Investment Income Taxes: On Portfolio Taxation
As an investor, one of your major responsibilities is understanding the implications that taxes can have on your overall financial plan, portfolio strategy, and investment income.
Transactions that result in realized capital gains are among the most common reasons you may owe taxes as an investor. Portfolio income, like dividends and interest from bonds, is another reason why you may be subject to portfolio income taxation.
This article will discuss what goes into portfolio income taxation. We will also cover what you should keep in mind regarding the subject as an investor.
Before we continue, Financial Professional wants to remind you that all materials in this article are educational in nature. Tax and investing situations can be very complex and laws vary by region. It may be wise to consider the help of an industry professional when it comes to tax- and investing-related decisions.
If you dont yet have industry professionals handling your portfolio, we can help! Check out Financial Professionals investment marketplace, where we partner with some of the best in the business to help find the right investment for you.
It Depends On The Account
The type of account that holds the investments that yields the investment income is probably the most important consideration when it relates to your taxes. Any income that is earned in tax-deferred accounts, like IRAs, 401Ks, pensions, etc. is NOT taxable in the year that the portfolio income is earned.
But why?
Remember, the only time that taxes apply within these accounts is when the account holder withdraws the funds. In that case, any amount you withdraw is added to the taxpayers income in the tax year of the withdrawal. This is true whether the income originates from either capital gains or other portfolio income. The 10% early withdrawal penalty may also apply.
Portfolio income, on the other hand, is ONLY currently taxable if it is earned in a taxable brokerage account. Typically, the income earned within a brokerage account is taxable as ordinary income. This means the earnings may be taxable at whatever the taxpayers federal and state marginal tax rate is.
As an over-simplified example, if an investor earned $50,000 from their annual salary and $3,000 from portfolio income, they would have $53,000 subject to ordinary income taxation. Again, this only applies if the earnings occur within a taxable brokerage account.
Note: If you earned portfolio income in a taxable brokerage account, you must report it, whether you reinvested the funds or not.
How To Minimize Taxes On Capital Gains
The most straightforward way to minimize capital gains tax is to hold your positions for as long as you can reasonably hold them. This ensures that your future gains will receive favorable tax treatment, and it also has the secondary effect of categorizing your dividends as qualified.
Further, if you’re not a high earner, you can attempt to take advantage of a 0% capital gains tax rate assuming your taxable income is less than $40,400 , or $80,800 , in 2021.
You May Like: Reverse Ein Lookup Irs
Line 652 Investment Tax Credit
A corporation can claim an investment tax credit to reduce Part I tax that it would otherwise have to pay, or in some cases this credit may be fully or partially refundable.
Use Schedule 31, Investment Tax Credit Corporations, to calculate the ITC.
A corporation earns ITCs by applying a specified percentage to the cost of acquiring certain property or on certain expenditures. However, you first have to reduce the capital cost of the property or the expenditure by any government or non-government assistance you received or will receive for that property or the expenditure. Any goods and services tax/harmonized sales tax input tax credit or rebate received for property acquired is considered government assistance.
On page 2 of Schedule 31, we list the percentages you have to apply to eligible investments and expenditures.
Available-for-use rule
A corporation is not considered to have acquired a property or made capital expenditures for earning an investment tax credit until the property becomes available for use.
For more information about the available-for-use rule, see When is property available for use?.
ReferencesSubsections 13 to 13 and 127
Investments and expenditures that qualify for an ITC
The following investments and expenditures earn an ITC:
A. the cost of acquiring qualified property
A.1. the cost of acquiring qualified resource property
B. SR& ED qualified expenditure pool
C. pre-production mining expenditures
D. apprenticeship expenditures
Note
Note
Tax On Interest Income
Interest income like the income produced by direct bond investments is taxable to you as ordinary income. You won’t have the opportunity to take advantage of lower long-term capital gains rates in the same way you would with qualified dividends or realized long-term gains from investing in stocks.
