No Income Tax Protection
Internal Revenue Code § 676 considers revocable trust assets as owned by the grantor for income tax purposes. Because of the grantors revocation rights, the grantor is deemed to own trust assets. As such, any income generated during the trust is reported under the grantors Social Security number. The income simply appears on the grantors personal income tax return.
The IRS considers a revocable trust to be a grantor trust for tax purposes if the grantor has the power to revoke the trust and revest the trust assets in himself. The power to revoke still invokes grantor trust status even if the grantor must exercise this power in conjunction with another person , unless that other person is an adverse party. IRC Section 672 states that adverse parties are someone who has a substantial beneficial interest in the trust, including a power of appointment over trust assets, and where the beneficial interest would be adversely affected by the exercise or non-exercise of the power to revoke.
Unless an adverse party must consent to the trusts revocation, all trust income is reported on the grantors personal return.
A revocable trust becomes irrevocable upon the grantors death. At death, the revocation right ends. The Trust becomes irrevocable. The irrevocable trust reports any trust income generated after the grantors death.
What Are The Trustees Responsibilities
Serving as trustee is no simple task. While very important, the prudent investment of trust assets is not a trustees only responsibility. Your trustees exact powers and duties will depend on the instructions in your trust agreement. But, in general, your trustee will:
- Hold trust property
- Distribute trust income and/or principal to the beneficiaries, as directed in the trust agreement
- Make tax decisions concerning the trust
- Keep records of all trust transactions
- Issue statements of account and tax reports to the trust beneficiaries
- Answer any questions you and the beneficiaries may have concerning the trust
Your trustee may have broad powers or very limited powers. In either case, your trustee is a fiduciary and must follow a strict standard of care when performing trust functions.
Insurance Segregated Fund Trust
This is a related segregated fund of a life insurer for life insurance policies and is considered to be an inter vivos trust. The fund’s property and income are considered to be the property and income of the trust, with the life insurer as the trustee.
Note
You have to file a separate T3 return and financial statements for each fund. If all the beneficiaries are fully registered plans, complete only the identification and certification areas of the T3 return and enclose the financial statements. If the beneficiaries are both registered and non-registered plans, report and allocate only the income that applies to the non-registered plans.
