What Is The Small Business Tax Rate
The small business tax rate for the 2019 tax year is a flat 21% for a C-corporation and will remain so for the 2020 tax year. On average, the effective small business tax rate is 19.8%. However, businesses pay different amounts in taxes based on their entities. Generally, sole proprietorships pay a 13.3% tax rate, small partnerships pay a 23.6% tax rate, and small S-corporations face a 26.9% tax rate.
Taxes are complicated, and many small business owners struggle to understand how their tax liability is determined. Many business owners dont know the corporate income tax rate, what tax cuts they are eligible for, or what terms like pass-through income even mean. Plus, in addition to income taxes, businesses also have to pay payroll taxes, unemployment taxes, and other kinds of taxes.
To make things even more complex, small business tax rates, deductions, and applicable laws can change from year to year, meaning you have to stay up to date on these changes to ensure youre meeting your tax obligations completely and accurately.
While understanding how small business taxes are calculated and applied can seem overwhelming to any business owner, learning some basics can help you make the right decisions and work with your tax professional. This guide breaks down the types of taxes your company may be subject to, as well as the different small business tax rates applied to your earningsâplus, it also includes updates to tax laws that may affect your business.
Small Business Tax Rate
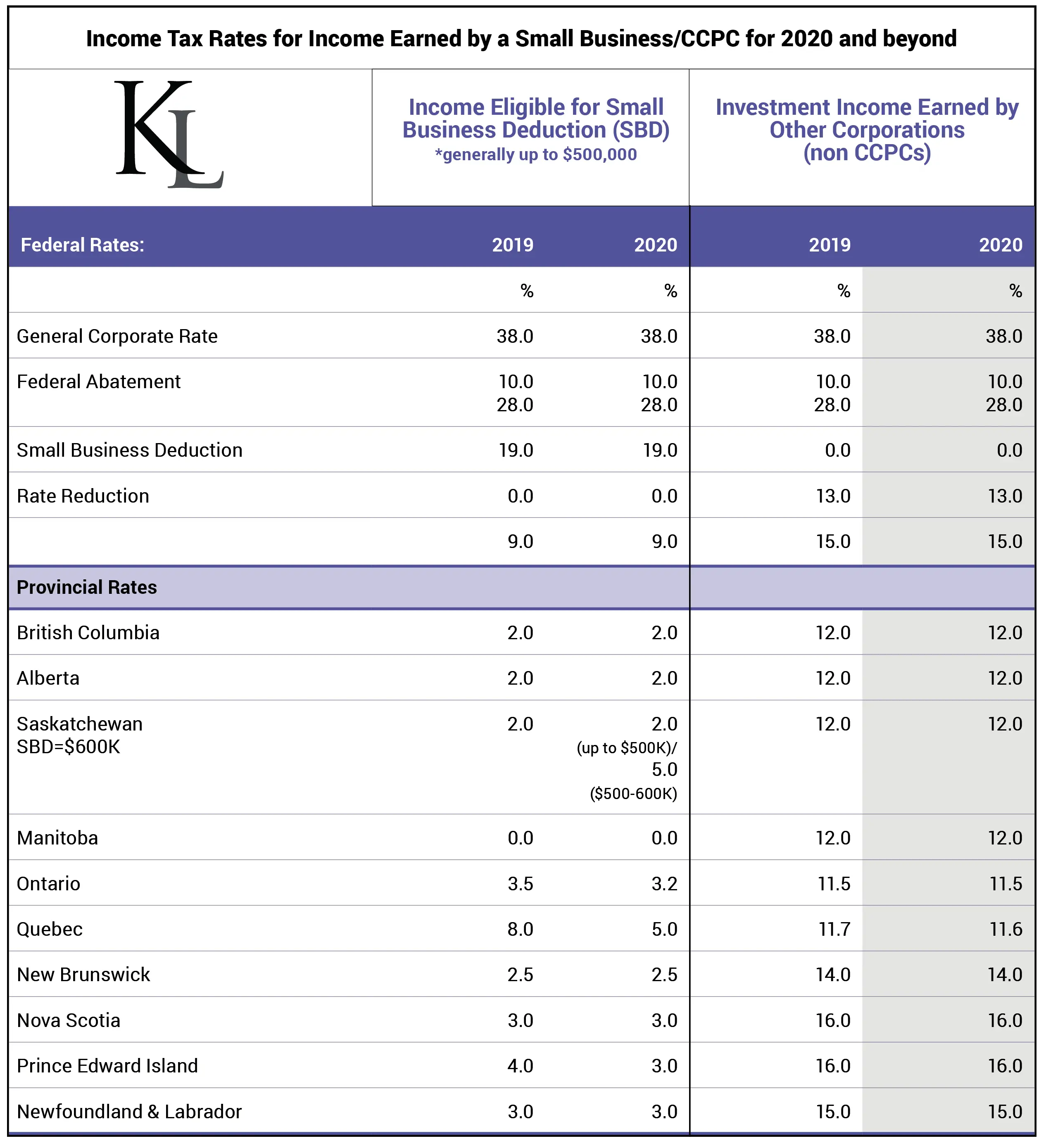
For small business owners in the province, a reduced rate of 3% will be used to determine your corporate income tax payable instead of the general corporate income tax rate of 15%.
The reduced rate of 3% applies to the first $500,000 of active business income earned in the province and that qualifies for the federal small business deduction.
In order to qualify for the small business deduction, the taxpayer must be a Canadian controlled private corporation throughout the tax year and maintain a permanent establishment in the province. In addition, the small business must carry on an active business in the province.
The Small Business Tax Rate is imposed under Section 40.1 of the Income Tax Act, 2000.
How Much Does The Average Small Business Pay In Taxes
Small businesses of all types pay an average tax rate of approximately 19.8 percent, according to the Small Business Administration.
