How Are Payroll Taxes Different From Personal Income Taxes
Tax rate, levies, employee, and employer, are factors to consider when comparing payroll taxes vs income taxes. Furthermore, how you calculate personal income and payroll tax differ based on their rates, and understanding the difference is significant. Payroll and personal income tax rates vary in various ways, and we will discuss each more in-depth to improve your knowledge.
State Unemployment Insurance Tax
State unemployment insurance tax is one of the payroll taxes you pay as an employer towards unemployment insurance benefits for employees. As a part of payroll taxes, Arizona employers have to pay state unemployment insurance tax . This is in addition to a federal unemployment insurance tax FUTA which is given below under federal payroll taxes.
Placement And Employment Agency Workers
The following guidelines apply to placement or employment agencies that hire workers:
The gross earnings of workers described in paragraphs b) and c) must be reported on their T4 slip. For reporting instructions, see Guide RC4120, Employers Guide Filing the T4 Slip and Summary.
Also Check: How To Calculate Tax Rate
Employer Payroll Tax Responsibilities
The responsibility for payroll taxes continues even after paychecks have been issued to employees. The company is also responsible for:
- Paying the employer’s share of payroll taxes
- Depositing tax dollars withheld from the employees’ paychecks
- Preparing various reconciliation reports
- Accounting for the payroll expense through their financial reporting
- Filing payroll tax returns
Payroll Tax Vs Income Tax: What’s The Difference Between Them
America has a complicated tax system, and payroll and income taxes confuse many taxpayers, especially when dealing with revenue agents. While all taxes are not the same, understanding the employment tax difference is significant for employers. But what factors come into play when you evaluate payroll tax vs income tax? Income tax comprises federal, state, and local taxes, while payroll tax includes social security and unemployment taxes.
Taxpayers use these terms interchangeably, but there are apparent differences between payroll and income taxes. We’ll discuss the difference between payroll and income taxes, employee and employer taxes, and individual income tax vs payroll tax usage. Lastly, we’ll discuss the levies considered as payroll taxes to improve your knowledge.
Read Also: How To Apply For Income Tax Extension
Do I Have To Withhold Deductions If I Pay Myself A Salary
If the business is a sole proprietorship or partnership, deductions will not be sent to the CRA via the payroll account. For these businesses, payments are made when the T1 income tax and benefit return is filed, unless the sole proprietor or partner is required to pay by instalments.
For entrepreneurs employed by their incorporated business, their salary will be treated as employment income and deductions will be required. If the entrepreneur controls more than 40% of the common shares , he or she is exempt from Employment Insurance premiums and will not be entitled to Employment Insurance benefits. However, there are Employment Insurance special benefits for self-employed people.
What Is The Definition Of Payroll Tax
We live in a global marketplace. With businesses hiring across national boundaries, businesses need an excellent understanding of their tax obligations in each location they operate in. Alongside income taxes, it is essential that any business employing workers overseas considers their international payroll processing and the impact of payroll tax.
It should be noted that this Guide provides general information only, and any business operating internationally should seek professional advice on their individual circumstances to ensure compliance with payroll tax obligations.
There is no consistent definition of payroll tax that applies internationally. We discern at least four definitions that might apply, depending on where you are located. We consider each possible definition below:
- Employee income taxes
- In some countries, payroll tax simply means employee income tax.
- Generally, income earned as an employee is subject to income tax. Usually, this income tax is withheld by the employer from an employees gross wages or salary.
- Where payroll tax refers just to employer-withheld income tax, it is sometimes called Pay as You Go or Pay as You Earn tax.
- Under this definition, other compulsory payroll deductions such as social security, workers compensation and pension contributions are not referred to using the term tax.
Don’t Miss: When Do Taxes Have To Be Filed By
What Is A Payroll Tax
A payroll tax is a percentage withheld from an employee’s pay by an employer who pays it to the government on the employee’s behalf. The tax is based on wages, salaries, and tips paid to employees. Federal payroll taxes are deducted directly from the employee’s earnings and paid to the Internal Revenue Service .
