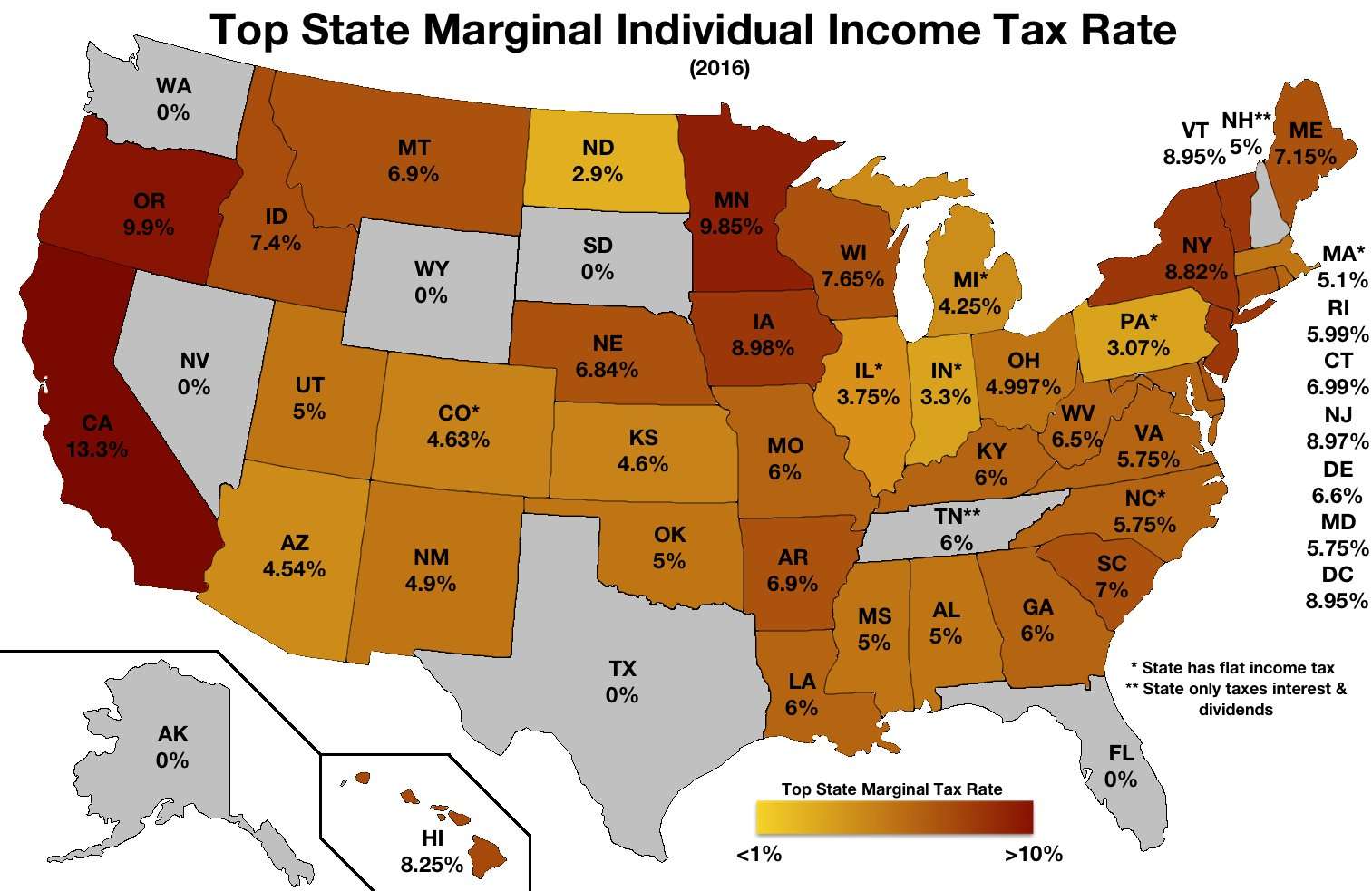
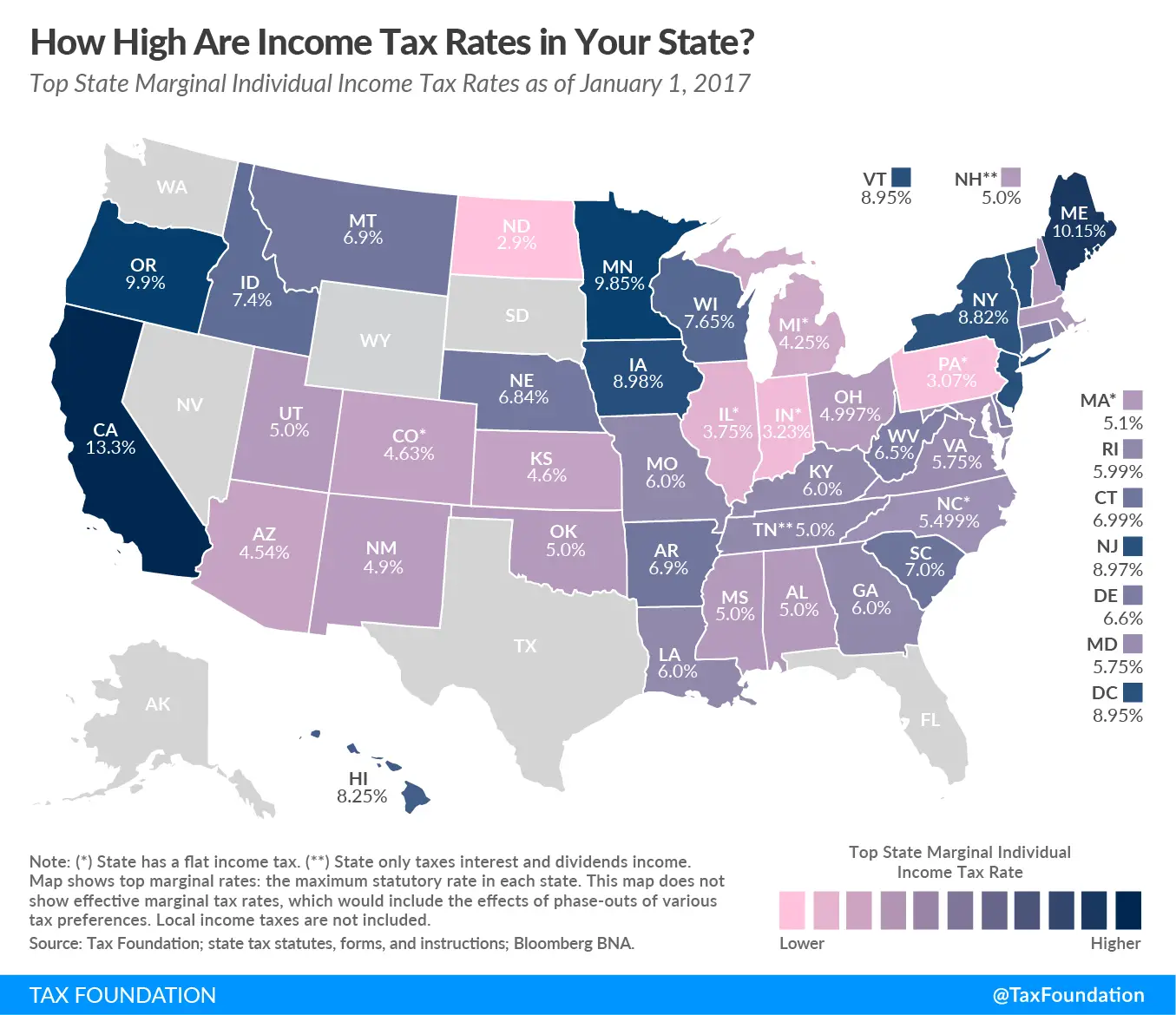
What Is The Difference Between State & Federal Taxes
In the United States you generally pay taxes twice first to the government, then to the state in which you work. Taxes paid to the government are called “federal” taxes, and the taxes paid to the state are called “state” taxes. Federal taxes are the same for all states, but state taxes vary by state.
Read Also: How To Buy Tax Lien Certificates In California
State And Local Income Taxes
Many states, as well as some cities and counties, have their own income taxes. These are collected in addition to the federal income tax. States that have a state income tax require that you file a separate state tax return, as they have their own rules. If you’re curious about a particular states tax system and rules, visit one of our state tax pages.