The key to minimizing the taxability of interest income is to hold interest-producing investments in tax-deferred or tax-exempt accounts. This prevents interest from being taxed as it is received.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Make Payments For My Taxes
The Proposed Regulations That Were Published On Dec 5 2012 Are Effective For Tax Years Beginning After Dec 31 2013 But The Net Investment Income Tax Went Into Effect On Jan 1 2013 May I Rely On Those Proposed Regulations The Proposed Regulations Published On Dec 2 2013 And/or The Final Regulations Also Published On Dec 2 2013 For Guidance On The Net Investment Income Tax During 2013
Yes. For taxable years beginning before Jan. 1, 2014 , taxpayers may rely on the 2012 proposed regulations , the 2013 proposed regulations , or the 2013 final regulations for purposes of completing Form 8960. However, to the extent that taxpayers take a position in a taxable year beginning before Jan. 1, 2014 that is inconsistent with the final regulations, and such position affects the treatment of one or more items in a taxable year beginning after Dec. 31, 2013, then such taxpayer must make reasonable adjustments to ensure that their Net Investment Income Tax liability in the taxable years beginning after Dec. 31, 2013 is not inappropriately distorted. For example, reasonable adjustments may be required to ensure that no item of income or deduction is taken into account in computing net investment income more than once, and that carryforwards, basis adjustments and other similar items are adjusted appropriately.
Ways To Mitigate A Tax Bill
If you realize that you have capital gains and could be hit with a tax bill at the end of the year, there are a few things you could do now to offset what you’d owe.
One is tax-loss harvesting, which is basically selling assets at a loss which can then offset your gains, according to Anjali Jariwala, CFP, CPA and founder of FIT Advisors in Torrance, California. These losses never expire and can be carried forward into future years, she said.
Another thing you can do to avoid a bill is to donate stock, according to Gorman.
“If you are a charitable person and your portfolio has increased in value, you can cherry-pick a few stocks to donate directly to charity,” she said. “Then you don’t have to recognize the capital gain and you potentially get a tax deduction, depending on what tax bracket you’re in and if you itemize.”
When you get to the point where you’re investing in the market, you can’t put your head in the sand about taxesMegan GormanManaging partner at Chequers Financial Management
People looking to begin investing who don’t want to have to worry about capital gains taxes and have longer-term time horizons, such as those who are saving up for retirement, can utilize a tax-deferred individual retirement account, such as a traditional or Roth IRA. These types of accounts won’t incur a capital gains tax, but there are other restrictions for taking out any earnings before retirement age.
You May Like: How Can I Make Payments For My Taxes
Types Of Investments Tax Software Can Help With
With tax software, figuring out what taxes you owe on your investments is straightforward. Well ask you simple questions about your investments, you can easily import your investments, and well search over 400 tax deductions to make sure you get every credit and deduction you qualify for.
With TurboTax, figuring out what taxes you owe on your investments is straightforward. Here are some of the most common types of investments TurboTax can help with:
- Investments within a retirement account
- Collectibles including rare stamps, coins, art and more
Whether you have stock, bonds, ETFs, cryptocurrency, rental property income or other investments, TurboTax Premier is designed for you. Increase your tax knowledge and understanding all while doing your taxes.
Line 616 Manufacturing And Processing Profits Deduction
Corporations that derive at least 10% of their gross revenue for the year from manufacturing or processing goods in Canada for sale or lease can claim the manufacturing and processing profits deduction . The MPPD reduces Part I tax otherwise payable.
The MPPD applies to the part of taxable income that represents Canadian manufacturing and processing profits. Calculate the MPPD at the rate of 13% on income that is not eligible for the small business deduction .
Use Schedule 27, Calculation of Canadian Manufacturing and Processing Profits Deduction, to calculate the manufacturing and processing profits deduction.
There are two ways to calculate Canadian manufacturing and processing profits: a simplified method for small manufacturing corporations, and a basic labour and capital employed in qualified activities formula for other corporations. These methods are outlined in Parts 1 and 2 of Schedule 27.
To qualify as a small manufacturing corporation, you have to meet all of the following requirements:
Corporations that do not qualify as small manufacturing corporations have to complete Part 2 of Schedule 27. In Part 2, you will find the basic formula for calculating Canadian manufacturing and processing profits, as well as detailed instructions on how to complete the schedule.
