Whats The Difference Between Federal Taxable And Adjusted Gross Income
Adjusted gross income is your gross income minus above-the-line adjustments . These can include certain business expenses, contributions to health savings accounts, educator expenses, student loan interest and other adjustments. After youve calculated your AGI on your Form 1040, you then deduct your standard deduction or itemized deductions, and any qualified business income, to arrive at your taxable income. Thats the amount of income youll have to pay taxes on.
How We Make Money
The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site, including, for example, the order in which they may appear within the listing categories. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you.
At Bankrate we strive to help you make smarter financial decisions. While we adhere to stricteditorial integrity, this post may contain references to products from our partners. Heres an explanation forhow we make money.
As Tax Changes Brew In Congress Outlook Is Grim For Pass
With the festivities starting for Halloween, Congress has chosen to provide tricks rather than treats in their desire to increase taxes and push through significant tax law changes through a process called budget reconciliation. As Congress holds the federal purse strings, they can focus on policy regarding spending and revenue through the budget reconciliation process, which ultimately impacts the federal taxation system. Bipartisan support can be avoided in the Senate when using the budget reconciliation process, which allows the Senate to pass legislation through a simple majority versus needing the traditional 60 votes. With our current Senate being split 50 Republicans, and essentially 50 Democrats , Vice President Kamala Harris can provide the tiebreaker vote to get to a simple majority and advanceanother substantial change to the tax code.
An American flag flies outside the U.S. Capitol in Washington, D.C., U.S., on Thursday, Sept. 16, … 2021. The biggest set of U.S. tax increases in a generation took a major step forward on Wednesday with approval by the House Ways and Means Committee of $2.1 trillion in new levies mostly focused on corporations and the wealthy. Photographer: Stefani Reynolds/Bloomberg
The House Ways and Means Committee issued a tax proposal that is expected to be acted on by the House of Representatives as part of Build Back Better reconciliation legislation. The most daunting impact for flow-through owners are highlighted below.
Bonadio
Read Also: How To Reduce Income Tax
Will The Top Tax Rate Be Raised
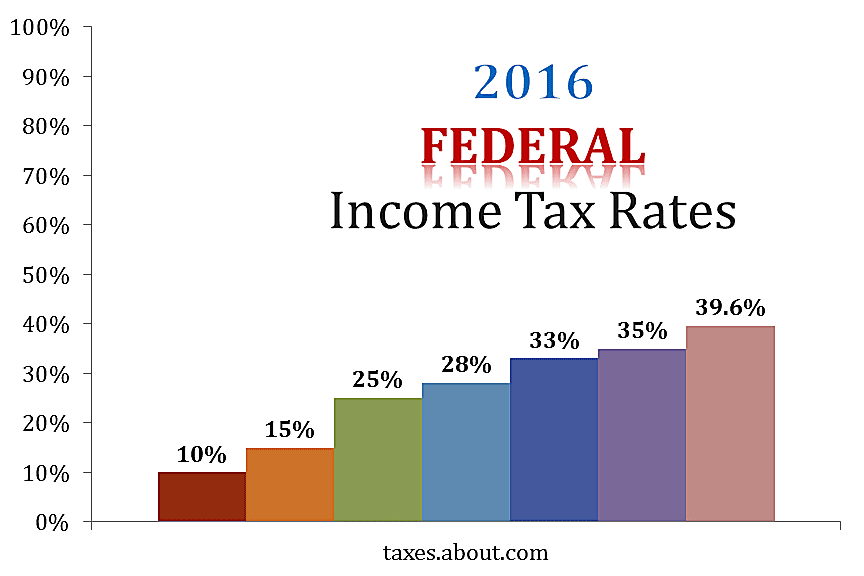
Will the top income tax rate go up in the near future? It will if President Biden gets his way. As part of his American Families Plan, the president has proposed increasing the highest tax rate from 37% to 39.6%, which is where it was before the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017. The 39.6% rate would apply to single filers with taxable income over $452,700 and joint filers with taxable income exceeding $509,300.