Recommended Reading: Do I Need W2 To File Taxes
How Do I Know If My Assets Are Properly Titled To My Revocable Trust
The account statement, stock certificate, title or deed will make some reference to the trust or to you as trustee. You might also elect to fund your trust by naming the trust as a beneficiary of life insurance or other similar arrangements. Your attorney and financial advisor may assist you with the transfer of assets to your trust. If your trust will own real estate then it is important to have the deed prepared by an attorney. The attorney will consider the impact of existing mortgages, title issues and homestead restrictions when the deed is prepared.
Revocable Trusts And Irrevocable Trusts
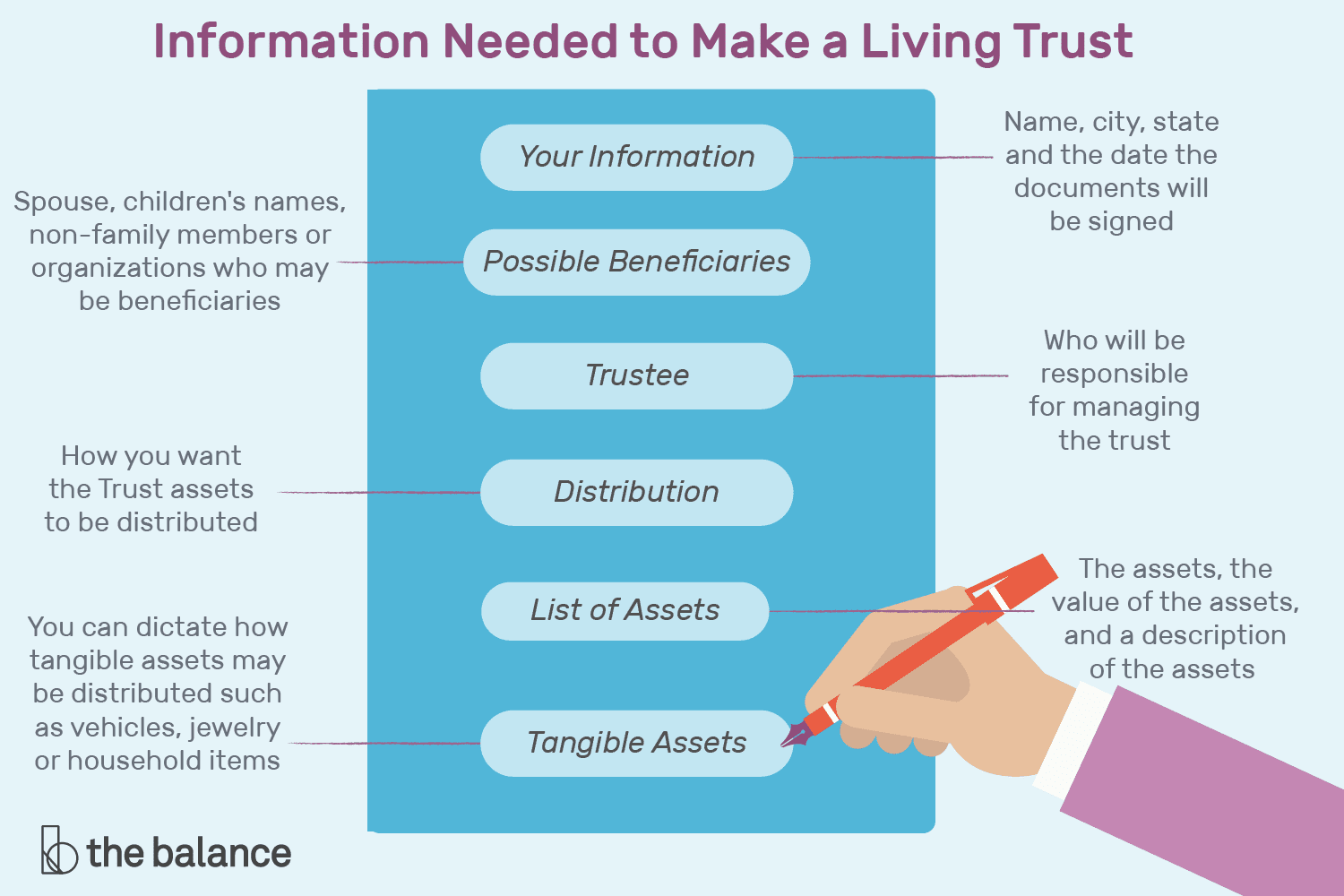
Revocable trusts and irrevocable trusts are two types of living trusts people use to have a trustee manage their estates during their lifetime and after their demise. Both have an advantage over traditional estate planning methods like wills, as they take effect right when the grantor is still alive. Another advantage of living trusts over wills is the ability to skip the probate process.
Here are some of the major differences between a revocable trust and an irrevocable trust:
Also Check: Harris County Property Tax Protest Services
Can The Trust Hold Title To My Homestead
In some situations your homestead property can be transferred to your trust. Most Florida counties have special requirements to maintain the homestead tax exemption and special language may be required in the trust agreement and the deed. However, homestead property may lose its exemption from creditors when title is held in a revocable trust-the bankruptcy law on this point is unsettled. Your attorney can advise you on whether placing your homestead in your trust is appropriate, and if so, the requirements for a valid transfer.
Why Do Revocable Trusts Provide No Tax Protection
Some trusts do create various tax benefits. So why does a Living Trust provide no tax benefit?
In most revocable trusts the grantor , is also the beneficiary. The grantor then transfers assets into the Living Trust. Typically people transfer real property, liquid assets, CDs and bank accounts. The Living Trust holds the assets for the Grantors benefit. Further, the Grantor is free to take those assets back at any time. After the grantors death, the trust acts like a Will. The trusts assets pass to others under the trusts terms.
These trusts are revocable trusts because the Grantor expressly reserves the right to revoke. Further, that right extends to amend the trust.