Small businesses with one owner pay a 13.3 percent tax rate on average and ones with more than one owner pay 23.6 percent on average. Small business corporations pay an average of 26.9 percent.
Corporations have a higher tax rate on average because they earn more income. This is easy to understand when you consider that over 18 percent of small S corporations earn at least $100,000 net per year while almost 60 percent of small businesses with one owner earn less than $10,000 net.
You May Like: Where To File Quarterly Taxes
Qualifying For The Small Business Deduction
The reduced business limit in the explanation from the T2 Corporation Income Tax Guide above refers to the fact that since large Canadian-controlled Private Corporations that have taxable capital employed in Canada of $15 million or more do not qualify for the Small Business Deduction, the business limit is reduced on a straight-line basis for CCPCs that have taxable capital employed in Canada of between $10 million and $15 million in the previous year.
Note that income refers to active business income. Income that does not qualify as active business income includes:
- Investment income
- Income from a specified investment business, which is a corporation that derives income from property in the form of rents, leases, royalties, etc., unless the business has more than five full-time employees.
- Income from a personal services business. A personal services business is a business that exists solely to provide services to another entity. The individual who performs the services is known as an incorporated employee. Relatives of the incorporated employee also qualify. The services provided would normally be performed by an employee or officer of the other entity. This type of arrangement is closer to an employer/employee relationship than a business-to-business one. Being classified as a personal services business can be avoided if the business has more than five employees.
Summarized Tax Rates For Small Businesses:
- C-corporations: Flat 21% on net business income
- Double taxation: Taxed on the corporate and individual level
Also Check: How Much Is Sales Tax In Kansas
Walkthrough Of Estimated Tax
The first thing to know: your business income is considered earned income and passes through, from your LLC to your personal taxes. What you need to know about earned income is that its exposed to higher tax rates. Pass through simply means your LLC doesnt affect how much you’re taxed, at least not by default .
How Does an LLC Get Taxed?
