Add Futa Taxes To Employee Pay Stubs
You may choose to add FUTA taxes paid for an employee in their pay stubs. With 123PayStubs, you can easily add the employer-paid taxes such as FUTA, SUTA, and other state-specific employer-paid taxes to the pay stubs, along with accurate tax calculations. to know how to add FUTA taxes to pay stubs..
Fica Futa And Suta Taxes Explained
There are many types of taxes from federal, state, sales, property, and FICA taxes which gives the government many sources of revenue. However, all these taxes pay for different items like property taxes being used to fund public schools. One main type of tax every taxpayer pays is called the Federal Insurance Contributions Act or FICA tax.
This tax is also referred to as the payroll tax and funds two main public insurance programs:
- Medicare: provides healthcare for seniors over 65
- Social Security: allows people to receive a monthly source of income or pension when they retire.
Unemployment Taxes At The State Level
Both the federal government and most state governments collect unemployment taxes. The federal government collects unemployment funds and pays into state fundsknown as State Unemployment Tax . The federal funds help to supplement what the states collect.
Many employers pay both federal and state unemployment taxes, depending on what state you are doing business in. To find out if you, as a business owner, need to pay state unemployment tax, contact your state’s employment agency. If your state collects this tax, you will need to register with your state.
All businesses with employees must get a Federal Employer ID Number , to be used for all employment taxes. This ID number qualifies as the registration for your business and federal unemployment insurance payments.
Recommended Reading: Where Can I Amend My Taxes For Free
When Is Futa Tax Due
Usually, the FUTA tax payments are due by the end of the last month following the end of the quarter. The employer has to make the payments to the IRS on time.
- For Quarter 1 , the FUTA Tax Payment is due by April 30.
- For Quarter 2 , the FUTA Tax Payment is due by July 31.
- For Quarter 3 , the FUTA Tax Payment is due by October 31.
- For Quarter 4 , the FUTA Tax Payment is due by January 31.
Note: If the FUTA tax liability of your business for a quarter is less than $500, theres no need to deposit taxes at the end of the quarter. You may roll over the tax liability to the next quarter and pay the tax amount if the liability exceeds the $500 threshold.
Who Pays Futa Tax
You as a small business owner and employer of workers are responsible for paying the federal unemployment tax. Your employees do not pay any FUTA tax or have anything withheld from their paychecks for federal unemployment tax. Instead, the employer pays for all of the FUTA tax. Any business that fits into either of the following criteria need to pay FUTA taxes:
-
Your business paid employees at least $1,500 in wages in a calendar quarter during the current or previous year.
-
Your business employed one or more workers for at least some part of the day during 20 or more different weeks in the current or previous year. This criteria pertains to full-time, part-time and seasonal W-2 employees, but not independent contractors.
Read Also: Appeal Taxes Cook County
Futa Tax Vs State Unemployment Tax
Take note that the FUTA tax is in addition to any state unemployment insurance your business is required to pay. The FUTA tax provides for paying unemployment compensation on the federal level while state unemployment taxes work towards helping the state pay for unemployment compensation. State unemployment insurance or taxes vary from state to state, so youll need to check with the appropriate state authorities to find out your state’s tax rate.
Futa : What Are Futa Taxes And How To Calculate Them
Advertiser & Editorial Disclosure
Small business owners carry a lot of responsibility on their shoulders. Depending on your company, you may be in charge of hiring and training the right employees or setting the vision for your brand. Your duties might include payroll, monitoring your business credit reports, and managing your business credit scores, just to name a few. And then, of course, theres employment taxes and payroll taxes.
The long-term success of your business depends in part on your ability to manage your taxes . Paying taxes is an obligation youll need to fulfill again and again often on a monthly, quarterly, and yearly basis.
One employment tax that you need to be aware of is known as FUTA. In this guide, we break down what FUTA means, why the tax is required, and how to calculate and pay it.
Financing Can Help Cover Costs
Business owners can face a lot of unforeseen expenses. Keeping tabs on your business credit can help you get financing to help out.
Don’t Miss: Do I Have To File Taxes For Doordash If I Made Less Than $600
Who Must File Form 940
Most employers pay both a federal and a state unemployment tax. There are three tests used to determine whether you must pay FUTA tax: a general test, household employees test, and farmworkers employees test.
Under the general test, you’re subject to FUTA tax on the wages you pay employees who aren’t household or agricultural employees and must file Form 940, Employer’s Annual Federal Unemployment Tax Return for 2020 if:
- You paid wages of $1,500 or more to employees in any calendar quarter during 2019 or 2020, or
- You had one or more employees for at least some part of a day in any 20 or more different weeks in 2019 or 20 or more different weeks in 2020. Count all full-time, part-time, and temporary employees.