Applicable Federal Payroll Taxes
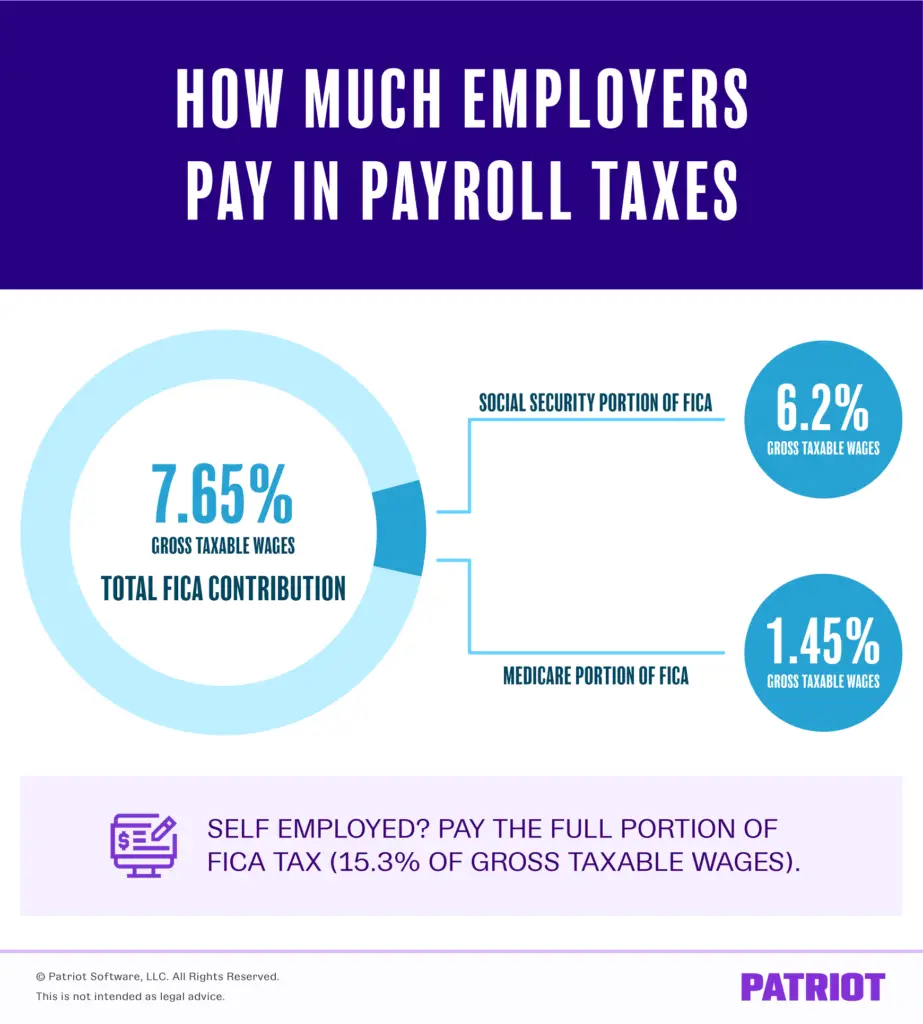
As an Arizona employer, you have to pay not just Arizona payroll taxes but also the applicable federal payroll taxes. These include the Federal Unemployment Insurance Tax , as well as payroll taxes mandated by FICA , which go towards Social Security and Medicare. You also pay withholding taxes towards federal income tax.
Recommended Reading: What Is Low Income Tax Credit
Payroll Tax Calculator: How To Withhold Payroll Tax
The process for calculating and processing employer payroll tax is slightly different in every country. Note, no matter how the payroll tax is calculated, it is usually a requirement to include these calculations in an employees pay stub or payslip.
In the United States, the processing of employment taxes, including payroll taxes, requires employers to take the steps set out below:
- 1. Gather necessary information
- In order to process taxes there is a range of information and payroll data you will need. This includes a copy of the employees withholding certificate, the W-4 form, as well as internal information on gross salary or wages of employees.
- Note, if you run a small business and have no employees , you may not need to submit payroll taxes, but may need to cover the same matters through self-employment taxes, and submitting a tax return as a self employed person.
- 2. Calculate federal income taxes withheld
- There are two federal income tax withholding methods for calculating the amount of employee federal income tax to withhold: The wage bracket and the percentage method. Each method sets out the applicable tax rate at different income levels.
