How Are Annuities Taxed To Beneficiaries
The taxation of any annuity which has been inherited by a beneficiary will be dictated by the age of the original owner upon their death.
| Annuity Owner Dies before the age of 75 | Annuity Owner Dies after the age of 75 |
| Beneficiaries will receive all the annuity payments free of income tax | Beneficiaries will pay income tax on all annuity payments at their marginal rate |
How Are Annuities Taxed When Distributed
- Qualified annuities entail a tax on the entire withdrawal amount. Only if the annuity is a non-qualified one will you have to pay taxes on the income it generates.
- The estimated number of payments from your annuity are divided equally by the principle and tax exclusions.
- An early withdrawal penalty of 10% usually applies if you take money out of your annuity before the age of 59 1/2.
Using An Annuity To Help Protect Against Taxes
How an annuity can be instrumental in protecting your hard-earned money from the huge impact of taxes.
|
You’ve always given everything for the people you’re responsible for., and, with the right strategy, you can ensure that you will fully benefit from the money youve saved for retirement. With tax rates reaching their highest levels in decades,1 minimizing tax exposure and safeguarding wealth and retirement income assets is more important than ever. An annuity can play a key role in helping to protect your savings from todaysand tomorrowstaxes, as you work toward planning for a reliable income stream through retirement. |
Read Also: When Do You Do Tax Returns
How Is An Annuity Taxed
Daniel Schorn
Many of the financial tools that you use for retirement have complicated tax rules. For instance, the money you put in 401s, Roth accounts and non-qualified investment accounts will be taxed at some point â but how and when differs depending on the type of account, how long youâve held your money in the account, and possibly even how much income you make.
Another tool often included in a diversified retirement plan is an annuity. Annuities, which can help you save for retirement or generate a guaranteed lifetime income after you retire, can protect you from the risk of outliving your assets.
But how is an annuity taxed? Understanding how they are taxed will help you get a clearer picture of how much money youâll likely have in retirement. First, letâs review some annuity basics.
Income Annuity Payments Are Only Partially Taxable

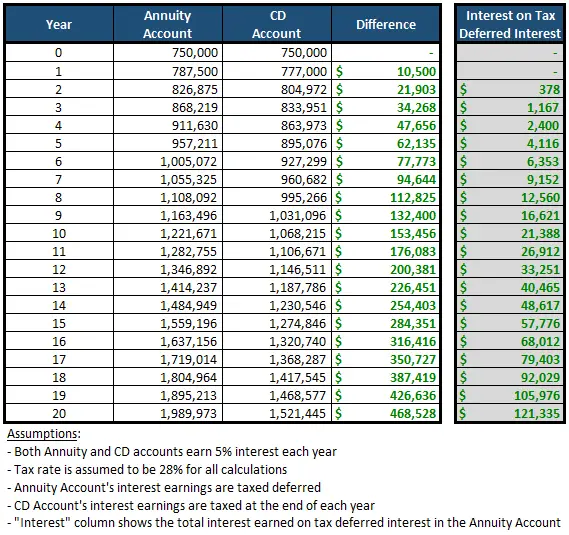
Your original investment the purchase premium you paid in a nonqualified annuity is not taxed when withdrawn. Only the interest portion of the payment is taxable.
With a deferred annuity, IRS rules state that you must withdraw all of the taxable interest first before withdrawing any tax-free principal. You can avoid this significant drawback by converting an existing fixed-rate, fixed-indexed or variable deferred annuity into an income annuity. Or you can buy an income annuity in the first place.
An income annuity provides a stream of guaranteed payments, starting either right away with an immediate annuity or in the future with a deferred income annuity. As mentioned above, each payment includes both taxable interest and tax-free return of your premium.
The exclusion ratio depends on how long youve held the annuity, how much interest youve earned and how long the payments will last, but, for example, 75% of each payment might be tax-free return of principal and 25% taxable.
Also Check: Employer Tax Identification Number Lookup
It Depends On The Annuity And How Long You Live
Tick, tock.
- Print icon
- Resize icon
Q.: A friend of mine bought an annuity and raves about how much tax-free income he is getting and that it is guaranteed for life. Another friend of mine says annuities are a tax time bomb. Who is right? Lester in Omaha
A.: Well, Lester I think the time bomb friend is more correct. Based on the description, I think they are talking about two entirely different types of annuities.
It sounds like your income friend has an immediate annuity. He is NOT getting tax-free interest income. He is getting a monthly annuity payment of which a portion is not taxed. It is not taxed because it is considered a return of his investment principal.
He traded a lump sum for a lifetime of steady checks. Those checks can stop before he gets all his money back.
For example, an online illustrator indicates a 65-year-old male that buys an immediate annuity for $100,000 can get a monthly payment of $565 until his death. Versions that would make any payments beyond his death payout less. So $565 a month equates to 6.78% a year of his investment but he is not getting anywhere near 6.78% in interest or earnings. He doesnt net any investment return until he gets back $100,000 in payments which will take until he reaches age 79 and nine months. If he dies before this time, his internal rate of return will be negative.