There’s also a separate proposal coming out of the House Ways and Means Committee that would also raise the top rate to 39.6%. Under this plan, the 39.6% rate would apply to single filers with more than $400,000 of taxable income and married couples filing a joint return with over $450,000 of taxable income. The House plan would also tack on an additional 3% surtax if for anyone with a modified adjusted gross income over $5 million, which would effectively push the tax rate up to 42.6% for the wealthiest Americans.
When Is The Federal Income Tax Paid
The Federal Income Tax must be paid throughout the year through either through tax withholding by an employer, or quarterly tax payments by the taxpayer. On Tax Day, you must reconcile your taxes and either pay any outstanding debt or request a refund from the IRS.
- Tax Withholding – If you are an employee, your employer will deduct a percentage of each paycheck you receive to submit to the IRS on your behalf. If your employer deducts more then you owe in tax, you will qualify for an income tax refund at the end of the year.
- Estimated Tax Payments – If you are self-employed or receive income from a source that does not withhold taxes for you, you need to submit estimated tax payments to the IRS yourself four times a year. See estimated tax payments.
| Single Businessman |
| 28% |
* Special long-term capital gains rates apply to gains from certain small-business stocks
The capital gains tax rates apply to gains made through the sale of capital assets including stocks and securities, bonds, real estate, and collectibles. Capital gains are taxed when the gain is realized , and the length the asset was held helps determine the tax rate paid.
- Long-term capital gains, which are taxed at a lower rate, are gains on capital assets held for more then one year.
- Short-term capital gains, usually taxed at the taxpayer’s normal tax bracket, are gains realized on capital assets held for under one year.
You May Like: What Is Tax Deadline 2021
How To File Your Taxes In 2021
You can file your tax return for the 2020 tax year using online tax preparation services such as TurboTax and SimpleTax. These tax software are CRA-certified and connect with NETFILE to import some of your tax directly numbers from the CRA .
Following submitting your tax return, you can expect your tax refund within 2 weeks or so if you have signed up for direct deposits.
Learn about the best free tax return software in Canada.
Related reading
Modern Interpretation Of The Power To Tax Incomes
The modern interpretation of the Sixteenth Amendment taxation power can be found in Commissioner v. Glenshaw Glass Co.348U.S.426. In that case, a taxpayer had received an award of punitive damages from a competitor for antitrust violations and sought to avoid paying taxes on that award. The Court observed that Congress, in imposing the income tax, had defined gross income, under the Internal Revenue Code of 1939, to include:
gains, profits, and income derived from salaries, wages or compensation for personal service … of whatever kind and in whatever form paid, or from professions, vocations, trades, businesses, commerce, or sales, or dealings in property, whether real or personal, growing out of the ownership or use of or interest in such property also from interest, rent, dividends, securities, or the transaction of any business carried on for gain or profit, or gains or profits and income derived from any source whatever.:p. 429
The Court held that “this language was used by Congress to exert in this field the full measure of its taxing power”, id., and that “the Court has given a liberal construction to this broad phraseology in recognition of the intention of Congress to tax all gains except those specifically exempted.”:p. 430
Read Also: How To Fill Out Taxes For Self Employed
Things Worth Remembering If You Havent Filed 2020 Taxes
Some items and notes for those who havent filed taxes on income they earned or received in 2020:
- The tax filing deadline has been moved from April 15 to May 15, 2021. The deadline extension only applies to federal taxes.
- Income from stimulus checks is not taxable.
- Income for the first $10,200 of unemployment compensation is not taxable for people whose modified adjusted gross income is less than $150,000. Unemployment compensation over $10,200 is taxable.
- The penalties and fines that normally accompany taxes filed late, will not be applied as long as you meet the May 17 deadline.
- You can ask the IRS for a filing extension to Oct. 15 by filing form 4868 before May 17.
- Even if you receive an extension, you still must pay taxes owed by May 17.
Accounting Periods And Methods
The US tax system allows individuals and entities to choose their tax year. Most individuals choose the calendar year. There are restrictions on choice of tax year for some closely held entities. Taxpayers may change their tax year in certain circumstances, and such change may require IRS approval.