Read Also: Where Is My State Tax Refund Ga
Assessing Tax Obligations On An Irrevocable Trust
An irrevocable trust can be created in one of two ways. If the grantor of the trust chooses to create an irrevocable trust during their lifetime, they will be actively choosing to forfeit ownership of specific assets and placing them under complete control of the trust and the trustee appointed to manage them. Alternatively, a trust may become irrevocable upon the death of a grantor who first created a revocable trust.
In a situation such as this, the control of assets within the trust are dictated by the terms laid out by the grantor prior to their death. As mentioned previously, the grantor may choose to grant total control of asset distribution to the trustee, who will then ensure that named beneficiaries receive what has been allotted to them or continue to manage the assets as per the original instructions of the grantor.
Trust Tax Rates For 2020
Trust income is taxed according to what type of income it was, so a capital gain from selling a stock can be taxed differently from business income. Overall, trust income is also subject to different rates than the personal income tax rates. The trust tax brackets include only four tax rates for 2020 taxes : 10% for income up to $2,600 24% for income between $2,600 and $9,450 35% for income between $9,450 and $12,950, and 37% for all income over $12,950.
Don’t Miss: Csl Plasma Taxable
Exploring Revocable Trust Taxes
A revocable trust provides a degree of flexibility and customization for grantors. During the lifetime of the grantor, the terms and provisions of the trust can be altered at will to ensure that it matches their needs and expectations. A trust can also be canceled entirely by the grantor after it has been established. Once the grantor has initiated the trust, a trustee must be appointed who will oversee daily operations. The trustee receives all directions and mandates from the grantor and is responsible for executing them. The grantor also has the ability to specify whether the trustee should immediately distribute assets to beneficiaries or continue to manage the property in question following the grantor’s passing. If desired, the grantor can name themselves trustee of the living trust until their death.
Throughout the lifespan of a revocable trust, it is not uncommon for the principal held within it to fluctuate due to appreciation or depreciation of the assets being held, as well as the expenses incurred through retaining a trustee. Principal values can also change significantly depending upon the actions of the grantor, who still has the ability to withdraw or contribute assets to the trust until their passing.
Is A Form 1041 Required For Revocable Trust
In general, you will not have to file Form 1041 for a revocable living trust so long as you are alive and well and serve as its trustee. The revocable living trust’s tax identification number is your own Social Security number because, technically, you still own all the assets the trust contains. Any income earned by a revocable living trust is reported on the personal Form 1040.
All interest, dividends, and other income earned by those assets are reported to the Internal Revenue Service on your tax return. All income earned by your revocable living trust is reported on your personal Form 1040, not on a separate revocable trust tax return.
For most purposes, you are your revocable trust. You have total control of the assets you place into it. You can take them back into your ownership if you choose. You can sell them or give them away. They remain yours.
Read Also: Do You Have To Pay Taxes On Plasma Donations
Example: Allocating Depreciation Between The Trust And The Beneficiary
- A trust has $20,000 of accounting income and $10,000 of depreciation.
- The single income beneficiary of the trust receives $8000.
- Because the trust document does not specify an allocation of depreciation, the trust can claim $10,000/$20,000Ã$10,000 = 1/2 Ã$10,000 = $5000 of depreciation.
- The income beneficiary can claim the other $5000 of depreciation, reducing the beneficiary’s taxable income = $8000â$5000 = $3000.
Direct expenses for tax-free income are not deductible, since no taxes are paid on such income. Indirect expenses, which are the expenses of administering the trust, are generally deductible, but if the trust has tax-free income, then a proportion, = tax-free income ÷ trust accounting income, of indirect expenses is not deductible.
| Nondeductible Indirect Expense Allocable to Tax-Free Income | = | Accounting Income |
Who Should I Name As Trustee
Any individual, other than the grantor, may serve as trustee of a trust, including the grantors spouse, children, family members, or friends. Of course, given the fiduciary duties required of a trustee, youll want to choose someone who is honest, diligent, and trustworthy . If you would rather have an independent party act as trustee, there are a number of very well qualified professional trust companies in the community. If desirable, more than one individual may be named to serve as co-trustee.