The time bomb comes over time as the contract continues to accrue earnings. Taxes are only deferred not avoided.
How A Nonqualified Variable Annuity Works
Variable annuities work like most kinds of annuity contracts sold by insurance companies. In return for the money you invest, the insurer promises to pay you a regular stream of income, often beginning at retirement age and continuing for the rest of your life.
A qualified annuity is a type of retirement account, much like a traditional individual retirement account , that typically entitles you to a tax deduction for the amount you contribute, up to Internal Revenue Service limits. A nonqualified annuity, on the other hand, is not considered a retirement account for tax purposes and doesnt earn you a deductioneven if you are using it to save for retirement.
You make contributions to a nonqualified variable annuity with after-tax dollars, like adding money to a bank account or any investment outside of a retirement plan. The insurer then invests your contributions in the subaccounts, which are similar to mutual funds, of your choosing. The value of the annuity will vary according to the performance of the investments you selected. With a fixed annuity, by contrast, the insurer picks the investments and promises you a predetermined return.
The earnings in your variable annuity account become taxable only when you withdraw money or receive income from the insurer in the payout phase of the annuity. At that point, the money you receive is taxed at the same rate as your ordinary income.
You May Like: Home Improvement Cost Basis
Q I Am 66 And I Have Two Fixed Annuities For Life With A Rider Attached I Plan To Start My Monthly Payments For Life At Age 71 Im Confused About How The Payments Are Taxed Ive Heard That For Federal Taxes It Goes By The Last In First Out Rule Meaning I Would Be Taxed On The Total Monthly Payment Until All The Interest And Gains Until I Was 84 And Then It Would Be Tax
A. The taxation of your specific annuities depends on a couple of assumptions.
Were going to assume that your fixed annuities were funded with after-tax money, meaning that theyre not funded with an IRA or a pension plan. Were also going to assume that the rider you mentioned means youre not annuitizing the balance or taking payments, but instead the rider will pay you a certain percentage of the account balance for the rest of your life.
Based on the above assumptions, you will indeed pay federal income tax on the annuity payments until you have recovered all of the earnings in the account, said Howard Hook, a certified financial planner and certified public accountant with EKS Associates in Princeton.
Hook offered this example. Lets say you invested $100,000 and the account is now worth $150,000. You will pay income tax on the first $50,000 of payments, representing the earnings in the account. Once you have received $50,000 in payments, the balance of the annuity payments will be tax-free to you, Hook said.
This is different than if you had annuitized the balance.
If you would have done that then a portion of each payment would have been considered a return of your original investment and a portion would have been considered earnings, Hook said. This would be the case until you have been paid out all of what you originally contributed, at which point future payments would be 100% taxed.
Email your questions to
What Is An Annuity Plan
An annuity plan is a contract between an individual and an insurance company, whereby the insurer promises to pay an amount at regular intervals to the individual in return for a lump-sum payment or a series of payments. The insurer invests the money received and pays back the returns generated from it to the individual. There are two types of annuity plans depending on the nature of payments.
Immediate annuity plan: These plans are purchased with a lump sum and the annuity payments start immediately either for a specified period or lifetime. There is no accumulation phase in immediate annuity plans and it starts working from the vesting phase.
Deferred annuity plans: These plans are similar to other investment instruments, whereby the money is invested for a specified period of time, and the annuity payments start after a certain date. It has two phasesaccumulation phase and vesting phase. In the accumulation phase, the premiums are paid and the corpus is accumulated, while in the vesting phase you start receiving the policy benefits in the form of pension.
Benefits of an immediate annuity
The deductions under the section are not limited to residents of the country, but can also be claimed by non-resident Indians who contribute towards a pension plan. It has to be noted that the deduction limit under Section 80CCC is clubbed with Section 80C and 80CCD, which essentially caps the overall limit at Rs 1.5 lakhs.
Get In Touch
Also Check: Where Can I Amend My Taxes For Free
What Is A Nonqualified Variable Annuity
Nonqualified variable annuities are tax-deferred investment vehicles with a unique tax structure. While you wont receive a tax deduction for the money you contribute, your account grows without incurring taxes until you take money out, either through withdrawals or as a regular income in retirement.
What Debt Ceiling Woes Could Mean For Social Security Benefits
- Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen suggested this week that Social Security benefits will be impacted if Congress doesnt raise or suspend the debt ceiling.
- The programs funds that it uses to pay benefits will likely not face long-term consequences from any political gridlock on Capitol Hill.
- However, there is the possibility that monthly checks could be delayed.
Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen made headlines this week with an op-ed suggesting government checks could run dry if Congress doesnt raise the debt ceiling.
Nearly 50 million seniors could stop receiving Social Security checks for a time,Yellen wrote.
The House of Representatives has passed a bill to temporarily fund the government and suspend the debt limit. However, that legislation could fail in the Senate. If lawmakers cannot come to an agreement, the government would shut down on Oct. 1.
Social Security beneficiaries may breathe a sigh of relief to know that the programs funds will still be there to pay their checks, regardless of what happens with the debt ceiling negotiations, according to Nancy Altman, president of Social Security Works, an advocacy group focused on expanding benefits.