- These amounts are withheld from employee pay checks and remitted to the IRS on a scheduled basis. Two deposit schedules are available monthly and semi-weekly.
How Much Payroll Tax Will I Pay
Heres a Q & A recap of your employer payroll tax responsibilities:
- Do employers have to pay taxes on employees?
- Yes
Never calculate payroll taxes again. Patriots online payroll will automatically calculate taxes so you can keep your time and money for what matters most: your small business. Start your free trial today!
This is not intended as legal advice for more information, please
Read Also: What Online Tax Service Should I Use
Employment Benefits And Payments From Which You Do Not Deduct Ei Premiums
Note
Enter an X or a check mark in the EI box only if you did not have to withhold EI premiums from the earnings for the entire reporting period.
Employment
Even if there is a contract of service, payments for the following types of employment are not insurable and EI premiums do not have to be deducted:
- Casual employment if it is for a purpose other than your usual trade or business. For more information about casual employment, go to Casual employment.
- Employment when you and your employee do not deal with each other at arms length. There are two main categories of employees who could be affected:
- Related persons: individuals connected by a blood relationship, marriage, common-law relationship, or adoption. In cases where the employer is a corporation, the employee is considered related to the corporation when they are related to a person who either controls the corporation or is a member of a related group that controls the corporation. However, these individuals can be in insurable employment if you would have negotiated a similar contract with a person with whom you deal at arms length.
- Non-related persons: an employment contract between you and a non-related employee can be non-insurable if it is apparent from the circumstances of employment that you were not dealing with each other in the way arms length parties normally would.
For more information, go to Not dealing at arms length for purposes of the Employment Insurance Act .
Benefits and payments
Vacation Pay And Public Holidays
When you pay vacation pay, how you calculate deductions will depend on whether your employee takes holidays. When part of the pay period includes a public holiday calculate deductions as you normally would.
The employee takes holidays
The following procedures apply when you pay vacation pay and your employee takes holidays.
Note
If your employee takes holidays but does not receive vacation pay at that time, see the next section, The employee does not take holidays.
CPP contributions
Deduct CPP contributions from vacation pay in the same way as you would from regular pay. Do not change the pay period table you normally use. Do not deduct more than the maximum employee contribution for the year.
EI premiums
Deduct EI premiums from vacation pay in the same way you would from regular pay. Do not deduct more than the maximum employee premium for the year.