Theres one simple idea that will put you ahead of nearly all small business owners, in your tax knowledge. Your income is taxed twice. You read that right: you first pay Self-Employment taxes and pay again via income taxes. You might be surprised to learn Self Employment taxes are almost always more important.
Self Employment Taxes
Round one of your taxes is made up of Social Security and Medicare or an estimated 15%. Most people fixate on income taxation because of the higher rates, but they are missing the big picture. Because Self-Employment taxes are the first round of taxes they often are the larger amount you pay!
Take this example:
Your business earns $100k in revenue and has $50k in business expenses, thats a $50k profit on your form Schedule C. Youre guaranteed only one deduction here, effectively making your Self-Employment tax 14.13% or $7,065.
Compare this to income taxation for this person at $5,235 . That means even though weve heavily exaggerated things still they’ve paid far more into Self-Employment!
Income Taxes
How Much Should an LLC Set Aside For Taxes?
Your Effective Tax Rate
Income Tax Rates For Pass
The federal small business tax rate for pass-through entities and sole proprietorships is equal to the owners personal income tax rate. For the 2019 tax year, personal income tax rates range from 10% to 37% depending on income level and filing status. For example, a single filer who reports $100,000 in net business income will pay a 24% tax rate.
Its important to note, however, as of the 2018 tax year, sole proprietors and owners of pass-through entities can deduct up to 20% of their business income before their tax rate is calculated. In the above example, the tax filer could deduct up to $20,000 from the net business income. Then, theyd only have to report $80,000 in income, reducing their tax rate to 22%.
There are limits, however, on this small business tax deduction based on income and type of business. In general, you must earn less than $157,500 or $315,000 to qualify for the full deduction. Additionally, professional service businesses, such as law firms and doctors offices, typically cant claim the full deduction either.
Also Check: How To Pay Back Taxes Online
Learn How Small Businesses Are Taxed And What Tax Breaks Small Business Owners Can Take Advantage Of
- The type of business structure you set up for your company sole proprietorship, partnership, S corporation or C corporation governs which tax return you’ll need to use to file your taxes and how much you’ll owe.
- Small business owners often have to pay income tax and self-employment tax.
- Keep detailed expense records so you can take advantage of tax deductions.
Preparing your business tax return is a complicated, frustrating process. However, it’s important to do it right you could face steep penalties for filing an inaccurate return.
The starting point for preparing your business tax return hinges on the structure of your business. Whether you’re a sole proprietorship , a partnership, or a C or S corporation, your business entity will define which form you must use to file your business return and how much you may owe the IRS.
How Can I File My Business Taxes
To file taxes for your small business, youll need to determine whether you are a sole proprietorship business or an incorporated small business.
As a sole proprietorship business, you will use the T1 individual tax return. You will enter your business tax information on the T2125 form, and this form ends up as part of your personal T1 tax income.
For an incorporated small business, youll use the T2 tax return, which is completely separate from your personal income return on T1.
- Enter your expenses for the business
- Enter your income for the business
- Calculate your owed taxes, based on your net income
- Make a payment or determine how youd like to receive your refund.
- You almost certainly will be able to file your forms electronically, although you also have the right to print your forms and mail the paper copies.
- Calculate the tax instalment payments youll need to make for the following year if you are incorporated or if you are self-employed.
You May Like: How To Efile Just State Taxes
Corporate Income Tax Rates And Business Limits
Corporate income tax rates are expressed as a percentage of taxable income earned in the province.
B.C. has two rates of corporation income tax the general rate and the lower small business rate.
The lower small business rate is applicable to Canadian-controlled private corporations with active business income eligible for the federal small business deduction.
Generally, active business income is income earned by a corporation from a business other than a specified investment business or a personal service business.
The lower small business rate applies to active business income up to the B.C. business limit of:
- $500,000 effective January 1, 2010
- $400,000 effective January 1, 2005 to December 31, 2009
- $300,000 from April 1, 2002 to December 31, 2004
The general rate applies to income over $500,000 and any income that is not eligible for the lower small business rate .