Corporations that produce electricity or steam for sale have to complete Parts 10 to 13 of Schedule 27.
ReferencesS4-F15-C1, Manufacturing and Processing
You May Like: How To Buy Tax Lien Properties In California
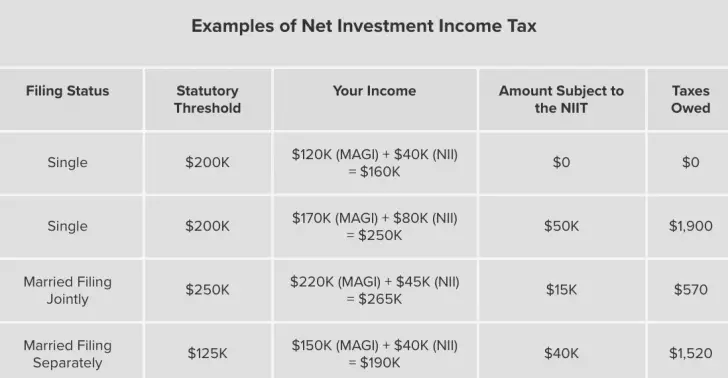
Single Taxpayer With Income Greater Than The Statutory Threshold
Taxpayer, a single filer, has $180,000 of wages. Taxpayer also received $90,000 from a passive partnership interest, which is considered Net Investment Income. Taxpayers modified adjusted gross income is $270,000.
Taxpayers modified adjusted gross income exceeds the threshold of $200,000 for single taxpayers by $70,000. Taxpayers Net Investment Income is $90,000.
The Net Investment Income Tax is based on the lesser of $70,000 or $90,000 . Taxpayer owes NIIT of $2,660 .
Lines 638 And 639 General Tax Reduction
Calculate this reduction on page 5.
If you were a CCPC throughout the tax year, enter the amount on line 638.
If you were a corporation other than a CCPC, an investment corporation, a mortgage investment corporation, a mutual fund corporation, or a corporation that has income that is not subject to the corporation tax rate of 38% enter the amount on line 639.
See General tax reduction for details.
You May Like: How To Get A Pin To File Taxes
What Is A Deferral Charge
A deferral charge is an additional tax payment imposed when an asset is sold after being held for more than 1 year to account for the fact that the gains on the asset were not taxed on an annual basisin other words, that taxes have been deferred. Deferral charges are an alternative approach to limiting or eliminating the tax benefit of deferral, while still relying on realization as the trigger for tax liability. The primary advantage of a deferral charge system, relative to a mark-to-market system, is that it avoids the need to value assets on an annual basis, which may be difficult in certain cases.
Some proposals for mark-to-market taxation combine mark-to-market taxation of certain assets with deferral charges for other assets.6 In general, the mark-to-market system is applied to assets for which independent valuations are more readily available, such as a stock traded on a public exchange, and deferral charges are used for assets for which an independent valuation may not be as readily available, such as a privately owned business. These approaches aim to balance competing goals in designing the system. A mark-to-market system requires valuations for hard-to-value assets, while a deferral charge system creates opportunities for tax avoidance through exploiting differences in the tax resulting from the deferral charge and the tax that would have resulted from annual taxation of accrued gains and losses.
Capital Gains Taxes On Owner
If you sell your home for a profit, thats considered a capital gain. But you may be able to exclude up to $250,000 of that gain from your income, or up to $500,000 if you and your spouse file a joint tax return.
To qualify, you must pass both the ownership test and the use test. This means you must have owned and used the real estate as your main home for a total period of at least two years out of the five years before the sale date. The two-year periods for owning the home and using the home dont have to be the same two-year periods. Typically, you cant take this exclusion if youve taken it for another home sale in the two years before the sale of this home.