Taxpayers must determine their taxable income based on their method of accounting for the particular activity. Most individuals use the cash method for all activities. Under this method, income is recognized when received and deductions taken when paid. Taxpayers may choose or be required to use the accrual method for some activities. Under this method, income is recognized when the right to receive it arises, and deductions are taken when the liability to pay arises and the amount can be reasonably determined. Taxpayers recognizing cost of goods sold on inventory must use the accrual method with respect to sales and costs of the inventory.
Methods of accounting may differ for financial reporting and tax purposes. Specific methods are specified for certain types of income or expenses. Gain on sale of property other than inventory may be recognized at the time of sale or over the period in which installment sale payments are received. Income from long-term contracts must be recognized ratably over the term of the contract, not just at completion. Other special rules also apply.
Don’t Miss: When Do You Pay Quarterly Taxes
What Is A Federal Allowance
A federal withholding allowance refers to information that is on the W-4 form for tax years before 2020. You generally fill out a W-4 when you start a new job or experience a life change, like having a child. Your W-4 helps your employer understand how much tax to withhold from your paycheck. Before 2020, the number of personal allowances you took helped determine the amount your employer withheld the more allowances you claimed, the less tax your employer would withhold. But the IRS changed the W-4 starting with the 2020 tax year. The new form eliminates personal allowances.Learn more about the new W-4.
How To Find Your Tax Bracket
There are numerous online sources to find your specific federal income tax bracket. The IRS makes available a variety of information, including annual tax tables that provide highly detailed tax filing statuses in increments of $50 of taxable income up to $100,000.
Other websites provide tax bracket calculators that do the math for you, as long as you know your filing status and taxable income. Your tax bracket can shift from year to year, depending on inflation adjustments and changes in your income and status, so its worth checking on an annual basis.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is California State Tax
Income Tax Law Changes
Following the results of the 2020 elections, I think we all knew an increase in individual income tax rates was expected. The taxable income base is also not significantly different from 2017. However, many were caught off guard with the surcharge tax proposed on high income individuals. Included in the proposal, is that for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2021, married filing joint, head of household, surviving spouse, and single taxpayers, will be required to pay an additional 3% on taxable income in excess of $5,000,000. I would like to highlight that in the proposal there is no taxable income deviation for married versus single taxpayers. In other words, if there are two high earning spouses, you are hit with a double whammy.
Unfortunately, this is only the beginning. There are also proposals to limit the pass-through entity deduction and expand the net investment income tax as well.
Section 199A Qualified Business Income Deduction Limitation
Under the House Ways and Means Committee proposal, there will be a maximum 199A deduction allowed for taxpayers depending on their filing status.
Proposed 199A Limitation
The Bonadio Group
However, even if your current 199A deduction does not come close to those limits, your 199A deduction still may be in jeopardy. There is still a lot of negotiating currently underway, and some are suggesting that more stringent limitations may be placed on the 199A deduction.
Increase in capital gains rates
The Bonadio Group
How To Get Into A Lower Tax Bracket And Pay A Lower Federal Income Tax Rate
Two common ways of reducing your tax bill are credits and deductions.
-
Tax credits directly reduce the amount of tax you owe they don’t affect what bracket you’re in.
-
Tax deductions, on the other hand, reduce how much of your income is subject to taxes. Generally, deductions lower your taxable income by the percentage of your highest federal income tax bracket. So if you fall into the 22% tax bracket, a $1,000 deduction could save you $220.
In other words: Take all the tax deductions you can claim they can reduce your taxable income and could kick you to a lower bracket, which means you pay a lower tax rate.
Recommended Reading: Where To Mail Federal Tax Return 2021
Effects On Income Inequality
According to the CBO, U.S. federal tax policies substantially reduce income inequality measured after taxes. Taxes became less progressive measured from 1979 to 2011. The tax policies of the mid-1980s were the least progressive period since 1979. Government transfer payments contributed more to reducing inequality than taxes.
The 2020 Ordinary Income Tax Brackets
The United States tax system provides for graduated taxation based on levels of ordinary income. Higher levels of income are taxed at higher rates. If your pension or Social Security income is taxed, it will be taxed at the ordinary income tax rates, just as if it were income from a job.