When the rate or the business limit changes during the tax year, you have to base your calculation on the number of days in the year that each rate or limit is in effect.
Business Income Tax Rate For S
Pass-through entities include sole proprietorships, partnerships, S corporations and LLCs that have not elected to be taxed like a C-corp. Roughly 95% of businesses in the U.S. are pass-through entities.
The term pass-through stems from the fact that the business doesnt pay federal income taxes directly. Instead, business income and losses pass through to the owners and members, who pay taxes on business profits via their individual income tax returns.
On individual tax returns, business income is taxed at the same rates as other ordinary income, such as wages from a job or interest earned from a savings account. For the 2021 tax year , the federal income tax brackets are:
| Personal Income Tax Rates for 2021 |
| Rate |
Source: IRS
At first glance, it might appear as though it would be beneficial to be taxed as a C corporation, since corporations pay a top tax rate of 21% and individuals in the highest tax bracket pay a rate of 37% on their pass-through income. However, when Congress lowered the corporate tax rate, it also created a new qualified business income deduction.
For 2021 taxes, this 20% deduction is available to all single pass-through business owners with taxable income at or below $164,900 . For taxpayers with income over those limits, the QBI deduction may be limited.
Tax rate for LLCs
Don’t Miss: How To Determine Taxes On Paycheck
What Is A Corporate Or Business Tax
A corporate or business tax is charged on the profits of a company. The figure used as a basis for taxes varies, depending on the business type.
- Small business owners pay tax on Schedule C as part of their personal tax return.
- Partners in partnerships and LLC owners are taxed on their share of business net income.
- Corporations are taxed on net earnings.
Profit, net income, and net earnings mean essentially the same thing. Profit and loss is an accounting concept calculated as income minus expenses. Net income is a tax term indicating the difference between the gross income of the business and its deductible business expenses. Net earnings is a sum used to calculate income tax for corporations.
How Do You Calculate Small Business Taxes
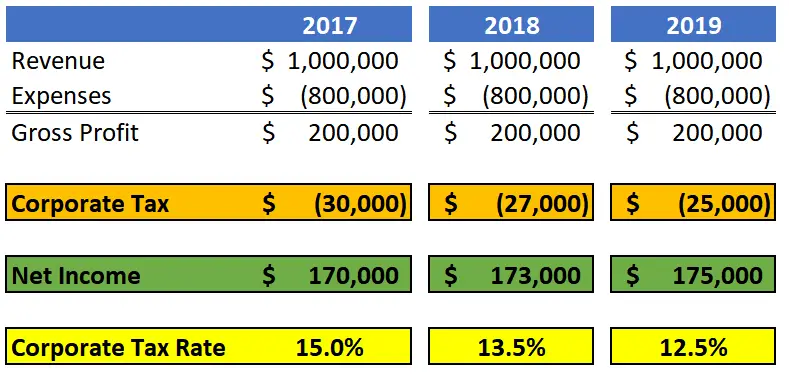
A C-corp simply applies the corporate tax rate of 21% to its taxable income. For example, if the company has taxable income of $100,000, the tax due would be $21,000 .
For pass-through businesses, its not quite as simple. Pass-through business owners pay tax on all their taxable income, including their share of business profits. Federal income tax rates for individuals are progressive, meaning the higher your income, the higher your marginal tax rate will be.
For example, using the 2021 tax brackets above, if a single taxpayer had total taxable income of $100,000, they would pay:
- 10% on the first $9,950 = $995
- 12% on the next $30,575 = $3,669
- 22% on the next $45,850 = $10,087
- 24% on the last $13,625 = $3,270
Their total tax liability would be $18,021.
You May Like: When Are Irs Taxes Due
Canada Small Business Tax Rate
In Canadas federal tax system, the small business tax rate is the tax rate paid by a small business. As of 2019, the small business tax rate is 9% The general corporate tax rate is 28%. Additionally, each province or territory operates its own corporate tax system, with varying treatment for small businesses.