Don’t Miss: Do You Have To Pay Taxes On Plasma Donations
Researching The Tax Responsibilties Of The Grantor
Due to the privileges and flexibility offered to the grantor of the revocable trust, it perhaps should come as no surprise that the tax burden of the trust will fall back on this individual. Any income derived from assets within a revocable trust must be reported by the grantor of the trust as part of their regular income tax filing. The named beneficiaries of the trust are not responsible for any tax obligations attached to it due to the fact that the grantor will already have paid taxes on all items placed within the trust itself. To summarize, the assets placed in a revocable trust remain the full property of the grantor until their death. They can sell these properties, remove them from the trust or gift them to individuals as they see fit.
When the grantor of the trust passes away, the status of the revocable trust shifts to irrevocable. At this time, both the control of the trust and the tax obligations associated with it will change significantly.
How Are Family Trusts Taxed
The taxation of family trusts can be complex. It’s always a good idea to consult a tax professional to determine how your specific family trust may be taxed.
Grantor trusts, where the grantor has control over the assets, generally require grantors to report all income from a trust on their own individual tax returns. Non-grantor trusts, on the other hand, work differently. Typically, the trust itself or its beneficiaries pay tax on taxable income.
Income kept in the trust is paid on a trust tax return using Form 1041. Income distributed to beneficiaries is reported to the beneficiaries by the trust using Form K-1. This form specifies how much of the distribution is a principal distribution, which generally isn’t taxable, versus an interest, capital gains or other income distribution, which may be taxable.
If a non-grantor trust has more than one beneficiary, the trust will divide the income between each beneficiary based on the terms of the trust. Then, it will issue a Form K-1 to each beneficiary specify each individual’s portion of the income. Beneficiaries input information from Form K-1 into their personal tax returns.
Don’t Miss: How Can I Make Payments For My Taxes
Do Revocable Trusts Have To File A Federal Income Tax Return
The creator of a revocable trust, legally called the grantor, has the right to change, amend or revoke do away with the trust at any time. Also known as a grantor trust, the income earned on the trust is apportioned to the grantor while living. The grantor must then report any income, dividends, deductions and gains on their own personal income tax return. The beneficiaries of a revocable trust have no tax responsibility upon receiving income distributions at the death of the grantor. Grantors of a revocable trust are personally responsible for listing the income from the trust on personal income tax returns, and for paying any applicable taxes while living, the beneficiaries are not liable. Understanding these grantor trust tax return filing requirements is absolutely essential for all parties involved.
Tips
-
If the grantor of a revocable trust earns income from the sale of assets in a revocable trust during the year, they will be required to report these earnings as part of their personal income tax return. Once the grantor dies, the trust is converted into an irrevocable trust, at which point tax regulations change significantly.
Understanding Trusts And Beneficiaries
A trust is a fiduciary relationship whereby the trustor or grantor gives another partythe trusteethe right to hold property or assets for the benefit of a third party .
Trusts are established to provide legal protection and to safeguard assets usually done as part of estate planning. Trusts can be used to ensure the assets are properly distributed to the beneficiaries according to the wishes of the grantor. Trusts can also help to reduce estate and inheritance taxes as well as avoid probate, which is the legal court process of distributing assets upon the death of the owner.