Don’t Miss: How Can I Make Payments For My Taxes
How Are Capital Gains Taxes Calculated
You can calculate capital gains taxes using IRS forms. To calculate and report sales that resulted in capital gains or losses, start with IRS Form 8949. Record each sale, and calculate your hold time, basis, and gain or loss. Next, figure your net capital gains using Schedule D of IRS Form 1040. Then copy the results to your tax return on Form 1040 to figure your overall tax rate.
Find Out If Net Investment Income Tax Applies To You
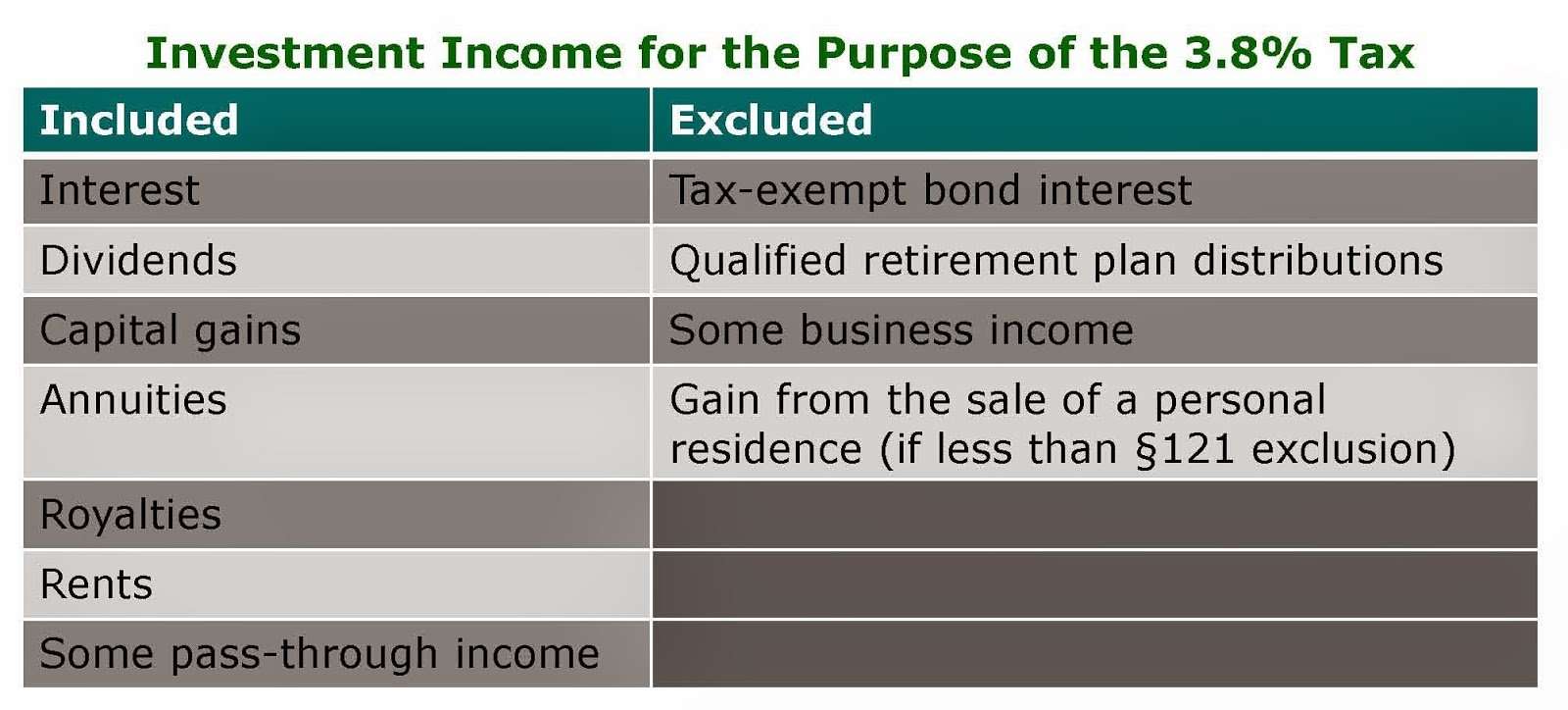
If an individual has income from investments, the individual may be subject to net investment income tax. Effective Jan. 1, 2013, individual taxpayers are liable for a 3.8 percent Net Investment Income Tax on the lesser of their net investment income, or the amount by which their modified adjusted gross income exceeds the statutory threshold amount based on their filing status.