Licenses And Occupational Taxes
Many jurisdictions within the United States impose taxes or fees on the privilege of carrying on a particular business or maintaining a particular professional certification. These licensing or occupational taxes may be a fixed dollar amount per year for the licensee, an amount based on the number of practitioners in the firm, a percentage of revenue, or any of several other bases. Persons providing professional or personal services are often subject to such fees. Common examples include accountants, attorneys, barbers, casinos, dentists, doctors, auto mechanics, plumbers, and stock brokers. In addition to the tax, other requirements may be imposed for licensure.
All 50 states impose vehicle license fee. Generally, the fees are based on type and size of vehicle and are imposed annually or biannually. All states and the District of Columbia also impose a fee for a driver’s license, which generally must be renewed with payment of fee every few years.
Also Check: File Missouri State Taxes Free
Payment Or Withholding Of Taxes
The United States federal and state income tax systems are self-assessment systems. Taxpayers must declare and pay tax without assessment by the taxing authority. Quarterly payments of tax estimated to be due are required to the extent taxes are not paid through withholdings. The second and fourth “quarters” are not a quarter of a year in length. The second “quarter” is two months and the fourth is four months . Employers must withhold income tax, as well as Social Security and Medicare taxes, from wages. Amounts to be withheld are computed by employers based on representations of tax status by employees on Form W-4, with limited government review.
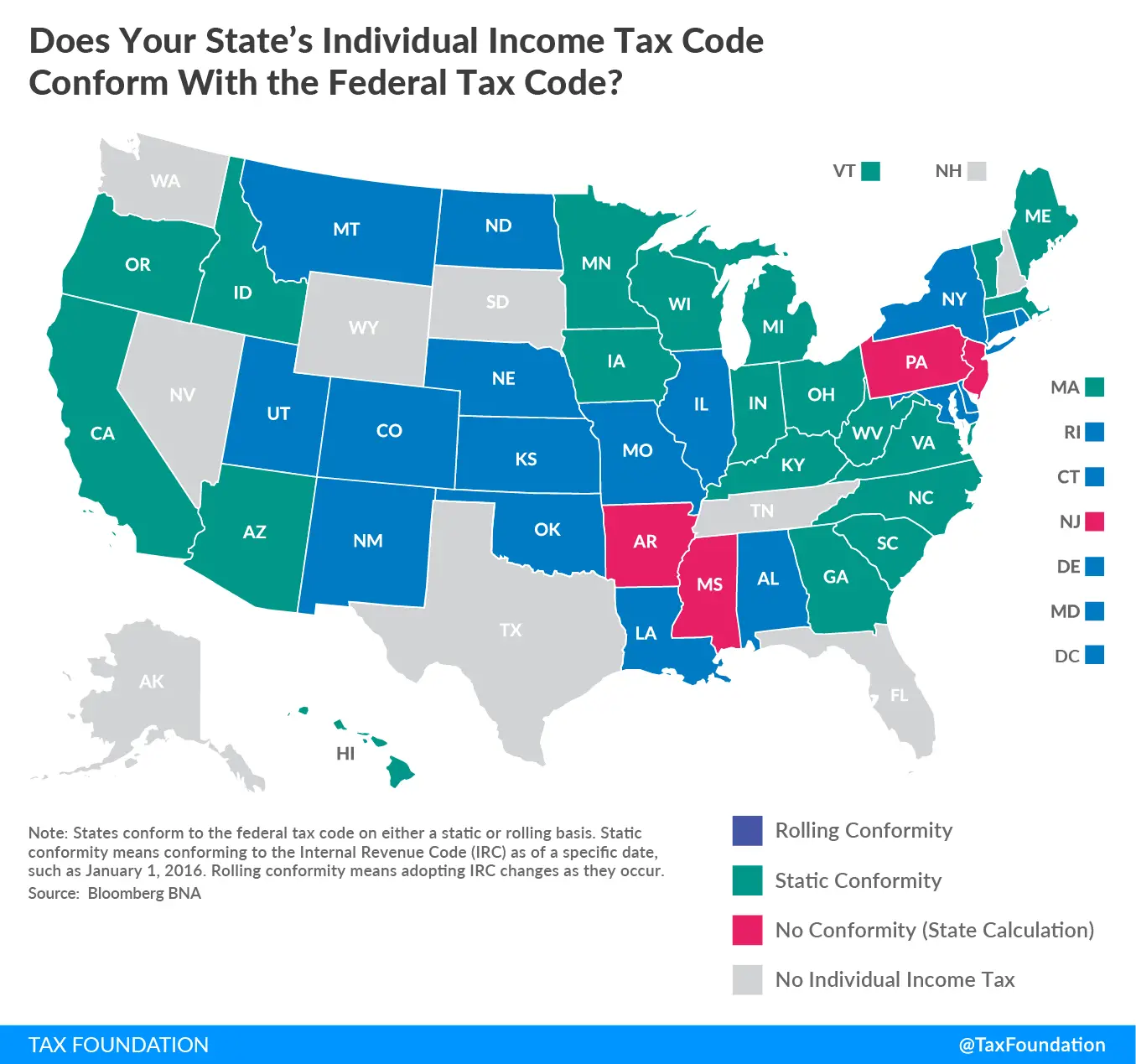
Forty-three states and many localities in the U.S. impose an income tax on individuals. Forty-seven states and many localities impose a tax on the income of corporations. Tax rates vary by state and locality, and may be fixed or graduated. Most rates are the same for all types of income. State and local income taxes are imposed in addition to federal income tax. State income tax is allowed as a deduction in computing federal income, but is capped at $10,000 per household since the passage of the 2017 tax law. Prior to the change, the average deduction exceeded $10,000 in most of the Midwest, most of the Northeast, as well as California and Oregon.
Some states have alternative measures of taxable income, or alternative taxes, especially for corporations.
When To Check Your Withholding:
- Early in the year
- When the tax law changes
- When you have life changes:
- Lifestyle – Marriage, divorce, birth or adoption of a child, home purchase, retirement, filing chapter 11 bankruptcy
- Wage income – You or your spouse start or stop working or start or stop a second job