If a business was sold or transferred during the year, each employer who meets one of the conditions above must file Form 940. However, don’t include any wages paid by the predecessor employer on your Form 940 unless you’re a successor employer. For details, see “Successor employer” in the Instructions for Form 940. If you won’t be liable for filing Form 940 in the future, see “Final: Business closed or stopped paying wages” under Type of Return in the Instructions for Form 940 PDF.
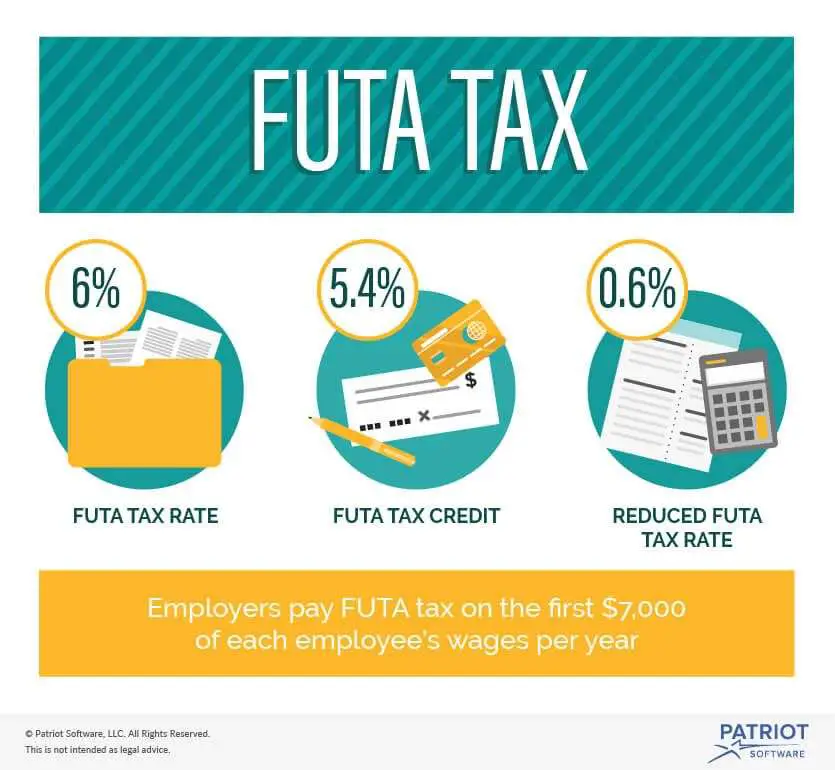
FUTA tax rate: The FUTA tax rate is 6.0%. The tax applies to the first $7,000 you paid to each employee as wages during the year. The $7,000 is often referred to as the federal or FUTA wage base. Your state wage base may be different based on the respective states rules.
What Are The Different Rates For Fica And Futa
Under FICA, you must withhold 6.2% from your employees wages for social security, up to a wage cap of $128,400, and your matching amount. You must also withhold 1.45% from your employees wages for Medicare, and your matching amount.
FUTAs rates are a bit different. Currently, the FUTA tax rate is 6% on the first $7,000 of an employees wages in a single year. However, this rate can also be reduced via contributions to state unemployment programs, making the current minimum FUTA rate 0.6%.
Also Check: Does Doordash Tax Your Earnings
Current Fica Tax Rates
The current tax rate for social security is 6.2% for the employer and 6.2% for the employee, or 12.4% total. The current rate for Medicare is 1.45% for the employer and 1.45% for the employee, or 2.9% total.
Combined, the FICA tax rate is 15.3% of the employees wages.
Do any of your employees make over $137,700? If so, the rules are a little different. Read more at the IRS website.
What Is Futa Payroll Tax
FUTA is an acronym for the Federal Unemployment Tax Act, similar to State Unemployment Tax (SUTA, and is a federal law requiring employers to pay unemployment tax. This payment funds state unemployment programs and is equal to 6 percent of the first $7,000 paid to each employee each year. Employers should stop paying the tax after the employee has been paid more than $7,000.
Many employers receive a FUTA tax credit of 5.4 percent, which lowers their total FUTA tax rate to 0.6 percent. This means the most FUTA tax the average employer will ever pay is $420 per employee .
Employers must file a FUTA tax form every year, as well as pay the tax in the form of a quarterly deposit. FUTA taxes are due the last day of the month at the end of the quarter.