The statutory threshold amounts are:
- Single or head of household $200,000, or
- Qualifying widow with a child $250,000.
In general, net investment income includes, but is not limited to: interest, dividends, capital gains, rental and royalty income, and non-qualified annuities.
Net investment income generally does not include wages, unemployment compensation, Social Security Benefits, alimony, and most self-employment income.
Additionally, net investment income does not include any gain on the sale of a personal residence that is excluded from gross income for regular income tax purposes. To the extent the gain is excluded from gross income for regular income tax purposes, it is not subject to the Net Investment Income Tax.
If an individual owes the net investment income tax, the individual must file Form 8960 PDF. Form 8960 Instructions PDF provides details on how to figure the amount of investment income subject to the tax.
For additional information on Net Investment Income Tax, see our questions and answers posted on IRS.gov.
Read Also: How To Get Stimulus Check 2021 Without Filing Taxes
Certain Investments May Have Special Tax Treatment
Certain types of investments can have special tax treatment. For instance, municipal bonds are normally tax-free for federal income taxes but may be taxable on your state tax return, depending on the state you live in and the state that issued the bond you invested in.
- It’s also possible to trigger special taxes, such as the alternative minimum tax , through instances like exercising incentive stock options. TurboTax can guide you through the process of figuring out if this applies to your situation or not.
- A bigger exception is money in tax-advantaged retirement accounts. Traditional retirement accounts, such as a traditional IRA or traditional 401, may allow you to take a tax deduction today. Then, the investments within the account can grow tax-free. When you withdraw the money in retirement after meeting the age requirements, the money typically counts as ordinary income and you will likely have to pay ordinary income taxes on this income.
- The other main type of tax-advantaged retirement accounts that are treated differently are Roth retirement accounts, such as a Roth IRA or Roth 401. You don’t get a tax deduction for contributing to these accounts. However, the money can grow tax-free and you can withdraw it tax-free, including the investment gains, in retirement after meeting age and other requirements.
There may be other exceptions depending on your specific investments and circumstances as well. TurboTax can help you navigate these more complex areas.
Keep Records Of Your Losses
One strategy to offset your capital gains liability is to sell any underperforming securities, thereby incurring a capital loss. If there arent capital gains, realized capital losses could reduce your taxable income, up to $3,000 a year.
Additionally, when capital losses exceed that threshold, you can carry the excess amount into the next tax season and beyond.
For example, if your capital losses in a given year are $4,000 and you had no capital gains, you can deduct $3,000 from your regular income. The additional $1,000 loss could then offset capital gains or taxable earnings in future years.
This strategy allows you to rid your portfolio of any losing trades while capturing tax benefits.
Theres one caveat: After you sell investments, you must wait at least 30 days before purchasing similar assets otherwise, the transaction becomes a wash sale.
A wash sale is a transaction where an investor sells an asset to realize tax advantages and purchases an identical investment soon after, often at a lower price. The IRS qualifies such transactions as wash sales, thereby eliminating the tax incentive.
Also Check: Michigan.gov/collectionseservice
Taxes On 401 Investments
401s are tax-deferred retirement accounts, typically sponsored by an employer does exist to serve self-employed people, too). This means that contributing to a traditional 401 will give you a tax deduction today and allow for invested money to grow tax-deferred.
As your money grows, you won’t be taxed on any dividends received or any capital gains realized. You can buy and sell every day in your 401 and still won’t be liable for any taxes due.
You’ll only pay 401 taxes when you withdraw money from your account, which hopefully takes place after you’re already retired. When you do ultimately withdraw money, you’ll be taxed on the entire distribution and at ordinary income rates, which are higher than long-term capital gains rates.
Usually, the benefit of investing in tax-deferred accounts will override the cost of any tax ultimately due. But it’s important to know that by deferring taxes now, you’ll eventually owe taxes in retirement.