- Taxable income not subject to withholding – Interest income, dividends, capital gains, self employment income, IRA distributions
- Adjustments to income – IRA deduction, student loan interest deduction, alimony expense
- Itemized deductions or tax credits – Medical expenses, taxes, interest expense, gifts to charity, dependent care expenses, education credit, child tax credit, earned income credit
Recommended Reading: Where’s My Refund Ga State Taxes
Federal Withholding Tax Vs State Withholding Tax: An Overview
In simplest terms, the amount of withholding from your paycheck is an estimate of how much you’ll owe in taxes at year’s end based upon your level of income and other factors. That number is divided by the number of pay periods you have in a year or, in the case of hourly employees, by how many hours you work in a pay period.
If it’s likely that you’ll owe the government $10,000 and you’re paid a weekly salary, $192.30 will be withheld from each of your paychecks and forwarded to the government on your behalf: $10,000 divided by 52.
There’s very little difference between state and federal withholding taxes. The chief distinction is that state withholding is based on state-level taxable income, while federal withholding is based on federal taxable dollars. State withholding rules tend to vary among the states, while federal withholding rules are consistent everywhere throughout the United States.
California Payroll Tax Rate Example
New employers pay 3.4% in SUTA for employees making more than $7,000 per year. Theyve renamed SUTA as State Unemployment Insurance . Existing employers pay between 1.5% and 6.2% depending on their unemployment experience. Those who lay off or terminate fewer employees will typically have a lower rate. These taxes are calculated on top of the FICA and FUTA taxes that employers in California and all states must pay.
Also Check: Www.myillinoistax
Penalties For Late Employment Tax Payments
| Penalty | |
|---|---|
| 16 or more days but before 10 days from the date of the first IRS notice | |
| 10% | Amounts that should have been deposited, but instead were paid directly to the IRS or paid with your tax return |
| 15% | Amounts still unpaid more than 10 days after the date of the first IRS notice or the day you receive notice and demand for immediate payment |
Florida Taxes A Quick Look
Major taxes collected in Florida include sales and use tax, intangible tax and corporate income taxes. Information regarding these and additional taxes can be located from the list below. There is no personal income tax in Florida.
- Florida Sales Tax: Florida sales tax rate is 6%.
- Florida State Tax: Florida does not have a state income tax.
- Florida Corporate Income Tax: Corporations that do business and earn income in Florida must file a corporate income tax return .
- Florida Property Tax: Florida Property Tax is based on market value as of January 1st that year.