Income tax
When you calculate the amount of income tax to deduct, use the tax table that applies to the period of vacation. For example, for one week of paid vacation, use the weekly tax deduction table. If your payroll is biweekly and the employee is paid one week of vacation pay and one week of regular pay, use the biweekly tables. If the employee is paid one week of vacation pay and the second week is unpaid, also use the biweekly tables.
The employee does not take holidays
The following procedures apply when you pay vacation pay and your employee does not take holidays.
CPP contributions
EI premiums
Income tax
Read Also: How Do I Pay My New York State Taxes
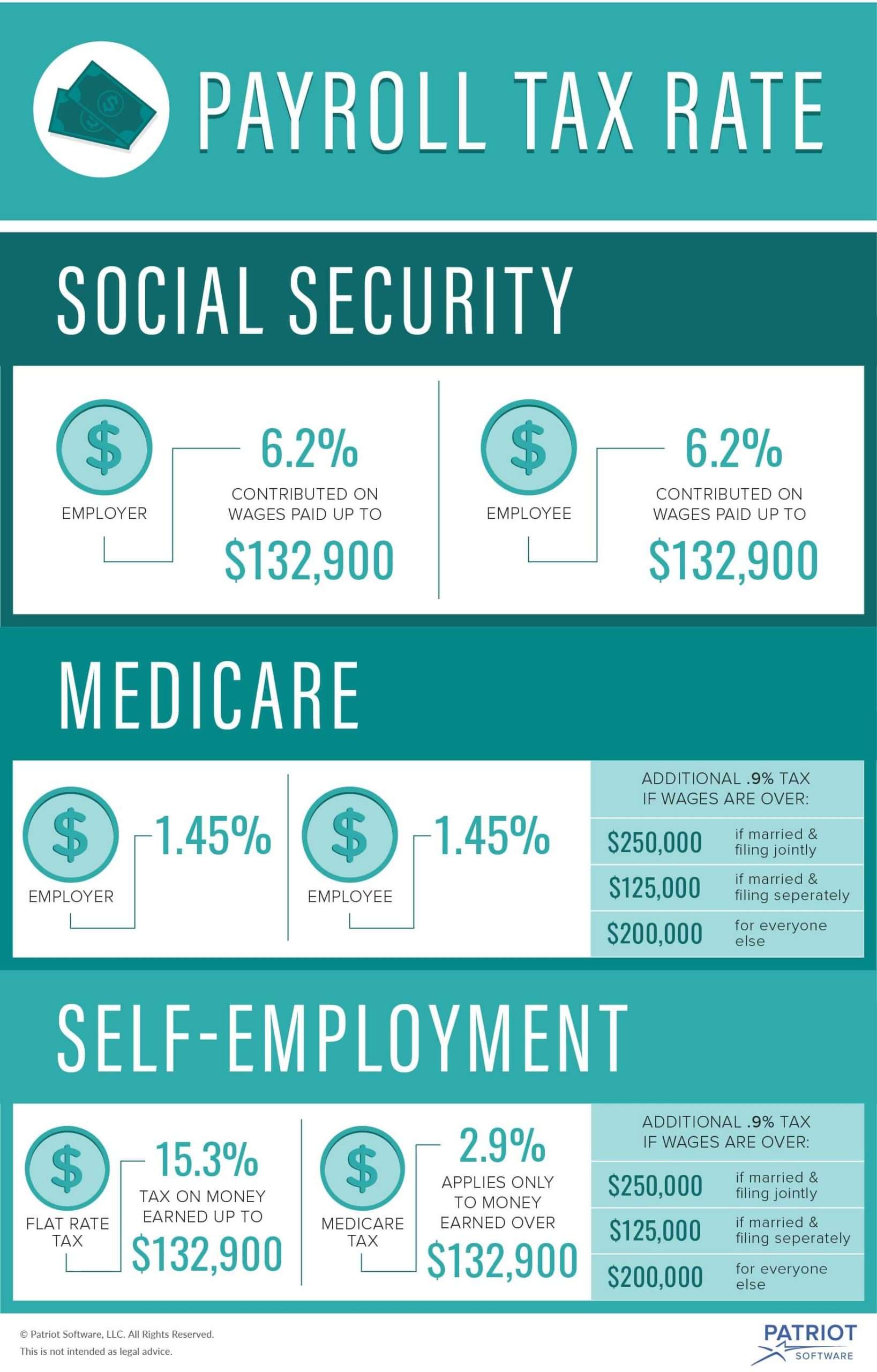
The Additional Medicare Tax
Since 2013, an additional Medicare tax of 0.9% has been applied to unmarried employees who file an individual tax return and whose Medicare wages exceed $200,000. The additional Medicare tax applies to income over $250,000 for married taxpayers who file a joint return and to income over $125,000 for married couples who file separate returns.
The additional Medicare tax is an employee-only tax. There’s no corresponding tax imposed on the employer.
Tax Rates And Income Thresholds
For 2022, the Ontario tax rates and income thresholds are:
Chart 2 2022 Ontario tax rates and income thresholds
| Annual taxable income |
|---|
For 2022, the Ontario health premium is:
- when taxable income is less than or equal to $20,000, the premium is $0
- when taxable income is greater than $20,000 and less than or equal to $36,000, the premium is equal to the lesser of $300 and 6% of taxable income greater than $20,000
- when taxable income is greater than $36,000 and less than or equal to $48,000, the premium is equal to the lesser of $450 and $300 plus 6% of taxable income greater than $36,000
- when taxable income is greater than $48,000 and less than or equal to $72,000, the premium is equal to the lesser of $600, and $450 plus 25% of taxable income greater than $48,000
- when taxable income is greater than $72,000 and less than or equal to $200,000, the premium is equal to the lesser of $750 and $600 plus 25% of taxable income greater than $72,000 and
- when taxable income is greater than $200,000, the premium is equal to the lesser of $900 and $750 plus 25% of taxable income greater than $200,000
Also Check: How To File My 2015 Taxes
Other Employer Payroll Tax Requirements
As the pay periods go by and tax money is withheld from employees paychecks , businesses may eventually have to file quarterly tax returns with federal, state and local governments. The deadline for filing IRS Form 941, Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return is usually the last day of the month following the end of a quarter. So, if the first quarter of the year ends March 31, then the first Form 941 would be due April 30. Payments can be made via the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System® .