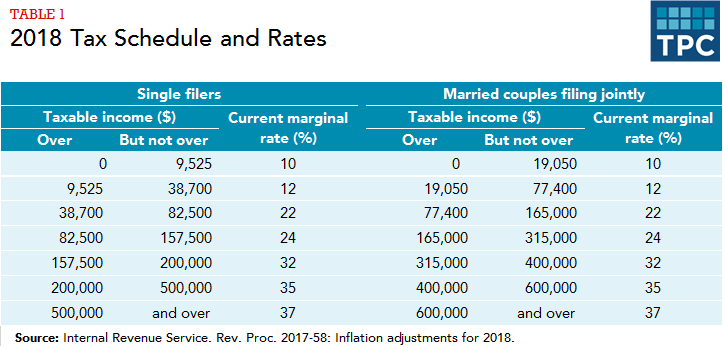
For the 2020 tax year, the tax rates for a single person are:
- 10 percent of the first $9,875 of income.
- 12 percent of all income between $9,875 and $40,125.
- 22 percent of all income between $40,125 and $85,525.
- 24 percent of all income between $85,525 and $163,300.
- 32 percent of all income between $163,300 and $207,350.
- 35 percent of all income between $207,350 and $518,400.
- 37 percent of all income above $518,400.
If you’re single and your sole source of income in 2020 is your pension, and you receive $2,500 per month from your pension fund, your annual income is $30,000. You’ll pay 10 percent tax on the first $9,875 and 12 percent tax on the remaining $20,125 for a total tax of $3,402.50.
For a married couple, the tax rates are:
- 10 percent of the first $19,750 of income.
- 12 percent of all income between $19,750 and $80,250.
- 22 percent of all income between $80,250 and $171,050.
- 24 percent of all income between $171,050 and $326,600.
- 32 percent of all income between $326,600 and $414,700.
- 35 percent of all income between $414,700 and $622,050.
- 37 percent of all income above $622,050.
For individuals filing as heads of household, the tax rates are:
You May Like: Does Llc Pay Self Employment Tax
Tax Rates For Previous Years
To find income tax rates from previous years, see the Income Tax Package for that year. For 2018 and previous tax years, you can find the federal tax rates on Schedule 1. For 2019, 2020 and later tax years, you can find the federal tax rates on the Income Tax and Benefit Return. You will find the provincial or territorial tax rates on Form 428 for the respective province or territory . To find the Quebec provincial tax rates, go to Income tax return, schedules and guide .
Understanding How Federal Income Tax Brackets Work
Once you know your filing status and amount of taxable income, you can find your tax bracket. However, you should know that not all of your income is taxed at that rate. For example, if you fall in the 22% tax bracket, not all of your income is taxed at 22%. Why is that?
The reason is that the U.S. income tax system uses a graduated tax system, designed so that individual taxpayers pay an increasing rate as their income rises as outlined in the 2020 tax table above.
Lets look at Sarah, whose filing status is Single and who has a taxable income of $50,000. Using the 2020 information above, we can determine Sarahs total tax.
For 2020, Sarah will pay $6,790 in tax.
Also Check: When Does The Irs Start Accepting Tax Returns For 2021
How To Get Into A Lower Tax Bracket
Americans have two main ways to get into a lower tax bracket: tax credits and tax deductions.
Tax credits are a dollar-for-dollar reduction in your income tax bill. If you have a $2,000 tax bill but are eligible for $500 in tax credits, your bill drops to $1,500. Tax credits can save you more in taxes than deductions, and Americans can qualify for a variety of different credits.
The federal government gives tax credits for the cost of buying solar panels for your house and to offset the cost of adopting a child. Americans can also use education tax credits, tax credits for the cost of child care and dependent care and tax credits for having children, to name a few. Many states also offer tax credits.
While tax credits reduce your actual tax bill, tax deductions reduce the amount of your income that is taxable. If you have enough deductions to exceed the standard deduction for your filing status, you can itemize those expenses to lower your taxable income. For example, if your medical expenses exceed 10 percent of your adjusted gross income in 2021, you can claim those and lower your taxable income.