However, there is the possibility that a government shutdown could delay how fast that money reaches people.
Don’t Miss: Efstatus.taxact.com Login
When To Buy An Annuity
The best time to buy depends on your personal income needs and sources of income.
For example, you may want more money early in your retirement to pay for travel or new hobbies. Or you may want more guaranteed income later in your retirement to pay for health care costs or accommodations.
If you want more money later you could consider waiting to buy an annuity, or buying a deferred annuity. This means that you pay for the annuity ahead of time but wont start receiving payments right away. Deferred life annuities provide higher regular payments than immediate life annuities. This is because you will receive fewer payments during your life.
If you buy an advanced life deferred annuity with money from your employer pension plan or your registered retirement savings, certain tax rules apply in terms of age and amount limits.
Topic No 410 Pensions And Annuities
If you receive retirement benefits in the form of pension or annuity payments from a qualified employer retirement plan, all or some portion of the amounts you receive may be taxable.
This topic doesn’t cover the taxation of social security and equivalent railroad retirement benefits. For information about tax on those benefits, refer to Topic No. 423 and Are My Social Security or Railroad Retirement Tier I Benefits Taxable?
Don’t Miss: 1040paytax.com Safe
Do Beneficiaries Pay Taxes On Annuities
The difference between the principal paid into the annuity and the value of the annuity upon the annuitants death is subject to income tax for those who inherit an annuity. An inherited annuitys tax status will be determined by the payout structure chosen and the beneficiarys status. Taxes must be paid promptly if a lump sum is chosen by the beneficiaries.
Unlike the annuitant, the beneficiary does not have to pay taxes until the money is withdrawn from the annuity, like the annuitant does.
Purchased With Taxable Income
If you bought your annuity with post-tax dollars, meaning money that you declared on your tax return and paid income taxes on, then your annuity payments will be partially taxable. The percentage of the payment that’s considered a return on your initial investment will not be taxable the rest, which is your gain on the investment, will be taxed.
Also Check: Plasma Donation Taxes
Your Annuity If You Die
When you buy an annuity you can either nominate a reversionary beneficiary or choose a guaranteed period option.
- Reversionary beneficiary Your nominated beneficiary will get your income payments for the rest of their life. This is usually at a reduced level, for example, 60% of your income stream.
- Guaranteed period A minimum payment period is set when you buy the annuity. If you die, your beneficiary will get your payments, either as a lump sum or income stream. The income payments will not reduce.
You May Like: How To Change Your Name With The Social Security Administration
How We Use Your Personal Data
How we use your information depends on the product and service that you use and your relationship with us. We may use it to:
- Verify your identity, personalize the content you receive, or create and administer your account.
- Provide specific products and services to you, such as portfolio management or data aggregation.
- Develop and improve features of our offerings.
To learn more about how we handle and protect your data, visit our privacy center.
Recommended Reading: Irs Federal Returns
Trusts Listed As An Annuitys Beneficiary
Most annuities offer three primary distribution options to listed beneficiaries lump sum payment, even payments over a five year period or income payments over the life of the named beneficiary. Should the beneficiary of the annuity be the spouse of the original owner, an additional option may be presented for the surviving spouse to step in as the new owner of the annuity. If a trust is listed as the annuitys beneficiary, no-look through provisions are offered. Essentially what this means is that the trust is ineligible to receive lifetime income payments. One exception to this general rule does apply should the trust act as an agent of the spouses named beneficiary.
Foreign Social Security Pensions
Absent application of a particular treaty provision, foreign social security pensions are generally taxed as if they were foreign pensions or foreign annuities. They are not eligible for exclusion from taxable income the way a U.S. social security pension might be unless a tax treaty provides for an exclusion.
Most income tax treaties have special rules for social security payments. Generally, U.S. treaties provide that social security payments are taxable by the country making the payments. However, a foreign social security payment may also be taxable in the United States if you are a U.S. citizen or resident, as a result of the saving clause. And remember, not all treaties have the same provisions for foreign social security pensions, so always refer to the specific treaty at issue.
You May Like: Www 1040paytax
Tax Benefits Are Complicated
Annuities can be tools for deferring and managing taxes. Evaluate how best to structure your retirement, charitable giving and other financial goals with the help of a financial professional and tax advisor. A tax-aware strategy could help you take advantage of annuity benefits and avoid surprises down the road.
Related Product
WS20200130154633& bullet Last Updated 2/6/2020
Gerber Life Insurance is a trademark. Used under license from Société des Produits Nestlé S.A. and Gerber Products Company.
Is A Widows Annuity Taxable

An annuity with a predetermined duration is an option. This means that even if you die before the conclusion of the annuity period, we will continue to pay the annuity payments.
If you purchased an annuity from us that includes a beneficiary who is a dependant or a nominee, that beneficiary will get an annuity if they are still alive when you pass away. For the rest of their lives, they will have to pay for this. Tax-free annuity payments are available if you die before the age of 75 if you die beyond that, any payouts will be taxed at your marginal rate.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to taxation, and the rules can change.
You May Like: Doordash 1099-nec Schedule C