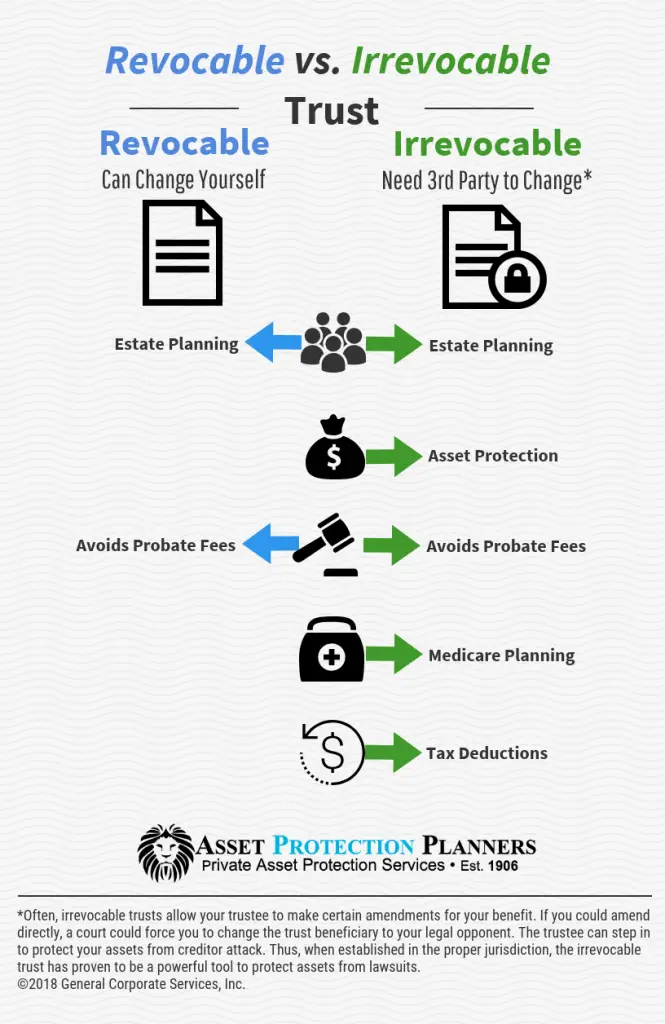
Although there are several types of trusts, they typically fall into one of two categories. A revocable trust can be changed or closed at any time during the grantor’s lifetime.
Conversely, an irrevocable trust cannot be amended or closed once it has been opened, including those trusts that become irrevocable upon the grantor’s death. The grantorby establishing an irrevocable trustessentially has transferred all ownership or title of the assets in the trust.
There are various tax rules for beneficiaries of income from trusts, depending on whether the trust is revocable or irrevocableas well as the type of income received from the trust.
Recommended Reading: Louisiana Payroll Calculator
Q: What Is A Grantor Trust
A: “Grantor trust” is a term used in the Internal Revenue Code to describe any trust over which the grantor or other owner retains the power to control or direct the trust’s income or assets. If a grantor retains certain powers over or benefits in a trust, the income of the trust will be taxed to the grantor, rather than to the trust. All “revocable trusts” are by definition grantor trusts. An “irrevocable trust” can be treated as a grantor trust if any of the grantor trust definitions contained in Internal Code §§ 671, 673, 674, 675, 676, or 677 are met. If a trust is a grantor trust, then the grantor is treated as the owner of the assets, the trust is disregarded as a separate tax entity, and all income is taxed to the grantor.
Do I Need To File A Gift Tax Return For Transfers To The Trust
Gifts to an irrevocable trust are treated as gifts to the underlying trust beneficiaries. If the grantors aggregate annual gifts to a beneficiary did not exceed the gift tax annual exclusion amount, a federal gift tax return is not required . However, a gift tax return is required if the grantor made gifts in excess of the annual exclusion the grantor desired to use his or her spouses annual exclusion amount or the trust was designed as a generation skipping trust.
You May Like: Do You Have To Pay Taxes On Plasma Donations
Do People Aware Of Revocable Vs Irrevocable Living Trusts In California
After your death, Living Trust assets pass to family and friends you have chosen as your beneficiaries. Living trusts are gaining popularity as an estate planning tool. Surprisingly only about 5% of the population takes advantage of them. Up-front costs of a Trust ranging from $250-$2500 may contribute to the low participation rates. I suspect a general lack of information keeps more folks from taking advantage of the Trust as an asset protection mechanism. Additionally, no one wants to think about their demise, let alone plan for their death or incapacity.
Q: How Does A Trust Compute Its Income Tax Liability
A: A trust computes its income tax liability in much the same way that an individual does and is allowed most of the credits and deductions that an individual is allowed. Similarly, deductions not allowed to individuals are not allowed to trusts. For example, personal living expenses such as food, utilities, recreational expenses, children’s education, depreciation of one’s personal residence, etc. are not allowed as a trust deduction any more than as an individual deduction. Trusts are also required to prepare a Schedule K-1 for their beneficiaries, showing them the amounts distributed by the trust to them. These amounts must be reported on the beneficiaries’ returns.
Also Check: Is Plasma Money Taxable