Recommended Reading: Efstatus.taxact 2013
How To Calculate Payroll Taxes:
As the employer, it is your responsibility to withhold income tax and pay it to the government on behalf of your employees. The responsibility to calculate and withhold the correct amount from each paycheck falls on your shoulders.
You can outsource. There are companies that offer payroll tax services. We suggest OnPay, and Wagepoint.
You can use payroll software.Payroll software simplifies the task of calculating and distributing employee pay and calculating taxes. We suggest Gusto, AccountEdge Pro, BambooHR, and SurePayroll Inc..
Setting Aside Futa Money

An easy way to keep track of FUTA savings on your books, and make sure you have enough, is to set aside money every time you pay an employee.
Hereâs a step-by-step process:
Based on how much your employee typically earns , estimate their average quarterly gross earning.
Calculate the FUTA for that amount .
Count the number of paychecks the employee will receive for the quarter. Then divide the FUTA you calculated by the number of paychecks.
Every time you withdraw your employeeâs pay, set aside the resulting amount in an appropriately named accountâ like “payroll taxesâ or “unemployment taxesâ. The money you set aside should come from your retained earnings.
To simplify things, you can carry out these calculations for each employee, and set aside a lump sum every pay cycle.
You May Like: Efstatus.taxact.com.
How Do You File
To report annual FUTA tax payments, employers use IRSForm 940. The form must be filed by January 31 however, if you deposited all tax when it was due, then you dont need to file it until February 10. If this due date falls on a Saturday, Sunday, or legal holiday, then you have until the next business day to file. To file, the form can be mailed or e-filed.
Its important to file your Form 940 on time or youll risk late payment penalties. In fact, the IRS imposesa late filing penalty on the unpaid tax amount that ranges from 2% to 15% depending on when you submit your form.
What Is Futa Tax
FUTA is an abbreviation for Federal Unemployment Tax Act. FUTA Tax is a United States federal tax imposed on employers to help fund unemployment payments. The tax is imposed solely on employers who pay wagesRemunerationRemuneration is any type of compensation or payment that an individual or employee receives as payment for their services or the work that they do for an organization or company. It includes whatever base salary an employee receives, along with other types of payment that accrue during the course of their work, which to employees.
FUTA Tax is used to pay employees who leave employment involuntarily and are eligible to claim unemployment insurance. The act requires employers to file Form 940 annually with the Internal Revenue Service . In some cases, the IRS may allow some employers to pay the tax in installments during the year.
Don’t Miss: Does Doordash Issue 1099
Federal Unemployment Tax Deposits
The IRS requires employers to make payments to the federal tax agency by the last day of the month after the end of the quarter. The FUTA tax liability for the quarter must be $500 or more for the employer to make a deposit with the IRS. If it is less than $500, it is carried forward to the next quarter.
The frequency of FUTA tax payments depends on the amount of tax owed and the number of employees. Employers must use the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System to make payments to the IRS.
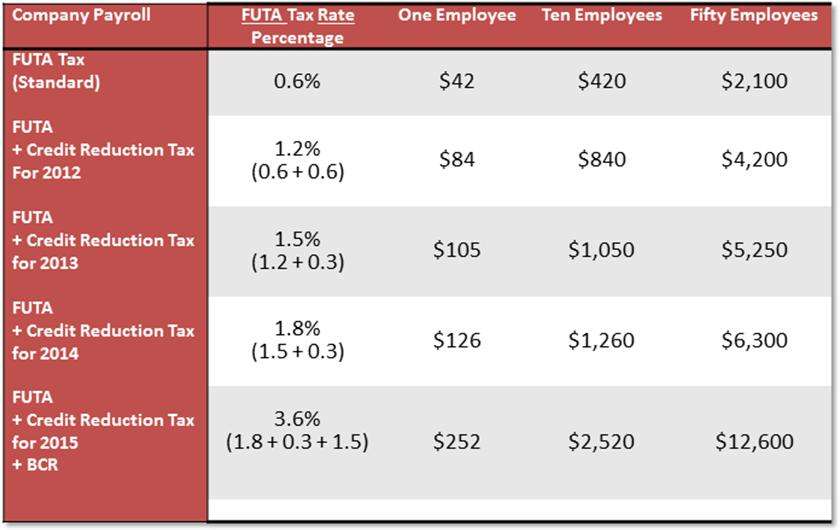
Lets take the example of a company that owes the IRS $400 in Quarter 1, $350 in Quarter 2, $490 in Quarter 3, and $550 in Quarter 4. Since the FUTA tax liability in Q1 is less than the required $500, the company will carry forward the $400 for Q1 to Q2. That will bring the total tax liability for Q2 to $750 , which the company will be required to remit to the IRS by July 31st .