Recommended Reading: How To Appeal Property Taxes Cook County
The Us Has One System For All Taxpayers But State Rules Vary Widely
Lea Uradu, J.D. is graduate of the University of Maryland School of Law, a Maryland State Registered Tax Preparer, State Certified Notary Public, Certified VITA Tax Preparer, IRS Annual Filing Season Program Participant, Tax Writer, and Founder of L.A.W. Tax Resolution Services. Lea has worked with hundreds of federal individual and expat tax clients.
What Are Six Things That State Taxes Pay For
Services provided by state government are financed by a combination of revenues generated from both state and federal governments. However, many state programs are funded exclusively by the state using state taxes. In addition, some state services and programs are mandated by the federal government but are not fully paid for with federal money these are called “unfunded mandates.”
Also Check: How Much Time To File Taxes
Federal Payroll Tax Rates
At the federal level, in addition to income tax, there are two categories of employment taxes: FUTA and FICA. Well cover each briefly as youll process these as tax deductions on employees paychecks. You must also pay these taxes on your employees behalf, regardless of the state in which you operate.
- Income tax: The tax rate is based on withholdings chosen on the employees W-4 form.
- FUTA: This 6% federal tax is to cover unemployment in most cases, youll be credited back 5.4% of this amount for paying your state taxes on time, resulting in a net tax of 0.6%.
- FICA: This 15.3% federal tax is made up of two parts: 12.4% to cover Social Security and 2.9% to cover Medicare. For employees earning more than $200,000, the Medicare tax rate goes up by an additional 0.9% therefore, FICA can range between 15.3% and 16.2%.
Similarities With Federal Tax Forms
The most commonly used federal tax form for reporting income taxes is the 1040. In most cases, you will find that there is a single dominant form for your state income tax needs as well. This makes preparing your state income tax return much easier since you can transfer your federal information onto your state tax return. And if you use tax preparation software such as TurboTax, the information you report on your federal return automatically transfers to any state income tax forms you need to prepare. For example, California allows taxpayers to file their state income tax on Form 540, 540A or 540EZ. The complexity of your tax situation dictates which forms you can file with.
Remember, with TurboTax, we’ll ask you simple questions about your life and help you fill out all the right tax forms. With TurboTax you can be confident your taxes are done right, from simple to complex tax returns, no matter what your situation.
Also Check: How Much Does H & R Block Charge For Taxes
Estate And Inheritance Taxes
Both estate and inheritance taxes are imposed on the value of an individuals property at the time of their death. While estate taxes are paid by the estate itself, before assets are distributed to heirs, inheritance taxes are paid by those who inherit property. Both taxes are usually paired with a gift tax so that they cannot be avoided by transferring the property prior to death.
Estate and inheritance taxes are poor economic policy because they fall almost exclusively on a country or states capital stockthe accumulated wealth that makes it richer and more productive as a wholethus discouraging investment.
Both taxes are also complex, hard for jurisdictions to administer, and can incentivize high-net-worth individuals to either engage in economically inefficient estate planning or leave a state or country altogether.
For these reasons, most U.S. states have moved away from estate and inheritance taxes.
What To Know About Federal Vs State Taxes
If youre still a novice when it comes to filing your taxes, you may be pretty intimidated by the idea of filing two separate returns federal and state.
It sounds like double the work, right? Thankfully, thats not entirely the case. Filing state taxes after youve filed your federal taxes doesnt have to be difficult if you use a tax preparation software service like E-File.com.
So what makes your state taxes different from your federal taxes? Heres what you need to know.
Federal income tax applies to everyone
Federal income tax law is imposed by the federal government. As such, it applies to everyone in all 50 states it doesnt matter in which state you live.
Federal income tax law divides individuals into 7 tax brackets based on income, with the lowest bracket set at 10% and the highest around 39%. With the new federal tax code, passed into law at the end of 2017, this is due to change in 2018 so that the highest bracket drops to 37 percent.
Your tax bracket is decided once youve figured your taxable income in other words, after youve claimed your deductions and your personal exemption, if any. Once your tax bill is determined, you receive either a federal tax refund, if youve paid too much, or a tax bill, if you havent paid enough in taxes throughout the year .
State income tax is set by your states government
What do state taxes pay for?
Recommended Reading: How To Buy Tax Forfeited Land