The Small Business Tax Rates In 2021 Explained
- by David RodeckI am a professional freelance …more
- 5 Minute Read
Figuring out your taxes as a small business owner can feel like a guessing game. Not only do you need to plan around your future uncertain income you also need to keep track of changing federal laws.
As you get ready for another year, these strategies can help you determine your small business tax rate.
Recommended Reading: Can I File My Taxes Over The Phone
What Is The Federal Small Business Tax Rate
Your tax rate depends on the structure of your business.
For C corporations, the current tax rate is 21%. With other business entities, such as sole proprietorships, partnerships and S corporations, the income passes directly to owners, so you owe your personal income tax rate on your share of the profits. If your business is an LLC, your tax rate depends on whether youve elected to operate as a C corp, a partnership, an S corp or a sole proprietorship.
The IRS publishes small business tax rate adjustments every year. But be careful about using the current published rates to estimate what youll owe.
We have a new administration that said theyll raise tax rates for the rich, which can include business owners, said Steven Weil, president of RMS Accounting in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. We know the rates for 2020, but for 2021, you basically need a crystal ball. As you plan, it depends if you think the rates are going to change or not for your business.
Worst States For Llc Taxes
Theres generally two kinds of state-level taxes that your LLC profits may be paying: income and business taxes. The following are states that frequently find higher taxes for 1099’s or a single member LLC:
| State |
|---|
| 2 – 5.75% | – |
Please be aware that states with more progressive income rates , can make them poor choices for high business income earners. This table is designed for small business owners with ~$80,000/year in income.
You May Like: How Does Unemployment Tax Work
Sole Trader Personal Allowance Vs Earnings
| Earnings Bracket | |
|---|---|
| Over £125,140 | £0 |
The large multiplier is applicable to larger businesses with a RV of £51,000 and above and all premises which are empty with a RV of £2,900. As demonstrated in the table, the current multiplier in 2021/2022 has been frozen to accommodate for the drastic changes in the market following the Covid-19 crisis.
Another vital part of the rating system to understand is the new appeals scheme launched by the VOA in 2017 known as Check, Challenge, Appeal . This scheme places the onus on the ratepayer to check their assessment before challenging or appealing. The three stages are:
Check: At this stage factual matters about the property need to be carefully confirmed. Once the Check document is submitted the VOA has 12 months to consider it and respond.
Challenge: Once the facts have been confirmed and within four months of the Check decision, a detailed assessment accompanied with a valuation will make up a typical Challenge document to send to the VOA to change the RV. You cannot submit a challenge against the same valuation, for the same reason, more than once. If you do your submission will not be valid. Finally, the VOA will issue a decision notice on the Challenge submission accordingly. The matter should then be finalised. However, should the VOA disagree with your Challenge there is a right to appeal.
> See also: How can I reduce my business rates in England? A small business guide
How To Manage Small Business Taxes
Now that you know the different small business tax rates and what your business can expect, youre probably wondering how you can prepare so that you wont be caught off guard when it comes time to pay your taxes. Given that no two businesses will end up paying the same amount of tax, every businesss approach will be slightly different.
However, the best thing any business owner can do is put money aside ahead of time. You may want to allocate as much as 40% of your income to cover state and federal taxes each quarter, in accordance with your small business tax rate. This is especially important when you just start your business since you wont yet have a complete understanding of your businesss tax liabilities.
A best practice is to set aside money to pay taxes in a bank account separate from your businesss day-to-day finances. This way, you wont accidentally spend money that was earmarked for the IRS. You can even set up automatic transfers from your business bank account into a separate account, so that you know youre always putting away money to cover your tax bill.
If you miscalculate and end up underpaying what you owe, dont worry. Most business owners can avoid the underpayment penalty if they pay as much in taxes each quarter as they did the previous year. You can read more about this rule on the IRS website.
Don’t Miss: What Tax Bracket Are You In