The tax liability for Q3 is below the FUTA tax limit by $10. The tax liability will be carried forward to the last quarter of the year. It will bring the FUTA tax liability for Q4 to $1,040 . The company must remit the FUTA tax liability by January 31st of the following month.
Note: The article above is for educational purposes only. Always consult a professional adviser before making any tax-related or investment decisions.
Charges To Accounts Of Contributing Employers
A contributing employer’s account is charged with the unemployment benefits paid out based on the percentage of base period wages paid by the employer that were used to establish a claim. Charges for contributing employers are not amounts the employer must pay instead, the DES tracks these charges and uses them when figuring an employer’s tax rate.
Recommended Reading: Look Up Employer Ein Number
Are Any Wages Excluded From Futa Taxes
Some types of wages are not subject to FUTA taxes. Items that are excluded from FUTA taxes include:
- Wages paid to an employers spouse, parent, or child under the age of 21
- Group term life insurance benefits
- Company contributions to employee retirement or pension accounts
- Fringe benefits
- Payments for domestic services under $1,000 in cash
- Payments to nonemployees who are treated as employees by your states unemployment tax agency
Additionally, there are various laws that can help you determine if youre exempt from paying FUTA tax: the general test, household employees test, and farmworkers employees test.
Who Is Subject To The Tax
In general, most businesses other than those exempted like nonprofits and religious organizations must pay FUTA taxes. Specifically, employers are responsible if they paid wages of $1,500 or more or had at least one employee for some part of a day in 20 or more different weeks in the calendar year.
Moreover, there are specific tests to determine if you owe FUTA taxes for household employees orfarmworkers. For example, theres a partial exemption if you paid cash wages of less than $20,000 for agricultural labor during any calendar quarter of the current or preceding year or didnt employ at least 10 workers for some portion of a day in each of the 20 different weeks during the current or preceding calendar year.
Also Check: Will A Roth Ira Reduce My Taxes
Who Needs To Pay Futa
FUTA is paid by every employerânothing gets deducted from the employeeâs wages. But there are a couple other requirements to meet if youâre going to be eligible.
Youâre required to pay FUTA if:
-
You paid more than $1,500 to employees during at least one calendar quarter, and
-
Youâve had one or more employees during 20 or more different weeks of the year. Full-time, part-time, and temporary workers all count. The days they worked do not have to be full days.
An employee is anyone you file Form W-2 for. Contract workersâpeople who get Form 1099-NECâdonât count as âemployeesâ.
Further reading:1099s vs. W-2s: Which Should You Hire?
Calculating Federal Income Tax:
Check your employee’s Form W-4 for their , gross income, and number of allowances.
Open the IRS Publication 15-A.
Find the table that corresponds to your company’s payroll period .
Find the column that corresponds with the employee’s .
Find the number of allowances in the left-hand column that matches the number of allowances in the employee’s Form W-4.
Move across to columns A and B to find the employee’s gross income, which will fall between the numbers in A and B.
Now subtract the amount given in column C from the employee’s gross income.
Multiply the result by the percentage in column D.
Don’t Miss: Is Donating Plasma Taxable Income
What About Independent Contractors Or The Self
Well, independent contractors are not considered employees. Employers do not pay any payroll taxes on independent contractors they hire.
Be sure that the person or people you claim to be an independent contractor are actually classified as an independent contractor.
According to the IRS, an individual is an independent contractor if the payer has the right to control or direct only the result of the work and not what will be done and how it will be done.
Independent contractors or those who are self-employed, pay self-employment tax on their net earnings from self-employment.
That tax is essentially the employee and employer share of FICA.
What Is Futa Tax Everything Employers Should Know
If youre hiring and paying employees for the first time, one of the things youll need to manage is calculating and filingpayroll taxes. One of these that youll more than likely have to pay as an employer is the Federal Unemployment Tax Act tax. Thats because most employers pay both FUTA and a state unemployment tax. But just what is FUTA tax and what do you need to know to comply with its requirements?
At Complete Payroll Solutions, weve been providing outsourced payroll to clients for over 18 years. One of our core offerings with any of our payroll packages is payroll tax filing. To help you understand your responsibilities when it comes to withholding FUTA tax from your employees pay and remitting it to the IRS, here well cover:
- What is FUTA tax
- Who must pay FUTA tax
- What is the FUTA tax rate
- When is FUTA tax due
- How do you file FUTA tax
After reading this, youll understand what you need to do to pay FUTA tax properly and on time to avoid potential penalties.
Recommended Reading: Tax Write Offs Doordash