After the year is over, employers typically need to issue Forms W-2 to employees and Forms 1099-MISC to independent contractors. They might also have to file three additional forms:
- Form W-3 reports the total W-2 earnings from all employees to the Social Security Administration
- Form 1096 is a summary and transmittal form that accompanies other IRS forms
Reducing The Rate Of Your Ei Premiums If You Have A Short
Some employers provide a wage-loss replacement plan for short-term disability to their employees. If the plan meets certain standards established by the Employment Insurance Regulations, the employers EI premiums could be paid at a reduced rate .
To benefit from a reduced employer premium rate, you have to register with the EI Premium Reduction Program by submitting both of the following:
- an initial application, which you can find in Service Canadas publication called the EI Premium Reduction Program
- a copy of the short-term disability plan provided to your employees
You can get the guide at your Service Canada Centre or by contacting:
Service Canada
Website: EI Premium Reduction Program For employers
The employers EI premiums are reduced only in respect of employees covered by the approved plan . These employees will continue to be reported under the current payroll program account, which will be set at a reduced rate. An officer of the EI Premium Reduction Program will ask you to open an additional payroll program account under your business number to make a separate remittance for employees not covered by the plan.
You have to file a separate T4 information return for each payroll program account under your BN:
Where an employee was transferred between both accounts in the same calendar year, file a separate T4 slip for each account.
You May Like: How To Find Real Estate Taxes Paid
Which Provincial Or Territorial Tax Table Should You Use
Before you decide which tax table to use, you have to determine your employee’s province or territory of employment. This depends on whether or not you require the employee to report for work at your place of business.
If the employee reports for work at your place of business, the province or territory of employment is considered to be the province or territory where your business is located.
To withhold payroll deductions, use the tax table for that province or territory of employment.
If you do not require the employee to report for work at your place of business, the province or territory of employment is the province or territory in which your business is located and from which you pay your employee’s salary.
For more information and examples, see Chapter 1, “General Information” in Guide T4001, Employers’ Guide Payroll Deductions and Remittances.
Statutory Payroll Tax Deductions
The law requires that payroll taxes must be withheld from an employee’s paycheck each pay period. Employers must then transmit these withholdings to various tax agencies. Payroll tax deductions include the following:
- Federal income tax withholding based on the withholding tables in Publication 15
- Social Security tax withholding of 6.2% in 2020 and 2021, up to the annual maximum taxable earnings or wage base of $137,700 for 2020 and $142,800 for 2021
- Medicare tax withholding of 1.45%
- Additional Medicare tax withholding of 0.9% for employees earning over $200,000
- State income tax withholding
- Various local tax withholdings, such as city, county, or school district taxes state disability or unemployment insurance
Also Check: How Much Do You Have To Make To Report Taxes
Payroll Tax Vs Income Tax Comparison Chart
When differentiating income vs payroll tax, employee and employer responsibility, levies, and tax rates are a few things to compare. We’ll create a comparison chart for income vs payroll tax to help you differentiate them properly without dependents.
| Comparison | ||
| The current federal payroll tax rate is 15.3%. | The federal income tax rate starts from 10% to 37%. | |
| Levies | The government levies payroll taxes on employees and employers. | Income taxes are levies on salaries and wages of an employee. |
| Employer responsibility | Withhold employer’s share of payroll taxes, Medicare, and social security. | Report employee earnings and remit deductions from employees’ wages. |
| Employee responsibility | Pay federal and state social security and Medicare tax. Employees pay local payroll taxes based on their country and city. | Paying income tax to the Internal Revenue Service. Make payments based on filing status and net income |
| How to calculate | Multiply employees’ Social Security tax rate by the gross pay for the current pay period . Employers and employees split payroll taxes 50/50. Calculate payroll tax by multiplying the Medicare tax rate by the employee’s gross pay. | The higher your income, the more income tax you pay. Calculate income tax based on your household income. Subtract deductions and exemptions to get your taxable income. |
